Settling a Question about Pythagorean Triples
... have a < c and b < c . Furthermore, from (0) and the fact that x 2 has an even number of factors 2, follows that a ≠b . Hence, the three numbers in a Pythagorean triple are distinct. Observe that (b , a , c ) is also Pythagorean. Therefore, a set of three positive integers defines zero or two (essen ...
... have a < c and b < c . Furthermore, from (0) and the fact that x 2 has an even number of factors 2, follows that a ≠b . Hence, the three numbers in a Pythagorean triple are distinct. Observe that (b , a , c ) is also Pythagorean. Therefore, a set of three positive integers defines zero or two (essen ...
Class Field Theory
... He studied the Gaussian integers ZŒi in order to find a quartic reciprocity law. He studied the classification of binary quadratic forms over Z, which is closely related to the problem of finding the class numbers of quadratic fields. D IRICHLET (1805–1859). He introduced L-series, and used them t ...
... He studied the Gaussian integers ZŒi in order to find a quartic reciprocity law. He studied the classification of binary quadratic forms over Z, which is closely related to the problem of finding the class numbers of quadratic fields. D IRICHLET (1805–1859). He introduced L-series, and used them t ...
Nearly Prime Subsemigroups of βN
... (b) If there is carrying into the rth place, αr (u + q) ≡ 1 + αr (q) (mod ar ). Consequently, if there is any r > `(u) for which there is no carrying into th the r place we have from (a) and the fact that µ(u + q) = 1 , that eventually αt (q) ≤ 1 . Alternately, for all r ≥ `(u) one has carrying into ...
... (b) If there is carrying into the rth place, αr (u + q) ≡ 1 + αr (q) (mod ar ). Consequently, if there is any r > `(u) for which there is no carrying into th the r place we have from (a) and the fact that µ(u + q) = 1 , that eventually αt (q) ≤ 1 . Alternately, for all r ≥ `(u) one has carrying into ...
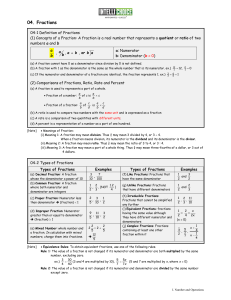
Lecture 5 Message Authentication and Hash Functions
... First observe that ZN* is closed under multiplication modulo N. This is because is a,b are relatively prime to N, then ab is also relatively prime to N. Associativity and commutativity are trivial. 1 is the identity element. It remains to show that for every a є ZN* there always exist an b є ZN* tha ...
... First observe that ZN* is closed under multiplication modulo N. This is because is a,b are relatively prime to N, then ab is also relatively prime to N. Associativity and commutativity are trivial. 1 is the identity element. It remains to show that for every a є ZN* there always exist an b є ZN* tha ...
Hartshorne Ch. II, §3 First Properties of Schemes
... this is possible since νi |Xij = νj |Xij on each Xij since normalization is unique. Finally, we must show that this scheme ν : X̃ → X satisfies the universal property for normalization. Let f : Z → X be dominant, and let Zi = f −1 (Xi ). Then, since Zi → Xi is then dominant, by the universal propert ...
... this is possible since νi |Xij = νj |Xij on each Xij since normalization is unique. Finally, we must show that this scheme ν : X̃ → X satisfies the universal property for normalization. Let f : Z → X be dominant, and let Zi = f −1 (Xi ). Then, since Zi → Xi is then dominant, by the universal propert ...