Tone and Voice: A Derivation of the Rules of Voice
... [D19.] Avoid Disjunct Approach to Fused Intervals Rule. If it is not possible to approach unisons, octaves and fifths by retaining the same pitch (oblique motion), step motion should be used. [D20.] Avoid Semblant Approach between Fused Intervals Rule. Avoid similar pitch motion in which the voices ...
... [D19.] Avoid Disjunct Approach to Fused Intervals Rule. If it is not possible to approach unisons, octaves and fifths by retaining the same pitch (oblique motion), step motion should be used. [D20.] Avoid Semblant Approach between Fused Intervals Rule. Avoid similar pitch motion in which the voices ...
The Lydian Mode Part 2 Licks, Intervals and Triads
... The following pages once again discuss the various ‘layers’ of the Lydian mode, from 2 note intervals through to 5 note pentatonic scales. Any idea in the following section can be used as an isolated approach or in combination with any other concept. ...
... The following pages once again discuss the various ‘layers’ of the Lydian mode, from 2 note intervals through to 5 note pentatonic scales. Any idea in the following section can be used as an isolated approach or in combination with any other concept. ...
Fundamentals of Music G9-12
... Both of them are built from different combinations of whole steps and half steps. The major scale and minor scale are both seven-note scales having five whole steps and two half steps, yet they sound strikingly unlike each other because of the pattern of whole steps and half step is different. Scale ...
... Both of them are built from different combinations of whole steps and half steps. The major scale and minor scale are both seven-note scales having five whole steps and two half steps, yet they sound strikingly unlike each other because of the pattern of whole steps and half step is different. Scale ...
Night in Tunisia thoughts,
... Arpeggiating A7 over a C7b9 chord would be an example of that type of sub. Various interesting upper structure voivings are formed by the dim scale. For the C7 dim scale again: Eb/C7 (C7+9) A/C7 (C13b9) and the very dissonant F#/C7 (C7b9#11, but I don’t really hear it in that way) 5) goes great with ...
... Arpeggiating A7 over a C7b9 chord would be an example of that type of sub. Various interesting upper structure voivings are formed by the dim scale. For the C7 dim scale again: Eb/C7 (C7+9) A/C7 (C13b9) and the very dissonant F#/C7 (C7b9#11, but I don’t really hear it in that way) 5) goes great with ...
Intonation in Maqam - Sami Abu Shumays samiabushumays.com
... third to the major scale, then clearly the first example is using as its third note [one two three] another note somewhere in between the minor and major third. Is that third note exactly in between the major and the minor third? The hypothesis that the Arabic scale uses 24 equal divisions of the oc ...
... third to the major scale, then clearly the first example is using as its third note [one two three] another note somewhere in between the minor and major third. Is that third note exactly in between the major and the minor third? The hypothesis that the Arabic scale uses 24 equal divisions of the oc ...
The chromatic scale The major scale Scale degrees and
... described in this way, we call the notes scale degrees, because they're placed in context of a specific scale. Solfège syllables, a centuriesold method of teaching pitch and sight singing, can also be used to represent scale degrees (when used in this way, this system is specifically called movable ...
... described in this way, we call the notes scale degrees, because they're placed in context of a specific scale. Solfège syllables, a centuriesold method of teaching pitch and sight singing, can also be used to represent scale degrees (when used in this way, this system is specifically called movable ...
Notes - Stanford University
... The frequency of the first mode of oscillation for a string or tube is known as its fundamental frequency, or the first harmonic, and the frequency that is n times the fundamental frequency is the nth harmonic. That the frequencies of the harmonics are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency ...
... The frequency of the first mode of oscillation for a string or tube is known as its fundamental frequency, or the first harmonic, and the frequency that is n times the fundamental frequency is the nth harmonic. That the frequencies of the harmonics are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency ...
