Document
... Membrane proteins carry out func ons such as nutrient uptake, ATP synthesis or transmembrane signal transduc on. An increasing number of reports indicate that cellular processes are underpinned by regulated interac ons between these proteins. Consequently, func onal studies of these networks at a mo ...
... Membrane proteins carry out func ons such as nutrient uptake, ATP synthesis or transmembrane signal transduc on. An increasing number of reports indicate that cellular processes are underpinned by regulated interac ons between these proteins. Consequently, func onal studies of these networks at a mo ...
Transport
... • Requires series of proteins • Energy brings sugar in AND activates it for metabolism. ...
... • Requires series of proteins • Energy brings sugar in AND activates it for metabolism. ...
Membranes
... Cell membranes are made up of a double layer (bilayer) of these phospholipid molecules. This makes the membrane very stable but also allows flexibility. The phospholipid in the membrane are in a fluid state which allows the cell to change it’s shape easily. ...
... Cell membranes are made up of a double layer (bilayer) of these phospholipid molecules. This makes the membrane very stable but also allows flexibility. The phospholipid in the membrane are in a fluid state which allows the cell to change it’s shape easily. ...
MembraneStructure
... forming glycolipids, or, more commonly, to proteins, forming glycoproteins. • The oligosaccharides on the external side of the plasma membrane vary from species to species, individual to individual, and even from cell type to cell type within the same individual. • This variation marks each cell typ ...
... forming glycolipids, or, more commonly, to proteins, forming glycoproteins. • The oligosaccharides on the external side of the plasma membrane vary from species to species, individual to individual, and even from cell type to cell type within the same individual. • This variation marks each cell typ ...
bi 112 vital vocab #1
... Instructions: read each line, if no instructions are provided for the line, then define each term or provide an example for each term. If instructions are provide, define each term and also follow the instructions for an additional procedure. All work must be typed and emailed to me by the due date ...
... Instructions: read each line, if no instructions are provided for the line, then define each term or provide an example for each term. If instructions are provide, define each term and also follow the instructions for an additional procedure. All work must be typed and emailed to me by the due date ...
Golgi Apparatus
... Contains nuclear envelope, nucleoli, chromatin, and distinct compartments rich in specific protein sets Gene-containing control center of the cell Contains the genetic library with blueprints for nearly all cellular proteins Dictates the kinds and amounts of proteins to be synthesized ...
... Contains nuclear envelope, nucleoli, chromatin, and distinct compartments rich in specific protein sets Gene-containing control center of the cell Contains the genetic library with blueprints for nearly all cellular proteins Dictates the kinds and amounts of proteins to be synthesized ...
Cell Physiology
... to move through a protein membrane channel or may have to use a carrier protein to complete their movement from high to low concentrations. ...
... to move through a protein membrane channel or may have to use a carrier protein to complete their movement from high to low concentrations. ...
Resting Membrane Potential
... negative, the membrane is not at resting potential because it now has too much Na+ inside and not enough K+ ions. The presence of high Na+ inside causes the Na+/K+ pumps to increase by a power of 3. The faster pump rate quickly restores the membrane back to its steady-state resting condition. ...
... negative, the membrane is not at resting potential because it now has too much Na+ inside and not enough K+ ions. The presence of high Na+ inside causes the Na+/K+ pumps to increase by a power of 3. The faster pump rate quickly restores the membrane back to its steady-state resting condition. ...
membrane structure and function
... entropy of the system (less order) • Molecular collisions result in molecules being moved along a gradient (concentration gradient or free energy gradient) • Through random molecular collisions directional motion can be accomplished ...
... entropy of the system (less order) • Molecular collisions result in molecules being moved along a gradient (concentration gradient or free energy gradient) • Through random molecular collisions directional motion can be accomplished ...
Special Guest Speaker Dr. Christopher Colbert
... to Identify Novel Bio-Based Solutions Metalloproteins comprise approximately one-third of all proteins, and are critical for many of the biochemical processes responsible for life. Our longterm goal is to elucidate how cells import, incorporate, and utilize metals within proteins by using a combinat ...
... to Identify Novel Bio-Based Solutions Metalloproteins comprise approximately one-third of all proteins, and are critical for many of the biochemical processes responsible for life. Our longterm goal is to elucidate how cells import, incorporate, and utilize metals within proteins by using a combinat ...
Analysis of the outer membrane insertion mechanism of yeast
... the TOM40 complex, small TIMs and the Sorting and Assembly Machinery (SAM) of the OM. As for α-helical proteins, the insertion machinery is still not quite clear. Therefore, there are still unidentified pathways for the import of α-helical OM proteins. Yeast Om45 is one of the most abundant proteins ...
... the TOM40 complex, small TIMs and the Sorting and Assembly Machinery (SAM) of the OM. As for α-helical proteins, the insertion machinery is still not quite clear. Therefore, there are still unidentified pathways for the import of α-helical OM proteins. Yeast Om45 is one of the most abundant proteins ...
chapt05_lecture_anim
... transmembrane protein can create a pore through the membrane – Cylinder of sheets in the protein secondary structure called a -barrel • Interior is polar and allows water and small polar molecules to pass through the membrane ...
... transmembrane protein can create a pore through the membrane – Cylinder of sheets in the protein secondary structure called a -barrel • Interior is polar and allows water and small polar molecules to pass through the membrane ...
