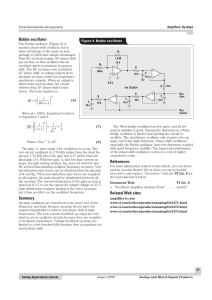
Band-pass filter
... Resonance:In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate with larger amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as systems ...
... Resonance:In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate with larger amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as systems ...
Practical Sample and Hold Circuit
... Sampling Rate To accurately reproduce the analog input data with samples the sampling rate, fs, must be twice as high as the highest frequency expected in the input signal. This is known as the Nyquist criterion. fs(min) = 2fh Where ...
... Sampling Rate To accurately reproduce the analog input data with samples the sampling rate, fs, must be twice as high as the highest frequency expected in the input signal. This is known as the Nyquist criterion. fs(min) = 2fh Where ...
Unusual Frequency Dividers
... Here is a simple trick for dividing a frequency well above the toggle frequency of a particular logic family. The clock inputs of a logic family respond to frequencies well above the frequency that the devices can successfully divide. The output becomes a chaotic jumble of unpredictable sub-harmonic ...
... Here is a simple trick for dividing a frequency well above the toggle frequency of a particular logic family. The clock inputs of a logic family respond to frequencies well above the frequency that the devices can successfully divide. The output becomes a chaotic jumble of unpredictable sub-harmonic ...
Spectral Induced Polarisation (SIP)
... the charge to build up (or dissipate) varies not only with the chargeability of the ground, but also with the frequency of the applied current. In IP and SIP surveying, non-polarisable electrodes are used (electrodes that do not retain any charge) so that all the signal observed comes from the groun ...
... the charge to build up (or dissipate) varies not only with the chargeability of the ground, but also with the frequency of the applied current. In IP and SIP surveying, non-polarisable electrodes are used (electrodes that do not retain any charge) so that all the signal observed comes from the groun ...
Lecture Notes - Bandpass Circuits File
... e(t) is called the Phase Error. The Phase Error voltage characteristics is SINUSOIDAL. A PLL can track the incoming frequency only over a finite range Lock/hold-in range The frequency range over which the input will cause the loop to lock pull-in/capture range Eeng 360 22 ...
... e(t) is called the Phase Error. The Phase Error voltage characteristics is SINUSOIDAL. A PLL can track the incoming frequency only over a finite range Lock/hold-in range The frequency range over which the input will cause the loop to lock pull-in/capture range Eeng 360 22 ...
Digital Metronome
... The output of the variable astable is also take to a series of counters and logic gates which divide the frequency of the output of the oscillator by 60 which gives an output of the same frequency in beats per minute as the frequency of the variable astable in Hertz (pulses per second). This means ...
... The output of the variable astable is also take to a series of counters and logic gates which divide the frequency of the output of the oscillator by 60 which gives an output of the same frequency in beats per minute as the frequency of the variable astable in Hertz (pulses per second). This means ...
Ch.14
... • They are very important circuits in that many technological advances would not have been possible without the development of filters. ...
... • They are very important circuits in that many technological advances would not have been possible without the development of filters. ...
The Microwave SDR project
... The input signal is amplified by two cascaded low-noise MMICs, type SPF-5043. The signal is then filtered with a 3-pole helical bandpass filter which covers the whole band 2300-2450MHz, part number TTW3839B-2375M. The signal is then fed to a Linear Technology LT5575 which is a highperformance I/Q do ...
... The input signal is amplified by two cascaded low-noise MMICs, type SPF-5043. The signal is then filtered with a 3-pole helical bandpass filter which covers the whole band 2300-2450MHz, part number TTW3839B-2375M. The signal is then fed to a Linear Technology LT5575 which is a highperformance I/Q do ...
Spectrum analyzer

A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure the power of the spectrum of known and unknown signals. The input signal that a spectrum analyzer measures is electrical, however, spectral compositions of other signals, such as acoustic pressure waves and optical light waves, can be considered through the use of an appropriate transducer. Optical spectrum analyzers also exist, which use direct optical techniques such as a monochromator to make measurements.By analyzing the spectra of electrical signals, dominant frequency, power, distortion, harmonics, bandwidth, and other spectral components of a signal can be observed that are not easily detectable in time domain waveforms. These parameters are useful in the characterization of electronic devices, such as wireless transmitters.The display of a spectrum analyzer has frequency on the horizontal axis and the amplitude displayed on the vertical axis. To the casual observer, a spectrum analyzer looks like an oscilloscope and, in fact, some lab instruments can function either as an oscilloscope or a spectrum analyzer.