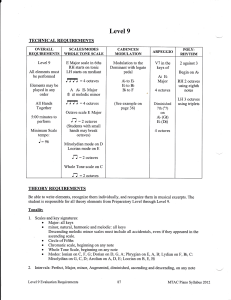
Level 9 - The Music Makers
... whole tone scale: a six-note scale consisting entirely of whole steps (Major 2nds) ...
... whole tone scale: a six-note scale consisting entirely of whole steps (Major 2nds) ...
Chapter 8 Intervals - G Major Music Theory
... • Intervals have two names, a general name and a specific name. • The general name is usually an ordinal number (2nd, 3rd, 4th and so on). • To find the general name of an interval, call the bottom note “one” and count the lines and spaces to the top note. Remember to count both the bottom and the t ...
... • Intervals have two names, a general name and a specific name. • The general name is usually an ordinal number (2nd, 3rd, 4th and so on). • To find the general name of an interval, call the bottom note “one” and count the lines and spaces to the top note. Remember to count both the bottom and the t ...
Jewish Music - Hazzan Rob Menes
... Jewish musicologists have devoted great effort to defining nusah as it relates to the musical delivery of the liturgy. Mark Slobin, in Chosen Voices1, presents an interesting assortment of views on the meaning of nusah: “The nusach is the cement that holds the service together.” “These melodies and ...
... Jewish musicologists have devoted great effort to defining nusah as it relates to the musical delivery of the liturgy. Mark Slobin, in Chosen Voices1, presents an interesting assortment of views on the meaning of nusah: “The nusach is the cement that holds the service together.” “These melodies and ...
PERSIAN TRADITIONAL MUSIC - Foundation for Iranian Studies
... time, or, for that matter, on instruments that are known today. All the measurements given by Safiaddin and others were based on the position of fingers on the fingerboard of the ud. The ud has a short unfretted fingerboard, making it virtually impossible to produce tones of absolute precision. All ...
... time, or, for that matter, on instruments that are known today. All the measurements given by Safiaddin and others were based on the position of fingers on the fingerboard of the ud. The ud has a short unfretted fingerboard, making it virtually impossible to produce tones of absolute precision. All ...
Bemidji Public Schools Course Map—Music Grades 9
... chromatically up from Bb including: Bb, B, C, Db, D, Eb, for one octave maintaining a steady tempo using or not using music (student choice) ...
... chromatically up from Bb including: Bb, B, C, Db, D, Eb, for one octave maintaining a steady tempo using or not using music (student choice) ...
Octave - Philip Tagg
... as ‘the same note’. For example, men are understood to be singing the same tune as women and children if both parties follow the same pitch contour at the same time in parallel octaves. The octave’s property of ‘unison at another pitch’ is also illustrated by the fact that: (i) a common chord consis ...
... as ‘the same note’. For example, men are understood to be singing the same tune as women and children if both parties follow the same pitch contour at the same time in parallel octaves. The octave’s property of ‘unison at another pitch’ is also illustrated by the fact that: (i) a common chord consis ...
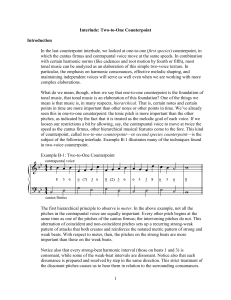
1 Interlude: Two-to-One Counterpoint Introduction In the last
... pull too much in one direction, multiple focal points, an overly small range, nonresolving leading tones (except for stepwise descending lines), dissonant melodic intervals, same-direction motion before and after large leaps (or after fourths), more than two consecutive leaps in the same direction, ...
... pull too much in one direction, multiple focal points, an overly small range, nonresolving leading tones (except for stepwise descending lines), dissonant melodic intervals, same-direction motion before and after large leaps (or after fourths), more than two consecutive leaps in the same direction, ...