Organic chemistry and Biological chemistry for Health Sciences
... Concentration gradient of many ions has to be maintained between cells interior and the fluid outside for the cells to function. Proteins in the membrane maintain the concentration gradient of those ions. F.example Virtually every animal cell maintains a lower concentration of Na+ and a higher conce ...
... Concentration gradient of many ions has to be maintained between cells interior and the fluid outside for the cells to function. Proteins in the membrane maintain the concentration gradient of those ions. F.example Virtually every animal cell maintains a lower concentration of Na+ and a higher conce ...
Lecture 9
... • Joined by specific protein structures called gap junctions (specialized ionic channels that connect the cytoplasm of both cells) • Action potential comes to gap junction depolarizes or hyperpolarizes the membrane induces opening of the channels diffusion of ions from one neuron to the other ...
... • Joined by specific protein structures called gap junctions (specialized ionic channels that connect the cytoplasm of both cells) • Action potential comes to gap junction depolarizes or hyperpolarizes the membrane induces opening of the channels diffusion of ions from one neuron to the other ...
File
... 1) Sodium ions are binding to the sodium/potassium pump. 2) ATP molecules are phosphorylates, where a phosphate breaks off, releases energy, and binds to the sodium potassium pump. 3) the binding of the phosphate stimulates the pump to change shapes and open to the outside of the cell, thus releasin ...
... 1) Sodium ions are binding to the sodium/potassium pump. 2) ATP molecules are phosphorylates, where a phosphate breaks off, releases energy, and binds to the sodium potassium pump. 3) the binding of the phosphate stimulates the pump to change shapes and open to the outside of the cell, thus releasin ...
Lecture 16 - Biology Courses Server
... targeting proteins to the lysosome • Recessive mutation in single gene… • Fibroblasts of patients contain large inclusions (I-cells)… • Lysosomes lack normal complement of acid hydrolases… • All lysosomal enzymes secreted (secretion is the “default” fate for proteins in the ER-Golgi pathway)… • Lyso ...
... targeting proteins to the lysosome • Recessive mutation in single gene… • Fibroblasts of patients contain large inclusions (I-cells)… • Lysosomes lack normal complement of acid hydrolases… • All lysosomal enzymes secreted (secretion is the “default” fate for proteins in the ER-Golgi pathway)… • Lyso ...
• The cell is the structural and functional unit of life • Human adults
... Cell Membrane Proteins • Integral or transmembrane proteins – completely pass through the bilayer • extracellular portion is exposed to the ECF –composed of polar amino acids • intracellular portion is exposed to the ICF –composed of polar amino acids • “connect” the ICF and ECF –composed of nonpol ...
... Cell Membrane Proteins • Integral or transmembrane proteins – completely pass through the bilayer • extracellular portion is exposed to the ECF –composed of polar amino acids • intracellular portion is exposed to the ICF –composed of polar amino acids • “connect” the ICF and ECF –composed of nonpol ...
Cells
... Cell Membrane Proteins • Integral or transmembrane proteins – completely pass through the bilayer • extracellular portion is exposed to the ECF –composed of polar amino acids • intracellular portion is exposed to the ICF –composed of polar amino acids • “connect” the ICF and ECF –composed of nonpol ...
... Cell Membrane Proteins • Integral or transmembrane proteins – completely pass through the bilayer • extracellular portion is exposed to the ECF –composed of polar amino acids • intracellular portion is exposed to the ICF –composed of polar amino acids • “connect” the ICF and ECF –composed of nonpol ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... • Polar and charged substances do not diffuse across lipid bilayers. • One way for these important raw materials to enter cells is through the process of facilitated diffusion. ...
... • Polar and charged substances do not diffuse across lipid bilayers. • One way for these important raw materials to enter cells is through the process of facilitated diffusion. ...
Presentation
... proteins with a central passage for ions and small molecules • Solutes of appropriate size, charge, and molecular structure can diffuse down a concentration gradient • Process requires no energy • Rate may approach diffusion-controlled limit ...
... proteins with a central passage for ions and small molecules • Solutes of appropriate size, charge, and molecular structure can diffuse down a concentration gradient • Process requires no energy • Rate may approach diffusion-controlled limit ...
Chapter 4
... - Allow transport of ions - They are specific to the size and charge of the ions Carrier Proteins – two types - change shape to allow certain molecules to cross the plasma membrane 2. Gates – one particle attaches to the carrier protein changing its shape – allowing particles to freely pass across t ...
... - Allow transport of ions - They are specific to the size and charge of the ions Carrier Proteins – two types - change shape to allow certain molecules to cross the plasma membrane 2. Gates – one particle attaches to the carrier protein changing its shape – allowing particles to freely pass across t ...
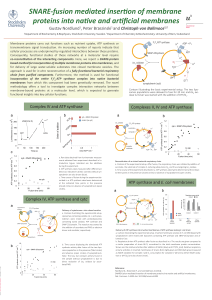
SNARE (protein)

SNARE proteins (an acronym derived from ""SNAP (Soluble NSF Attachment Protein) REceptor"") are a large protein superfamily consisting of more than 60 members in yeast and mammalian cells. The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate vesicle fusion, that is, the fusion of vesicles with their target membrane bound compartments (such as a lysosome). The best studied SNAREs are those that mediate docking of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane in neurons. These SNAREs are the targets of the bacterial neurotoxins responsible for botulism and tetanus.