Lecture 16. Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, and the Tree of Life
... 3. RNA polymerase more complex than bacteria 8 or more proteins (eukaryotes have 8-10) 4. RNA polymerase needs “help” from other proteins to begin making mRNA copies of genes (called transcription factors are similar to eukaryotes) 5. Signature sequences also tell RNA polymerase where to start makin ...
... 3. RNA polymerase more complex than bacteria 8 or more proteins (eukaryotes have 8-10) 4. RNA polymerase needs “help” from other proteins to begin making mRNA copies of genes (called transcription factors are similar to eukaryotes) 5. Signature sequences also tell RNA polymerase where to start makin ...
Prokaryote Gene Expression Section 1 Overview of RNA
... They are translated from the 5’ to the 3’ end Generally mRNAs are linear (although some prokaryotic RNA viruses are circular and act as mRNAs) ...
... They are translated from the 5’ to the 3’ end Generally mRNAs are linear (although some prokaryotic RNA viruses are circular and act as mRNAs) ...
Unit 7 Vocabulary _ Protein Synthesis
... molecules transcribed from DNA in the cell nucleus or in the mitochondrion or chloroplast, containing along the strand a linear sequence of nucleotide bases that is complementary to the DNA strand from which it is transcribed: the composition of the RNA molecule is identical with that of DNA except ...
... molecules transcribed from DNA in the cell nucleus or in the mitochondrion or chloroplast, containing along the strand a linear sequence of nucleotide bases that is complementary to the DNA strand from which it is transcribed: the composition of the RNA molecule is identical with that of DNA except ...
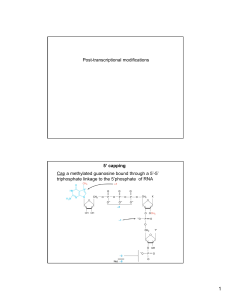
Post-transcriptional modifications Cap a
... In some cases, mobile, sequence-specific silencing signals can move from cell-to-cell or even over long distances in the plant. Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNA ...
... In some cases, mobile, sequence-specific silencing signals can move from cell-to-cell or even over long distances in the plant. Several current models hold that silencing signals are “aberrant” RNAs (aRNA), that differ in some way from normal mRNAs. The most likely candidates are small antisense RNA ...
Central Dogma - essentiavitae.com
... 9. Describe the events of transcription initiation. – transcription factors and RNA polymerase are attracted to a promoter of a gene 10. List the three major types of RNA and their functions. – mRNa carries the information that specifies a particular protein. rRNA associate with certain proteins ...
... 9. Describe the events of transcription initiation. – transcription factors and RNA polymerase are attracted to a promoter of a gene 10. List the three major types of RNA and their functions. – mRNa carries the information that specifies a particular protein. rRNA associate with certain proteins ...
Managing people in sport organisations: A strategic human resource
... the GAL4 site, the transcription factor does not recognize or bind the DNA. (C) An artificial protein made by combining a LexA binding domain with a GAL4 activator domain will not recognize the GAL4 site, but (D) will bind to the LexA recognition sequence and activate transcription. Thus, the GAL4 a ...
... the GAL4 site, the transcription factor does not recognize or bind the DNA. (C) An artificial protein made by combining a LexA binding domain with a GAL4 activator domain will not recognize the GAL4 site, but (D) will bind to the LexA recognition sequence and activate transcription. Thus, the GAL4 a ...
Model for transcriptional activation
... enhancers and silencers • Trans-acting factors - proteins - act in conjunction with cis-elements. • Enhancers stimulate transcription while silencers inhibit transcription. Certain elements can act as silencers or enhancers depending on the trans-acting factors present. • Enhancers and silencers are ...
... enhancers and silencers • Trans-acting factors - proteins - act in conjunction with cis-elements. • Enhancers stimulate transcription while silencers inhibit transcription. Certain elements can act as silencers or enhancers depending on the trans-acting factors present. • Enhancers and silencers are ...
Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein
... Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master the material. To give you an idea of the depth and time ...
... Chapter 14: Gene Expression: From Gene to Protein This is going to be a very long journey, but it is crucial to your understanding of biology. Work on this chapter a single concept at a time, and expect to spend at least 6 hours to truly master the material. To give you an idea of the depth and time ...