Dynamic Tonality - William A. Sethares
... arrangement of note-controlling buttons. A note-layout is a mapping of notes to a button-field. The word isomorphic comes from the Greek roots “iso” (equal) and “morph” (shape), and we use it to mean “same shape.” On an isomorphic note-layout, pressing any two buttonfield buttons that have a given g ...
... arrangement of note-controlling buttons. A note-layout is a mapping of notes to a button-field. The word isomorphic comes from the Greek roots “iso” (equal) and “morph” (shape), and we use it to mean “same shape.” On an isomorphic note-layout, pressing any two buttonfield buttons that have a given g ...
Major Scales - LearnMusicTheory.net
... The lower tetrachord and the upper tetrachord each follow the major tetrachord pattern: W-W-h, with a whole step between them. To visualize the whole step/half step pattern shown above, review 1.2 The Chromatic Scale and the Piano. Remember that E to F and B to C are natural half steps (no accidenta ...
... The lower tetrachord and the upper tetrachord each follow the major tetrachord pattern: W-W-h, with a whole step between them. To visualize the whole step/half step pattern shown above, review 1.2 The Chromatic Scale and the Piano. Remember that E to F and B to C are natural half steps (no accidenta ...
An Exhibition as a Tool to Approach Didactical and
... Presenting the history of the so-called Pythagoras’ experiment of monochord, this room allows the reproduction, as well as the exploration and experimentation of its main consequences -- ratios 1:2, 2:3 and 3:4 underlying the perfect consonances octave, fifth and fourth – culminating with the constr ...
... Presenting the history of the so-called Pythagoras’ experiment of monochord, this room allows the reproduction, as well as the exploration and experimentation of its main consequences -- ratios 1:2, 2:3 and 3:4 underlying the perfect consonances octave, fifth and fourth – culminating with the constr ...
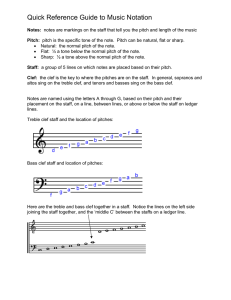
Quick Reference Guide to Music Notation
... Quick Reference Guide to Music Notation Notes: notes are markings on the staff that tell you the pitch and length of the music Pitch: pitch is the specific tone of the note. Pitch can be natural, flat or sharp. • Natural: the normal pitch of the note. • Flat: ½ a tone below the normal pitch of the n ...
... Quick Reference Guide to Music Notation Notes: notes are markings on the staff that tell you the pitch and length of the music Pitch: pitch is the specific tone of the note. Pitch can be natural, flat or sharp. • Natural: the normal pitch of the note. • Flat: ½ a tone below the normal pitch of the n ...
Major and Minor Pentatonic Scales
... however, learning only two different pentatonic scales will cover 99.9% of the playing situations that you will encounter. These two scales are referred to as the MAJOR PENTATONIC and the MINOR PENTATONIC. ...
... however, learning only two different pentatonic scales will cover 99.9% of the playing situations that you will encounter. These two scales are referred to as the MAJOR PENTATONIC and the MINOR PENTATONIC. ...
music terminology
... Decrescendo: Decrease in volume Diminuendo: Gradually become softer Diatonic: Pertaining to the notes of a major or minor scale Dissonance: A relation or state of tension between various tones Divisi: To divide; as into parts Dolce: Sweetly ...
... Decrescendo: Decrease in volume Diminuendo: Gradually become softer Diatonic: Pertaining to the notes of a major or minor scale Dissonance: A relation or state of tension between various tones Divisi: To divide; as into parts Dolce: Sweetly ...
essay - Dartmouth Math Home
... The more music is used to represent bird calls, echoes, train whistles, and similar phenomena, the more the line is blurred between music and sound. John Cage, in particular, was important for his philosophical explorations into the nature of music: his piece 4’33’’ consisted of a musician sitting ...
