Geo 1 and 2 review answers
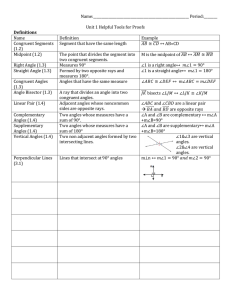
... acute angle – An angle whose measure is greater than zero and less than 90°. angle – A figure formed by two rays with a common endpoint. angle measure – The amount of degrees in an angle. bisect – To divide a segment or angle into two congruent parts. bisector – The line that divides the segment or ...
... acute angle – An angle whose measure is greater than zero and less than 90°. angle – A figure formed by two rays with a common endpoint. angle measure – The amount of degrees in an angle. bisect – To divide a segment or angle into two congruent parts. bisector – The line that divides the segment or ...
Perceived visual angle
In human visual perception, the visual angle, denoted θ, subtended by a viewed object sometimes looks larger or smaller than its actual value. One approach to this phenomenon posits a subjective correlate to the visual angle: the perceived visual angle or perceived angular size. An optical illusion where the physical and subjective angles differ is then called a visual angle illusion or angular size illusion.Angular size illusions are most obvious as relative angular size illusions, in which two objects that subtend the same visual angle appear to have different angular sizes; it is as if their equal-sized images on the retina were of different sizes. Angular size illusions are contrasted with linear size illusions, in which two objects that are the same physical size do not appear so. An angular size illusion may be accompanied by (or cause) a linear size illusion at the same time.The perceived visual angle paradigm begins with a rejection of the classical size–distance invariance hypothesis (SDIH), which states that the ratio of perceived linear size to perceived distance is a simple function of the visual angle. The SDIH does not explain some illusions, such as the Moon illusion, in which the Moon appears larger when it is near the horizon. It is replaced by a perceptual SDIH, in which the visual angle is replaced by the perceived visual angle. This new formulation avoids some of the paradoxes of the SDIH, but it remains difficult to explain why a given illusion occurs.This paradigm is not universally accepted; many textbook explanations of size and distance perception do not refer to the perceived visual angle, and some researchers deny that it exists. Some recent evidence supporting the idea, reported by Murray, Boyaci and Kersten (2006), suggests a direct relationship between the perceived angular size of an object and the size of the neural activity pattern it excites in the primary visual cortex.