Document
... d. When RNA polymerase II recognizes a chain terminator (stop codons—UAA, UAG, or UGA) on the DNA molecule, it terminates its association with the DNA and is released to repeat transcription. e. The primary transcript, pre-mRNA after the introns are removed, associates with proteins to form hnRNP. f ...
... d. When RNA polymerase II recognizes a chain terminator (stop codons—UAA, UAG, or UGA) on the DNA molecule, it terminates its association with the DNA and is released to repeat transcription. e. The primary transcript, pre-mRNA after the introns are removed, associates with proteins to form hnRNP. f ...
How Genes Work
... RNA polymerase starts at promoter Its complex unwinds DNA It copies bases using complimentary base pairing (U v.s. T) Moves down one strand Stops at terminator ...
... RNA polymerase starts at promoter Its complex unwinds DNA It copies bases using complimentary base pairing (U v.s. T) Moves down one strand Stops at terminator ...
RNA Molecules: More than Mere Information Intermediaries
... targets scattered throughout the chromosome. These more recently identified ncRNA molecules also show a relatively low level of complementarity to their mRNA targets. A few antisense ncRNAs function either by stimulating or repressing translation of their target. For some of these mRNA targets, the ...
... targets scattered throughout the chromosome. These more recently identified ncRNA molecules also show a relatively low level of complementarity to their mRNA targets. A few antisense ncRNAs function either by stimulating or repressing translation of their target. For some of these mRNA targets, the ...
o How is covariation used in RNA structure
... c. ____ The process in which information in DNA is copied into RNA is called transcription. d. ____ Peptide bonds are both planar and flexible. e. ____ Enzymes that catalyze reactions in the cell are always proteins. f. ____ Protein interactions are not required for the functions of most proteins. g ...
... c. ____ The process in which information in DNA is copied into RNA is called transcription. d. ____ Peptide bonds are both planar and flexible. e. ____ Enzymes that catalyze reactions in the cell are always proteins. f. ____ Protein interactions are not required for the functions of most proteins. g ...
Nuclear Pores Come into Sharper Focus Nuclear Pores Come into
... core is decorated with proteins called cytoplasmic filaments that participate in protein transport and mRNA export; on the inside, the symmetric core is associated with nuclear basket nucleoporins, which interact with chromatin and the transcription machinery. In the central transport channel, a dif ...
... core is decorated with proteins called cytoplasmic filaments that participate in protein transport and mRNA export; on the inside, the symmetric core is associated with nuclear basket nucleoporins, which interact with chromatin and the transcription machinery. In the central transport channel, a dif ...
CHAPTER 17
... contains a high number of CpG sites. CpG islands are often located near promoters. When the island is methylated, this inhibits transcription. This inhibition may be the result of the inability of the transcriptional activators to recognize the methylated promoter and/or the effects of methyl-CpG-bi ...
... contains a high number of CpG sites. CpG islands are often located near promoters. When the island is methylated, this inhibits transcription. This inhibition may be the result of the inability of the transcriptional activators to recognize the methylated promoter and/or the effects of methyl-CpG-bi ...
PDF
... mounting evidence suggests that Notch’s entry into endosomes promotes its signalling. In a search for factors that regulate Notch activation in endosomes, the researchers isolated mutants in the Drosophila genes that encode V-ATPase subunits. Their characterisation of these mutants indicates that V- ...
... mounting evidence suggests that Notch’s entry into endosomes promotes its signalling. In a search for factors that regulate Notch activation in endosomes, the researchers isolated mutants in the Drosophila genes that encode V-ATPase subunits. Their characterisation of these mutants indicates that V- ...
Transcription - OpenStax CNX
... degradation, factors involved in protein synthesis recognize the cap to help initiate translation by ribosomes. Once elongation is complete, an enzyme then adds a string of approximately 200 adenine residues to the 3' end, called the poly-A tail. This modi cation further protects the pre-mRNA from d ...
... degradation, factors involved in protein synthesis recognize the cap to help initiate translation by ribosomes. Once elongation is complete, an enzyme then adds a string of approximately 200 adenine residues to the 3' end, called the poly-A tail. This modi cation further protects the pre-mRNA from d ...
