Layers of the Ocean - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Ecosystem - a system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment (abiotic and biotic factors). Biosphere - the regions of the surface and atmosphere of the Earth (or other planet) where living organisms exist. Abiotic - are non-living chemical and physical f ...
... Ecosystem - a system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment (abiotic and biotic factors). Biosphere - the regions of the surface and atmosphere of the Earth (or other planet) where living organisms exist. Abiotic - are non-living chemical and physical f ...
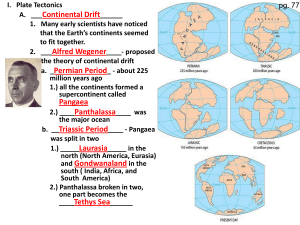
Theory of Continental Drift
... • He believed that molten rock rises from the mantle along mid ocean ridges, forcing the crust to move in opposite directions and creating a new seafloor in the process. • He also believed that crust was being destroyed as it sinks into deep ocean trenches in a process called subduction. • Based upo ...
... • He believed that molten rock rises from the mantle along mid ocean ridges, forcing the crust to move in opposite directions and creating a new seafloor in the process. • He also believed that crust was being destroyed as it sinks into deep ocean trenches in a process called subduction. • Based upo ...
Evidence for Plate Tectonics
... • As older ocean floor moves away from midocean ridges, it moves down deep into Earth along trenches. • Trenches are found close to continents or near strings of islands such as Alaska’s Aleutian Islands. ...
... • As older ocean floor moves away from midocean ridges, it moves down deep into Earth along trenches. • Trenches are found close to continents or near strings of islands such as Alaska’s Aleutian Islands. ...
Ocean Bathymetry and Plate Tectonics
... plates act as giant radiators of heat. They cool, thicken, and gradually subside as they progress from ridge to trench forming the broad-scale patterns of ridges and deep ocean basins. ...
... plates act as giant radiators of heat. They cool, thicken, and gradually subside as they progress from ridge to trench forming the broad-scale patterns of ridges and deep ocean basins. ...
M S P S T U D Y G U I D E 2014 MSP STUDY GUIDE 2014
... -landbreeze, seabreeze and how they occur Stable air mass VS. Unstable- temp and humidity Latent heat—heat needed to cause phase change from one state to another Condensation- L6 CovectionWeather fronts- front of the storm-boundary between two different air masses with different temperatures and hum ...
... -landbreeze, seabreeze and how they occur Stable air mass VS. Unstable- temp and humidity Latent heat—heat needed to cause phase change from one state to another Condensation- L6 CovectionWeather fronts- front of the storm-boundary between two different air masses with different temperatures and hum ...
A Changing World - Center Grove Elementary School
... Isthmus of Panama and found the Pacific ocean. • Balboa proved Amerigo Vespucci was right about an unknown continent. ...
... Isthmus of Panama and found the Pacific ocean. • Balboa proved Amerigo Vespucci was right about an unknown continent. ...
pdf
... Geostrophic gyres are gyres in balance between the pressure gradient and the Coriolis effect. Of the six great currents in the world’s ocean, five are geostrophic gyres. Note the western boundary currents in this map. ...
... Geostrophic gyres are gyres in balance between the pressure gradient and the Coriolis effect. Of the six great currents in the world’s ocean, five are geostrophic gyres. Note the western boundary currents in this map. ...
Planet Earth - Topic 4 (ANSWERS)
... Rocks: they found similarities of rocks on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean (different mountain ranges contained the same type of rock) Geological: in order for coal to be formed, it must have a tropical environment. Coal is found in many places where there is no tropical weather (Ex: Alberta). Most ...
... Rocks: they found similarities of rocks on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean (different mountain ranges contained the same type of rock) Geological: in order for coal to be formed, it must have a tropical environment. Coal is found in many places where there is no tropical weather (Ex: Alberta). Most ...
Unit 7 Test Review
... 17. How are islands made? They are created when a divergent boundary beneath the ocean spreads, allowing magma to flow upward to the surface, which then adds enough new land to the sea floor until it reaches the surface and continues to grow. 18. Explain the continued growth of the Himalayan Mounta ...
... 17. How are islands made? They are created when a divergent boundary beneath the ocean spreads, allowing magma to flow upward to the surface, which then adds enough new land to the sea floor until it reaches the surface and continues to grow. 18. Explain the continued growth of the Himalayan Mounta ...
Evidence for Sea-Floor Spreading
... • When scientists sampled the rocks, they found that the further away from the ridge the rocks were, the older they were! • The younger rocks were always in the center of the ridges ...
... • When scientists sampled the rocks, they found that the further away from the ridge the rocks were, the older they were! • The younger rocks were always in the center of the ridges ...
Tsunami Geology - What Causes a Tsunami?
... Many people have the mistaken belief that tsunamis are single waves. They are not. Instead tsunamis are "wave trains" consisting of multiple waves. The chart below is a tidal gauge record from Onagawa, Japan beginning at the time of the 1960 Chile earthquake. Time is plotted along the horizontal axi ...
... Many people have the mistaken belief that tsunamis are single waves. They are not. Instead tsunamis are "wave trains" consisting of multiple waves. The chart below is a tidal gauge record from Onagawa, Japan beginning at the time of the 1960 Chile earthquake. Time is plotted along the horizontal axi ...
Methodology Study area Results Introduction Conclusion Abstract
... control them. The enhanced biogenic flux at SBBT during summer monsoon could be explained with the help of bottom-up control wherein the physical processes controlled chlorophyll biomass through nutrient supply. The mismatch between the lack of seasonality of biogenic flux at EIOT and seasonality in ...
... control them. The enhanced biogenic flux at SBBT during summer monsoon could be explained with the help of bottom-up control wherein the physical processes controlled chlorophyll biomass through nutrient supply. The mismatch between the lack of seasonality of biogenic flux at EIOT and seasonality in ...
Notes: Plate Tectonics - Riverdale Middle School
... 2.) found in areas that vary greatly in climate, scientists believe these regions once were connected and had similar climates c. Fossils of warm weather plants were found in Arctic Ocean Islands d. Glacial deposits have been found where no glaciers exist today ...
... 2.) found in areas that vary greatly in climate, scientists believe these regions once were connected and had similar climates c. Fossils of warm weather plants were found in Arctic Ocean Islands d. Glacial deposits have been found where no glaciers exist today ...
CH07_Outline
... Warm (El Niño) and cold phases (La Niña) High pressure in eastern Pacific weakens Weaker trade winds ...
... Warm (El Niño) and cold phases (La Niña) High pressure in eastern Pacific weakens Weaker trade winds ...
Section 1: Earth`s Interior (pages 16 – 24)
... from an earthquake. The speed and paths the seismic waves take tell geologists how the planet is put together. Three main layers make up Earth’s interior: (Be able to label layers!) 1. Crust – layer of rock that forms Earths OUTER surface. - It includes both dry land and the ocean floor. - The crust ...
... from an earthquake. The speed and paths the seismic waves take tell geologists how the planet is put together. Three main layers make up Earth’s interior: (Be able to label layers!) 1. Crust – layer of rock that forms Earths OUTER surface. - It includes both dry land and the ocean floor. - The crust ...
Plate Tectonics
... basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean basins— consists of separate plates that ride on a denser, hot, gradually deformable layer of the earth. The crust sections move very slowly, pressing against ...
... basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean basins— consists of separate plates that ride on a denser, hot, gradually deformable layer of the earth. The crust sections move very slowly, pressing against ...
The North Pacific, a Global Backup Generator for Past Climate Change
... have catalyzed further warming and accelerated the glacial meltdown,” says Laurie Menviel, also at the International Pacific Research Center and a co-author on this study. The observational evidence for these circulation changes comes from analyses of radiocarbon data taken from 30 sediment cores a ...
... have catalyzed further warming and accelerated the glacial meltdown,” says Laurie Menviel, also at the International Pacific Research Center and a co-author on this study. The observational evidence for these circulation changes comes from analyses of radiocarbon data taken from 30 sediment cores a ...
Atmospheric - Penicuik High School
... The sun hits the area around the equator at right angles. This heats the water up and it expands. The expanding water pushes North and South from the equator to the poles. It carries heat energy with it. To compensate cold water is pushed out of the polar areas back to the equator to be re-heated. T ...
... The sun hits the area around the equator at right angles. This heats the water up and it expands. The expanding water pushes North and South from the equator to the poles. It carries heat energy with it. To compensate cold water is pushed out of the polar areas back to the equator to be re-heated. T ...
How can we minimise negative impacts on ocean health?
... decade; faster in some areas and slower in others. Coastal ecosystems such as corals and mangroves are at particular risk; furthermore, their loss increases coastal erosion and societal vulnerability to future sea level rise – which in the long term, is likely to be at the scale of metres if climati ...
... decade; faster in some areas and slower in others. Coastal ecosystems such as corals and mangroves are at particular risk; furthermore, their loss increases coastal erosion and societal vulnerability to future sea level rise – which in the long term, is likely to be at the scale of metres if climati ...
Physical oceanography

Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanographies.