Histology of Nervous Tissue
... • c. Multipolar neurons possess a single axon and more than one dendrite. • These neurons are the most common type of neuron in vertebrates. • d. Pseudounipolar neurons possess a single process that extends • from the cell body and subsequently branches into an axon and dendrite. • They are present ...
... • c. Multipolar neurons possess a single axon and more than one dendrite. • These neurons are the most common type of neuron in vertebrates. • d. Pseudounipolar neurons possess a single process that extends • from the cell body and subsequently branches into an axon and dendrite. • They are present ...
THERE IS A COMPUTER-LIKE SYSTEM IN OUR BODY
... over the body, about 100 millivolts in strength and lasting just 1 millisecond! These impulses “jump” from 1 neuron to another at the synapse. When the electrical impulse arrives at the synapse, it triggers the release of chemicals ...
... over the body, about 100 millivolts in strength and lasting just 1 millisecond! These impulses “jump” from 1 neuron to another at the synapse. When the electrical impulse arrives at the synapse, it triggers the release of chemicals ...
The Nervous System
... respect to the inside due to unequal concentrations of positive and negative ions on either side of the membrane. Action potential – a change in polarization and a return to the resting state This forms a nerve impulse that moves down an axon. ...
... respect to the inside due to unequal concentrations of positive and negative ions on either side of the membrane. Action potential – a change in polarization and a return to the resting state This forms a nerve impulse that moves down an axon. ...
Chapter 8 Nervous System
... 4. Homeostasis-Depends on the ability of the NS to detect, interpret, and respond to change in internal and external conditions. In response, the NS can stimulate or inhibit the activities of other systems to maintain homeostasis. ...
... 4. Homeostasis-Depends on the ability of the NS to detect, interpret, and respond to change in internal and external conditions. In response, the NS can stimulate or inhibit the activities of other systems to maintain homeostasis. ...
CNS Cellular Components - Johns Hopkins Medicine
... glia that line the ventricles. They form a continuous layer of single cuboidal or columnar cells with cilia and microvilli at their apical, ventricular surfaces. In addition to providing a barrier between the brain the CSF, ependymal cells are thought to function in secretion, absorption and transpo ...
... glia that line the ventricles. They form a continuous layer of single cuboidal or columnar cells with cilia and microvilli at their apical, ventricular surfaces. In addition to providing a barrier between the brain the CSF, ependymal cells are thought to function in secretion, absorption and transpo ...
The Nervous System
... normally occupied by the neurotransmitter can initiate a cellular response similar or identical to that produced by the neurotransmitter itself. Called a direct binding agonist ...
... normally occupied by the neurotransmitter can initiate a cellular response similar or identical to that produced by the neurotransmitter itself. Called a direct binding agonist ...
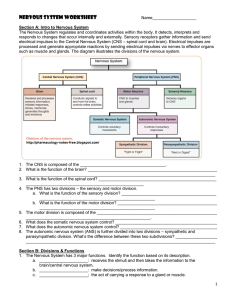
Nervous System Worksheet - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... 6. What does the somatic nervous system control? ____________________________________________ 7. What does the autonomic nervous system control? __________________________________________ 8. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is further divided into two divisions – sympathetic and parasympathetic di ...
... 6. What does the somatic nervous system control? ____________________________________________ 7. What does the autonomic nervous system control? __________________________________________ 8. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is further divided into two divisions – sympathetic and parasympathetic di ...
Chapter 12 - Marion ISD
... Sympathetic - (fight or flight) Parasympathetic-normal resting activities (rest/repair) ...
... Sympathetic - (fight or flight) Parasympathetic-normal resting activities (rest/repair) ...
neurohistology
... Many peripheral nerves are myelinatedresemble a string of sausages Each link of sausage corresponds to a length of axon wrapped in myelin with adjacent links separated by a gap in myelin ...
... Many peripheral nerves are myelinatedresemble a string of sausages Each link of sausage corresponds to a length of axon wrapped in myelin with adjacent links separated by a gap in myelin ...
A1990DM11000002
... ples that was emerging in integrative neurobiology The criteria we proposed (necessity and suffiwas that complex information may be encoded at ciency) had been long used in other contexts, but the level of individual neurons. On the sensory side, they provided a relatively clear methodology for rene ...
... ples that was emerging in integrative neurobiology The criteria we proposed (necessity and suffiwas that complex information may be encoded at ciency) had been long used in other contexts, but the level of individual neurons. On the sensory side, they provided a relatively clear methodology for rene ...
BOX 31.2 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE VESTIBULAR AND
... flocculonodular lobe. These excitatory neurons receive mossy fiber input, like granule cells, but synapse locally onto granule cells. Golgi cells feed back to unipolar brush cells with mixed glycinergic and GABAergic synapses, in contrast to the purely GABAergic feedback to granule cells (Dugue, Dum ...
