Gene Switches - Science Take-Out
... switching genes off when the proteins they produce are not needed. Genes for proteins that are only needed under certain conditions are regulated by “on‐off switches.” ...
... switching genes off when the proteins they produce are not needed. Genes for proteins that are only needed under certain conditions are regulated by “on‐off switches.” ...
Evidence for the design of life: part 1—genetic redundancy
... useful information. Ohno’s idea of evolution through duplication also provides an explanation for the nophenotype knockouts: if genes duplicate fairly often, it is then reasonable to expect some level of redundancy in most genomes, because duplicates provide an organism with back-up genes. As long a ...
... useful information. Ohno’s idea of evolution through duplication also provides an explanation for the nophenotype knockouts: if genes duplicate fairly often, it is then reasonable to expect some level of redundancy in most genomes, because duplicates provide an organism with back-up genes. As long a ...
Barcode - Statistical Center for HIV/AIDS Research and Prevention
... • Test how depletion impacts phenotype with simple in vitro functional assay. • Unbiased whole genome screens bring new targets into the “pipeline”. ...
... • Test how depletion impacts phenotype with simple in vitro functional assay. • Unbiased whole genome screens bring new targets into the “pipeline”. ...
Supplemental Appendix A: ClueGene Algorithm and Time
... G; G has size g = |G|. Each dataset corresponds to an experiment series and consists of clusters of genes derived from experimental data. The number of datasets is d = |D|. There are two steps in the ClueGene scoring algorithm. First, dataset-specific scores are calculated for each gene. That is, ea ...
... G; G has size g = |G|. Each dataset corresponds to an experiment series and consists of clusters of genes derived from experimental data. The number of datasets is d = |D|. There are two steps in the ClueGene scoring algorithm. First, dataset-specific scores are calculated for each gene. That is, ea ...
Lecture 4: codominance and complementation
... A great example: the Heidelberg mutagenesis screen performed by Christiane Nusslein-Volhard and Eric Wieschaus, which won the Nobel Prize for Medicine in 1995 They established and tested 27,000 fly lines (saturation screen of 5000 expected genes in Drosophila) They found 18,000 lethal mutations ...
... A great example: the Heidelberg mutagenesis screen performed by Christiane Nusslein-Volhard and Eric Wieschaus, which won the Nobel Prize for Medicine in 1995 They established and tested 27,000 fly lines (saturation screen of 5000 expected genes in Drosophila) They found 18,000 lethal mutations ...
Gene Section IGK@ (Immunoglobulin Kappa) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Cox JP, Tomlinson IM, Winter G. A directory of human germline V kappa segments reveals a strong bias in their usage. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Apr;24(4):827-36 ...
... Cox JP, Tomlinson IM, Winter G. A directory of human germline V kappa segments reveals a strong bias in their usage. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Apr;24(4):827-36 ...
Section 11–3 Exploring Mendelian Genetics
... shape segregate independently of those for seed color? He observed F2 offspring that had combinations of phenotypes—and therefore combinations of alleles—not found in either parent. ...
... shape segregate independently of those for seed color? He observed F2 offspring that had combinations of phenotypes—and therefore combinations of alleles—not found in either parent. ...
Section 11–3 Exploring Mendelian Genetics (pages 270–274)
... shape segregate independently of those for seed color? He observed F2 offspring that had combinations of phenotypes—and therefore combinations of alleles—not found in either parent. ...
... shape segregate independently of those for seed color? He observed F2 offspring that had combinations of phenotypes—and therefore combinations of alleles—not found in either parent. ...
Problem Set 8
... purple blotches on their skin. How might you explain this result, assuming that it results from an effect on the prpl gene? This might result from position effect variegation. Perhaps a chromosomal rearrangement in that family has put the prpl gene near a heterochromatic region. ...
... purple blotches on their skin. How might you explain this result, assuming that it results from an effect on the prpl gene? This might result from position effect variegation. Perhaps a chromosomal rearrangement in that family has put the prpl gene near a heterochromatic region. ...
LETTER The Preferential Retention of Starch Synthesis Genes
... Gene duplication is a major force in evolution and can provide the genetic material necessary for the origin of new genes with novel functions (Ohno 1970). Polyploidy, which duplicates all genes in the genome, is an important source of biological innovation (Wendel 2000). In paleopolyploids, gene lo ...
... Gene duplication is a major force in evolution and can provide the genetic material necessary for the origin of new genes with novel functions (Ohno 1970). Polyploidy, which duplicates all genes in the genome, is an important source of biological innovation (Wendel 2000). In paleopolyploids, gene lo ...
Chapter 11 Notes – Introduction to Genetics
... Polygenic Traits – traits controlled by interaction of two or more genes (often show a wide range of phenotypes) i.e. at least three genes are involved in making the reddish-brown pigment in the eyes of fruit flies. Different combinations of alleles for these genes produce very different eye colors. ...
... Polygenic Traits – traits controlled by interaction of two or more genes (often show a wide range of phenotypes) i.e. at least three genes are involved in making the reddish-brown pigment in the eyes of fruit flies. Different combinations of alleles for these genes produce very different eye colors. ...
