Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
... solenoid. The solenoid is cooled in liquid He jacketed with a liquid Nitrogen dewar such that a sufficiently low temperature can be achieved to allow the windings of the solenoid to exhibit superconductivity. This electromagnet is capable of producing very large magnetic fields, thereby increasing t ...
... solenoid. The solenoid is cooled in liquid He jacketed with a liquid Nitrogen dewar such that a sufficiently low temperature can be achieved to allow the windings of the solenoid to exhibit superconductivity. This electromagnet is capable of producing very large magnetic fields, thereby increasing t ...
Data and Computer Communications
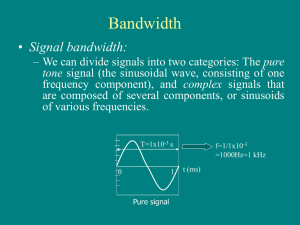
... then abruptly changes to another level periodic signal • signal pattern repeats over time aperiodic signal • pattern not repeated over time ...
... then abruptly changes to another level periodic signal • signal pattern repeats over time aperiodic signal • pattern not repeated over time ...
File - Mrmegaro.com
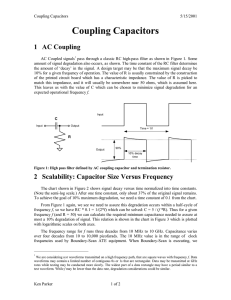
... Resistance (Re) - in electrical or electronic circuits, a characteristic of a material that opposes the flow of electrons. The higher the gauge of wire, the less cross sectional area contributing to DC series resistance (DCR). Roll-off (cut-off) - the attenuation that occurs at the lower or upper fr ...
... Resistance (Re) - in electrical or electronic circuits, a characteristic of a material that opposes the flow of electrons. The higher the gauge of wire, the less cross sectional area contributing to DC series resistance (DCR). Roll-off (cut-off) - the attenuation that occurs at the lower or upper fr ...
Electromagnetic Spectrum – Unit 1
... It means that it makes ions form by giving enough energy to electrons orbiting the atom to escape and leave a charged ion behind. When this happens in complex molecules like DNA it can cause the structure to change - change the coding of the DNA. No, they just increase the probability of it developi ...
... It means that it makes ions form by giving enough energy to electrons orbiting the atom to escape and leave a charged ion behind. When this happens in complex molecules like DNA it can cause the structure to change - change the coding of the DNA. No, they just increase the probability of it developi ...
CHEM 515 Spectroscopy Vibrational Spectroscopy I
... harmonic oscillator model with ωe = 2989 cm-1. ...
... harmonic oscillator model with ωe = 2989 cm-1. ...
MONOLITHIC PHASE LOCKED LOOPS (PLL IC 565)
... output voltage in order to stabilize the VCO frequency. ...
... output voltage in order to stabilize the VCO frequency. ...
Lab 1: AMPLITUDE MODULATION
... Generate an AM signal using the speech signal available from the Trunks Panel as your message. Observe the time domain waveform. The frequency spectrum will extend for about 3 kHz either side of the carrier. Since this is a stochastic (random) signal, the spectrum analyser may not give you much resp ...
... Generate an AM signal using the speech signal available from the Trunks Panel as your message. Observe the time domain waveform. The frequency spectrum will extend for about 3 kHz either side of the carrier. Since this is a stochastic (random) signal, the spectrum analyser may not give you much resp ...
MS Word - Sonoma State University
... Problem 3 White Filtered Noise (30 points) Noise is a random signal (also random noise power) without information content. In other words, it is unwanted, but nature provides noise power for free in electronic circuits. A “white noise model” is useful in analyzing the effect of noise on communicatio ...
... Problem 3 White Filtered Noise (30 points) Noise is a random signal (also random noise power) without information content. In other words, it is unwanted, but nature provides noise power for free in electronic circuits. A “white noise model” is useful in analyzing the effect of noise on communicatio ...
Teaming an AWG with a Digitizer for a Stimulus
... an amplifier or filter. The test requires a signal source with a bandwidth greater than that of the device under test. Furthermore, the source needs to deliver a constant output level over the entire testing bandwidth. A swept sinewave or impulse function waveforms offer broad band output with flat ...
... an amplifier or filter. The test requires a signal source with a bandwidth greater than that of the device under test. Furthermore, the source needs to deliver a constant output level over the entire testing bandwidth. A swept sinewave or impulse function waveforms offer broad band output with flat ...
EENG 3810 Chapter 4 - UNT College of Engineering
... Dynamic Range • Dynamic Range – Difference in dB between the minimum input level and the level that will over drive the receiver (produce distortion). – Input power range that the receiver is useful. – 100 dB is about the highest posible. ...
... Dynamic Range • Dynamic Range – Difference in dB between the minimum input level and the level that will over drive the receiver (produce distortion). – Input power range that the receiver is useful. – 100 dB is about the highest posible. ...
Spectrum analyzer

A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that a spectrum analyzer measures is electrical, however, spectral compositions of other signals, such as acoustic pressure waves and optical light waves, can be considered through the use of an appropriate transducer. Optical spectrum analyzers also exist, which use direct optical techniques such as a monochromator to make measurements.By analyzing the spectra of electrical signals, dominant frequency, power, distortion, harmonics, bandwidth, and other spectral components of a signal can be observed that are not easily detectable in time domain waveforms. These parameters are useful in the characterization of electronic devices, such as wireless transmitters.The display of a spectrum analyzer has frequency on the horizontal axis and the amplitude displayed on the vertical axis. To the casual observer, a spectrum analyzer looks like an oscilloscope and, in fact, some lab instruments can function either as an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer.