Flagship imaging SAG report
... to infer the presence of unseen planets. Objective 11: Understand the time evolution of circumstellar disk properties around a wider star sample at greater distances, from early protoplanetary stages through mature main sequence debris disks. Discussion These Objectives are not prioritized, but repr ...
... to infer the presence of unseen planets. Objective 11: Understand the time evolution of circumstellar disk properties around a wider star sample at greater distances, from early protoplanetary stages through mature main sequence debris disks. Discussion These Objectives are not prioritized, but repr ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... eye, similar clouds are numerously scattered throughout the Milky Way and some of them are close enough to Earth, so that they can be studied in great detail using telescopes. Stars are known to form inside these clouds and therefore moleclar clouds have been the subject of intense study during the ...
... eye, similar clouds are numerously scattered throughout the Milky Way and some of them are close enough to Earth, so that they can be studied in great detail using telescopes. Stars are known to form inside these clouds and therefore moleclar clouds have been the subject of intense study during the ...
Early stages of clustered star formation -massive dark clouds
... Dark globules, also referred to as Bok globules, are isolated, gravitationally bound molecular clouds that may have been removed from their parent molecular cloud by external events. Because of their isolation, the distance and consequently distancerelated properties of many globules are often uncer ...
... Dark globules, also referred to as Bok globules, are isolated, gravitationally bound molecular clouds that may have been removed from their parent molecular cloud by external events. Because of their isolation, the distance and consequently distancerelated properties of many globules are often uncer ...
Exoplanets - Polarisation.eu
... • These measurements have not yet been confirmed by other polarimeters. • To fit the data, this exoplanet should have a very high degree of polarization. • The model calculations include no multiple scattering of light. ...
... • These measurements have not yet been confirmed by other polarimeters. • To fit the data, this exoplanet should have a very high degree of polarization. • The model calculations include no multiple scattering of light. ...
Habitable Zone Lifetimes of Exoplanets around Main Sequence Stars
... The existence of surficial liquid water is thought to be a fundamental prerequisite for the emergence and continued survival of life because of its important role as a solvent for biochemical reactions. In addition, water is available in appreciable amounts across the Galaxy and in interstellar clou ...
... The existence of surficial liquid water is thought to be a fundamental prerequisite for the emergence and continued survival of life because of its important role as a solvent for biochemical reactions. In addition, water is available in appreciable amounts across the Galaxy and in interstellar clou ...
Script
... methods are indirect and exploit the influence of planets on their host star, e.g. the most successful radial velocity method, astrometry, or the transit method. These methods allow us to study basic parameters of planets (orbital parameters, mass, radius, density) More challenging methods aim at di ...
... methods are indirect and exploit the influence of planets on their host star, e.g. the most successful radial velocity method, astrometry, or the transit method. These methods allow us to study basic parameters of planets (orbital parameters, mass, radius, density) More challenging methods aim at di ...
PDF format
... – Transit missions will be capable of finding Earth-like planets that cross in front of their stars. – Astrometric missions will be capable of measuring the "wobble" of a star caused by an orbiting Earth-like planet. – Missions for direct detection of an Earth-like planet will need to use special ...
... – Transit missions will be capable of finding Earth-like planets that cross in front of their stars. – Astrometric missions will be capable of measuring the "wobble" of a star caused by an orbiting Earth-like planet. – Missions for direct detection of an Earth-like planet will need to use special ...
“From Planetesimals to Brown Dwarfs: What is a Planet
... sense we didn’t think we would find “terrestrial” planets with larger masses. This is because the supply of heavy elements in the protoplanetary disk is only something like one percent that of hydrogen and helium (which we will henceforth refer to as “gas”). It is hard to gather a more massive objec ...
... sense we didn’t think we would find “terrestrial” planets with larger masses. This is because the supply of heavy elements in the protoplanetary disk is only something like one percent that of hydrogen and helium (which we will henceforth refer to as “gas”). It is hard to gather a more massive objec ...
Evolution of Warm Debris Around Sun-like Stars: Clues to Terrestrial
... models for a collisional cascade in the inner regions (< 20 AU) of circumstellar disks at early times compared with the timescale to establish cascades at larger radii (> 20 AU) according to models of Kenyon and Bromley (2006). It is also interesting that the timescales to form large objects through ...