Maternal effect genes
... Nurse cells surrounding the oocyte in the ovarian follicle provide it with large amounts of mRNAs and proteins, some of which become localised in particular sites. The oocyte produces a local signal, which induces follicle cells at one end to become posterior follicle cells. The posterior follicle c ...
... Nurse cells surrounding the oocyte in the ovarian follicle provide it with large amounts of mRNAs and proteins, some of which become localised in particular sites. The oocyte produces a local signal, which induces follicle cells at one end to become posterior follicle cells. The posterior follicle c ...
Sex Chromosomes and Male Functions
... obvious: genes with male germline function would be enriched in autosomes after sufficient evolutionary time. This prediction is well corroborated by Drosophila expression analysis using DNA microarray technology26,28 and for many individual genes.17,25-28 Male germline genes also show a strong pref ...
... obvious: genes with male germline function would be enriched in autosomes after sufficient evolutionary time. This prediction is well corroborated by Drosophila expression analysis using DNA microarray technology26,28 and for many individual genes.17,25-28 Male germline genes also show a strong pref ...
exam 5 practice questions answers
... How many chromatids are present? 46 How many chromosomes are present? 46 Are these chromosomes duplicated, or unduplicated? Unduplicated How many pairs of homologous chromosomes are present? 23 What makes these chromosomes homologous? The fact that they exhibit the exact same banding in the same loc ...
... How many chromatids are present? 46 How many chromosomes are present? 46 Are these chromosomes duplicated, or unduplicated? Unduplicated How many pairs of homologous chromosomes are present? 23 What makes these chromosomes homologous? The fact that they exhibit the exact same banding in the same loc ...
Feature subset selection/ ANOVA
... 30. There are different ways of saving the results from the SAM analysis. We will now look at the different ways: Saving the table to a text file, branching a set of interesting genes to a sub dataset and storing the entire analysis in the project tree. 31. In the SAM window, select Save Table from ...
... 30. There are different ways of saving the results from the SAM analysis. We will now look at the different ways: Saving the table to a text file, branching a set of interesting genes to a sub dataset and storing the entire analysis in the project tree. 31. In the SAM window, select Save Table from ...
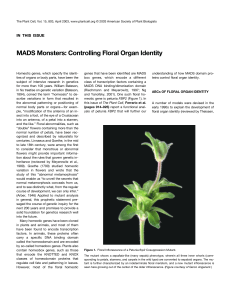
MADS Monsters: Controlling Floral Organ Identity
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
... 1894), coined the term “homeosis” to describe variations in form that resulted in the abnormal patterning or positioning of normal body parts or organs—for example, “modification of the antenna of an insect into a foot, of the eye of a Crustacean into an antenna, of a petal into a stamen, and the li ...
PDF - Circulation: Cardiovascular Genetics
... underestimated. Indeed, an early insight from exome sequencing has been the lack of trustworthiness of most existing human disease mutation catalogs.5,6 For some disease genes, all of the known mutations have been found in normal controls. How are we to build the knowledge base to interpret genomic ...
... underestimated. Indeed, an early insight from exome sequencing has been the lack of trustworthiness of most existing human disease mutation catalogs.5,6 For some disease genes, all of the known mutations have been found in normal controls. How are we to build the knowledge base to interpret genomic ...
NONRANDOM GENE DISTRIBUTION ON HUMAN CHROMOSOMES
... Human chromosomes are heterogeneous in structure and function. This is the reason for specific banding patterns produced by various chromosome staining techniques. The human genome is a mosaic of isochors and can be partitioned into five families, L1, L2, H1, H2 and H3, characterized by increasing G ...
... Human chromosomes are heterogeneous in structure and function. This is the reason for specific banding patterns produced by various chromosome staining techniques. The human genome is a mosaic of isochors and can be partitioned into five families, L1, L2, H1, H2 and H3, characterized by increasing G ...
Dragon Genetics
... The Law of Independent Assortment activities help students to understand that genes located on two separate chromosomes are inherited independently. First, the basis for understanding the Law of Independent Assortment is developed by analyzing expected outcomes of meiosis and fertilization. Then, a ...
... The Law of Independent Assortment activities help students to understand that genes located on two separate chromosomes are inherited independently. First, the basis for understanding the Law of Independent Assortment is developed by analyzing expected outcomes of meiosis and fertilization. Then, a ...
Solutions 9
... c) Suppose the new population consists of the six offspring individuals received by the crossover operations in the above question. Evaluate the fitness of the new population, showing all your workings. Has the overall fitness improved? Answer: ...
... c) Suppose the new population consists of the six offspring individuals received by the crossover operations in the above question. Evaluate the fitness of the new population, showing all your workings. Has the overall fitness improved? Answer: ...
Essential gene

Essential genes are those genes of an organism that are thought to be critical for its survival. However, being essential is highly dependent on the circumstances in which an organism lives. For instance, a gene required to digest starch is only essential if starch is the only source of energy. Recently, systematic attempts have been made to identify those genes that are absolutely required to maintain life, provided that all nutrients are available. Such experiments have led to the conclusion that the absolutely required number of genes for bacteria is on the order of about 250-300. These essential genes encode proteins to maintain a central metabolism, replicate DNA, translate genes into proteins, maintain a basic cellular structure, and mediate transport processes into and out of the cell. Most genes are not essential but convey selective advantages and increased fitness.