Gene Expression Overview
... Alleles are forms of the same gene with small differences in their sequence of DNA bases. Alternative splicing: is a very common phenomenon in higher eukaryotes. It is a way to get more than one protein product out of the same gene and a way to control gene expression in cells. Exon: a segment of a ...
... Alleles are forms of the same gene with small differences in their sequence of DNA bases. Alternative splicing: is a very common phenomenon in higher eukaryotes. It is a way to get more than one protein product out of the same gene and a way to control gene expression in cells. Exon: a segment of a ...
Promoter-proximal Elements
... Both enhancers and silencers affect transcription rate. Each has unique DNA sequence for the binding of regulatory proteins. Enhancer sequences contain multiple binding sites for trans-acting regulatory proteins. Enhancers could be located upstream from the promoter, downstream from the gene, or eve ...
... Both enhancers and silencers affect transcription rate. Each has unique DNA sequence for the binding of regulatory proteins. Enhancer sequences contain multiple binding sites for trans-acting regulatory proteins. Enhancers could be located upstream from the promoter, downstream from the gene, or eve ...
Unsuitability of Using Ribosomal RNA as Loading Control for
... ethidium bromide-stained gel image were also performed with this system. The densitometric value obtained for c-Ha-ras and c-erbB mRNAs for each sample was normalized relative to -actin, GAPDH, and p0 mRNAs, and to 28S rRNA. Among the 121 mammary tumors analyzed we detected the above described imba ...
... ethidium bromide-stained gel image were also performed with this system. The densitometric value obtained for c-Ha-ras and c-erbB mRNAs for each sample was normalized relative to -actin, GAPDH, and p0 mRNAs, and to 28S rRNA. Among the 121 mammary tumors analyzed we detected the above described imba ...
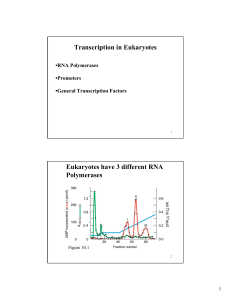
Transcription in Eukaryotes Eukaryotes have 3 different RNA
... binding to promoters and a basal level of transcription. •Gene-specific factors stimulate transcription further (or repress it) and allow fine regulatory control. ...
... binding to promoters and a basal level of transcription. •Gene-specific factors stimulate transcription further (or repress it) and allow fine regulatory control. ...
Dr. Peter John M.Phil, PhD Assistant Professor National University of
... National University of Sciences & Technology (NUST) ...
... National University of Sciences & Technology (NUST) ...
The importance ofRNA
... through base-pairing, which dictate that only complementary sequences will bind with each other, making RNA binding very specific. These properties – flexibility, catalytic activity and specificity – make RNA a fantastic tool for inactivating specific genes, either to discover their functions or for ...
... through base-pairing, which dictate that only complementary sequences will bind with each other, making RNA binding very specific. These properties – flexibility, catalytic activity and specificity – make RNA a fantastic tool for inactivating specific genes, either to discover their functions or for ...
humanvs
... together to create big organic molecules. Scientist also believe (hypothesize) the first organic molecules to form and replicate are RNA and soon came DNA. Those RNA molecules are probably much smaller than they are now a day; those are the molecules that are known to build different types of protei ...
... together to create big organic molecules. Scientist also believe (hypothesize) the first organic molecules to form and replicate are RNA and soon came DNA. Those RNA molecules are probably much smaller than they are now a day; those are the molecules that are known to build different types of protei ...
YES YES
... tissues was probed with the Fos gene as well as a house keeping gene; Actin. Explain the results obtained ...
... tissues was probed with the Fos gene as well as a house keeping gene; Actin. Explain the results obtained ...
1 Transcription in eukaryotes Eukaryotic RNA polymerases
... Problem – enzyme is very complex, difficult to say which polypeptides that co-purify with the polymerase activity are really subunits or contaminants. Two approaches to study: •Separate subunits and then reconstitute to structure and check the function But: It was not yet possible to reconstitute RN ...
... Problem – enzyme is very complex, difficult to say which polypeptides that co-purify with the polymerase activity are really subunits or contaminants. Two approaches to study: •Separate subunits and then reconstitute to structure and check the function But: It was not yet possible to reconstitute RN ...