... The more music is used to represent bird calls, echoes, train whistles, and similar phenomena, the more the line is blurred between music and sound. John Cage, in particular, was important for his philosophical explorations into the nature of music: his piece 4’33’’ consisted of a musician sitting ...
rhythm/duration/metre
... c) produce supported sound, co-ordinating hand and tongue d) produce a controlled column of air e) assemble and show care of the clarinet a) copy simple melodies using known notes b) recognise high and low notes c) echo a rhythm d) move in time to a piece of music d) identify simple moods in music ...
... c) produce supported sound, co-ordinating hand and tongue d) produce a controlled column of air e) assemble and show care of the clarinet a) copy simple melodies using known notes b) recognise high and low notes c) echo a rhythm d) move in time to a piece of music d) identify simple moods in music ...
About “Practicing”
... Tone Research This is the search for the most beautiful tone that can be made on that day by that bass, that bow and that bass player. (Actually the tuning procedure is also tone research because it is impossible to tune the bass correctly without using one’s best bow technique.) Tone research in it ...
... Tone Research This is the search for the most beautiful tone that can be made on that day by that bass, that bow and that bass player. (Actually the tuning procedure is also tone research because it is impossible to tune the bass correctly without using one’s best bow technique.) Tone research in it ...
Document
... - African tone scales are becoming more western like[3] Artistic input e.g. experimentation with microtonal compositions. Educational opportunities: improve intonation. ...
... - African tone scales are becoming more western like[3] Artistic input e.g. experimentation with microtonal compositions. Educational opportunities: improve intonation. ...
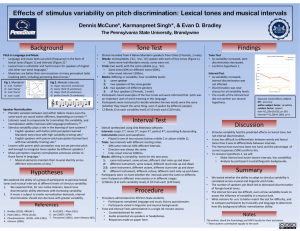
Background Tone Test Interval Test Hypotheses Procedure Findings
... Pitch in Language and Music • Language and music both use pitch (frequency) in the form of lexical tones (Figure 1) and intervals (Figure 2).1 • Lexical tone is unfamiliar and hard to learn for speakers of English and other non-tonal languages.1 • Musicians are better than non-musicians at many perc ...
... Pitch in Language and Music • Language and music both use pitch (frequency) in the form of lexical tones (Figure 1) and intervals (Figure 2).1 • Lexical tone is unfamiliar and hard to learn for speakers of English and other non-tonal languages.1 • Musicians are better than non-musicians at many perc ...
Just intonation

In music, just intonation (sometimes abbreviated as JI) or pure intonation is any musical tuning in which the frequencies of notes are related by ratios of small whole numbers. Any interval tuned in this way is called a pure or just interval. The two notes in any just interval are members of the same harmonic series. Frequency ratios involving large integers such as 1024:927 are not generally said to be justly tuned. ""Just intonation is the tuning system of the later ancient Greek modes as codified by Ptolemy; it was the aesthetic ideal of the Renaissance theorists; and it is the tuning practice of a great many musical cultures worldwide, both ancient and modern.""Just intonation can be contrasted and compared with equal temperament, which dominates Western instruments of fixed pitch (e.g., piano or organ) and default MIDI tuning on electronic keyboards. In equal temperament, all intervals are defined as multiples of the same basic interval, or more precisely, the intervals are ratios which are integer powers of the smallest step ratio, so two notes separated by the same number of steps always have exactly the same frequency ratio. However, except for doubling of frequencies (one or more octaves), no other intervals are exact ratios of small integers. Each just interval differs a different amount from its analogous, equally tempered interval.Justly tuned intervals can be written as either ratios, with a colon (for example, 3:2), or as fractions, with a solidus (3 ⁄ 2). For example, two tones, one at 300 Hertz (cycles per second), and the other at 200 hertz are both multiples of 100 Hz and as such members of the harmonic series built on 100 Hz. Thus 3/2, known as a perfect fifth, may be defined as the musical interval (the ratio) between the second and third harmonics of any fundamental pitch.