... models for a collisional cascade in the inner regions (< 20 AU) of circumstellar disks at early times compared with the timescale to establish cascades at larger radii (> 20 AU) according to models of Kenyon and Bromley (2006). It is also interesting that the timescales to form large objects through ...
The Habitability of Our Earth and Other Earths: Astrophysical
... and the life on it have coevolved. However, life is not infinitely adaptive. Some parts of Earth are habitable and some, even after approximately four billion years of evolution, are not. Life as we know it has limits, and we can explore these limits most easily on Earth. In a specific region, when so ...
... and the life on it have coevolved. However, life is not infinitely adaptive. Some parts of Earth are habitable and some, even after approximately four billion years of evolution, are not. Life as we know it has limits, and we can explore these limits most easily on Earth. In a specific region, when so ...
Figueira, Pont, Mordasini, Alibert, Georgy, Benz
... required, as established by Alibert et al. (2005). The contemporary work of Mordasini et al. (2008b) pushed this approach further, and studied the effect of not only f1 but also of the dustto-gas ratio and the disk viscosity parameter, among others, on the final population properties. In the end, a ...
... required, as established by Alibert et al. (2005). The contemporary work of Mordasini et al. (2008b) pushed this approach further, and studied the effect of not only f1 but also of the dustto-gas ratio and the disk viscosity parameter, among others, on the final population properties. In the end, a ...
Chapter 11
... 11.4 The Formation of Stars Like the Sun At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will re ...
... 11.4 The Formation of Stars Like the Sun At stage 6, the core reaches 10 million K, and nuclear fusion begins. The protostar has become a star. The star continues to contract and increase in temperature, until it is in equilibrium. This is stage 7: the star has reached the main sequence and will re ...
24_Testbank - Lick Observatory
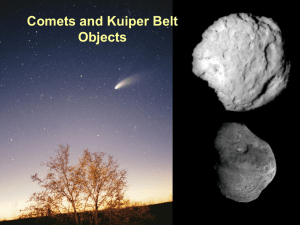
... planet in another solar system? Answer: A giant planet can "kick" comets out of the inner solar system out to an Oort-type cloud through gravitational encounters. This is good news because it means that life on the inner planets can evolve without sterilizing giant impacts. The bad news is that if a ...
... planet in another solar system? Answer: A giant planet can "kick" comets out of the inner solar system out to an Oort-type cloud through gravitational encounters. This is good news because it means that life on the inner planets can evolve without sterilizing giant impacts. The bad news is that if a ...
The Cosmic Perspective Other Planetary Systems: The New Science
... – Direct starlight is billions of times brighter than the starlight reflected from planets. • How can a star's motion reveal the presence of planets? – A star's periodic motion (detected through ...
... – Direct starlight is billions of times brighter than the starlight reflected from planets. • How can a star's motion reveal the presence of planets? – A star's periodic motion (detected through ...
Possible climates on terrestrial exoplanets
... As discussed in Section 2.2., because atmospheric escape is closely related to the stellar activity, it is strongly time dependent at early ages. The timescale on which the various species can be added to the atmosphere is thus critical in determining what is left in the matured atmosphere. Hence, w ...
... As discussed in Section 2.2., because atmospheric escape is closely related to the stellar activity, it is strongly time dependent at early ages. The timescale on which the various species can be added to the atmosphere is thus critical in determining what is left in the matured atmosphere. Hence, w ...
CO OBSERVATIONS OF SPIRAL STRUCTURE AND THE LIFETIME
... Scoville, and Sanders (1978) affords an excellent opportunity to trace large scale galactic features such as spiral arms or cloud clusters which do not necessarily maintain a constant latitude over their full longitude extent. Approximately 1100 points in the inner galactic plane at longitudes - 5 ° ...
... Scoville, and Sanders (1978) affords an excellent opportunity to trace large scale galactic features such as spiral arms or cloud clusters which do not necessarily maintain a constant latitude over their full longitude extent. Approximately 1100 points in the inner galactic plane at longitudes - 5 ° ...
Chapter 13 Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant
... – Transit missions will be capable of finding Earth-like planets that cross in front of their stars. – Astrometric missions will be capable of measuring the “wobble” of a star caused by an orbiting Earth-like planet. – Missions for direct detection of an Earth-like ...
... – Transit missions will be capable of finding Earth-like planets that cross in front of their stars. – Astrometric missions will be capable of measuring the “wobble” of a star caused by an orbiting Earth-like planet. – Missions for direct detection of an Earth-like ...
PTYS/ASTR 206
... – Most of the time, but not all of the time! Its orbit can bring it inside of Neptune’s (as it did from 1979-1999) • Only “planet” not visited by a spacecraft – New Horizons, launched in Jan. 2006, will reach Pluto in ...
... – Most of the time, but not all of the time! Its orbit can bring it inside of Neptune’s (as it did from 1979-1999) • Only “planet” not visited by a spacecraft – New Horizons, launched in Jan. 2006, will reach Pluto in ...
The Formation of Planetary Systems
... The origin of the planets and their moons is a complex and as yet incompletely solved puzzle, although the basic outlines of the processes involved are becoming understood. • (Sec. 6.7) Most of our knowledge of the solar system’s formative stages has emerged from studies of interstellar gas clouds, ...
... The origin of the planets and their moons is a complex and as yet incompletely solved puzzle, although the basic outlines of the processes involved are becoming understood. • (Sec. 6.7) Most of our knowledge of the solar system’s formative stages has emerged from studies of interstellar gas clouds, ...
Comets and astrobiology
... aerogel (porosity >99%), designed to allow a progressive deceleration of the captured material, in order to minimize any alteration by heating and pyrolysis of organic molecules. Once brought back to Earth, physical properties and chemical composition of part of the grains have been analysed with th ...
... aerogel (porosity >99%), designed to allow a progressive deceleration of the captured material, in order to minimize any alteration by heating and pyrolysis of organic molecules. Once brought back to Earth, physical properties and chemical composition of part of the grains have been analysed with th ...
New Indivisible Planetary Science Paradigm J. Marvin Herndon
... The first hypothesis about the origin of the Sun and the planets was advanced in the latter half of the 18th Century by Immanuel Kant and modified later by Pierre-Simon de Laplace. Early in the 20th Century, Laplace’s nebula hypothesis was replaced with the Chamberlin-Moulton hypothesis which held t ...
... The first hypothesis about the origin of the Sun and the planets was advanced in the latter half of the 18th Century by Immanuel Kant and modified later by Pierre-Simon de Laplace. Early in the 20th Century, Laplace’s nebula hypothesis was replaced with the Chamberlin-Moulton hypothesis which held t ...
No Slide Title
... • describe the formation of the extra-solar planets: • Planets form from dust which agglomerates into cores which then accrete gas from a disc. • A gravitational instability in a protostellar disc creates a number of giant planets. • Both models have trouble reproducing both the observed distributio ...
... • describe the formation of the extra-solar planets: • Planets form from dust which agglomerates into cores which then accrete gas from a disc. • A gravitational instability in a protostellar disc creates a number of giant planets. • Both models have trouble reproducing both the observed distributio ...
Molecular Cloud www.AssignmentPoint.com A molecular cloud
... The formation of stars occurs exclusively within molecular clouds. This is a natural consequence of their low temperatures and high densities, because the gravitational force acting to collapse the cloud must exceed the internal pressures that are acting "outward" to prevent a collapse. There is obs ...
... The formation of stars occurs exclusively within molecular clouds. This is a natural consequence of their low temperatures and high densities, because the gravitational force acting to collapse the cloud must exceed the internal pressures that are acting "outward" to prevent a collapse. There is obs ...
Atmospheric circulations of terrestrial planets orbiting low
... The primary goal of this study is to follow up on the above previous efforts to examine habitability and atmospheric circulation of M-star planets, focusing on their sensitivities to planetary rotation period. Previous modeling studies have shown that changes in rotation period can cause substantial ...
... The primary goal of this study is to follow up on the above previous efforts to examine habitability and atmospheric circulation of M-star planets, focusing on their sensitivities to planetary rotation period. Previous modeling studies have shown that changes in rotation period can cause substantial ...
Astrobiological Stoichiometry
... of that element (by number) in the Sun. Elements heavier than He are termed ‘‘metals.’’ Because the Sun is considered to sample the average interstellar medium, it is presumed that all stars will share the Sun’s relative proportions of metals. The relative sizes of the boxes for C, O, etc., are pres ...
... of that element (by number) in the Sun. Elements heavier than He are termed ‘‘metals.’’ Because the Sun is considered to sample the average interstellar medium, it is presumed that all stars will share the Sun’s relative proportions of metals. The relative sizes of the boxes for C, O, etc., are pres ...