... flocculonodular lobe. These excitatory neurons receive mossy fiber input, like granule cells, but synapse locally onto granule cells. Golgi cells feed back to unipolar brush cells with mixed glycinergic and GABAergic synapses, in contrast to the purely GABAergic feedback to granule cells (Dugue, Dum ...
Ascending Projections
... Modality-specific nociception: mechanical, thermal, itch Cutaneous input at neuroimmune interface: monitoring immune ...
... Modality-specific nociception: mechanical, thermal, itch Cutaneous input at neuroimmune interface: monitoring immune ...
nervous system jeopardy
... What is the tube-like structure that carries sound waves from the external ear to the ear drum? ...
... What is the tube-like structure that carries sound waves from the external ear to the ear drum? ...
The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 2003 • 23(11):4657– 4666
... antisera and distinct fluorophores identified neurons infected with one or both of the recombinants. Brainstem neurons coinfected with both PRV recombinants, which presumably had collateralized projections to both adrenal sympathetic preganglionic neurons and gastrocnemius motoneurons, were observed ...
... antisera and distinct fluorophores identified neurons infected with one or both of the recombinants. Brainstem neurons coinfected with both PRV recombinants, which presumably had collateralized projections to both adrenal sympathetic preganglionic neurons and gastrocnemius motoneurons, were observed ...
Introduction to Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (and what it`s for).
... A somatic reflex arc in which the final element in the chain is skeletal muscle. 1 Is some sensory transducer in the periphery, for example, a Golgi tendon organ, a Pacinian corpuscle or other tactile sensor in the skin. 2 The pseudounipolar sensory neuron in the circuit. Its soma is physically loca ...
... A somatic reflex arc in which the final element in the chain is skeletal muscle. 1 Is some sensory transducer in the periphery, for example, a Golgi tendon organ, a Pacinian corpuscle or other tactile sensor in the skin. 2 The pseudounipolar sensory neuron in the circuit. Its soma is physically loca ...
Shape of Thought
... th.e brain gets really good at it. One can master unfortunate skills that are hard to forget. Great for knowing how to protect oneself, balance a bike, or drive a car. Not great when it comes to deferise mechanisms still in use long after the threat that created them has vanished. The reason psychot ...
... th.e brain gets really good at it. One can master unfortunate skills that are hard to forget. Great for knowing how to protect oneself, balance a bike, or drive a car. Not great when it comes to deferise mechanisms still in use long after the threat that created them has vanished. The reason psychot ...
The Nervous System
... Some people have higher thresholds for pain, heat or other stimuli. This means they can tolerate a stronger stimulus before their nervous system reacts with an impulse. ...
... Some people have higher thresholds for pain, heat or other stimuli. This means they can tolerate a stronger stimulus before their nervous system reacts with an impulse. ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 8
... 3. Multipolar neurons: several dendrites and one axon, includes motor neurons; bipolar neurons: one dendrite and one axon, found in the eye and nose; unipolar neurons: a single process that functions as an axon and a dendrite, includes most sensory neurons. 4. Astrocytes: participate with the endoth ...
... 3. Multipolar neurons: several dendrites and one axon, includes motor neurons; bipolar neurons: one dendrite and one axon, found in the eye and nose; unipolar neurons: a single process that functions as an axon and a dendrite, includes most sensory neurons. 4. Astrocytes: participate with the endoth ...
The Nervous System
... Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". ...
... Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other "organelles". ...
neurons
... Structure of the Cortex Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of ...
... Structure of the Cortex Each brain hemisphere is divided into four lobes that are separated by prominent fissures. These lobes are the frontal lobe (forehead), parietal lobe (top to rear head), occipital lobe (back head) and temporal lobe (side of ...
Brain PowerPoint
... INTERIOR STRUCTURES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS Hippocampus: In temporal lobe, strongly involved in learning and memory formation ...
... INTERIOR STRUCTURES AND THEIR FUNCTIONS Hippocampus: In temporal lobe, strongly involved in learning and memory formation ...
PP text version
... Glia are the “glue” of the nervous system that support and surround neurons. Types: radial glia: tracks for neurons to travel along during development astrocytes: structural and metabolic support for neurons, communication between glia and neurons also likely. Astrocytes also aid in the genera ...
... Glia are the “glue” of the nervous system that support and surround neurons. Types: radial glia: tracks for neurons to travel along during development astrocytes: structural and metabolic support for neurons, communication between glia and neurons also likely. Astrocytes also aid in the genera ...
Everson Nervous system I. Functional/ Anatomical Divisions A
... d. Each contain a lateral ventricle (CSF) 2. Three main points about cerebral hemispheres: a. Each cerebral hemisphere receives sensory information from and sends motor information to the opposite side of the body b. The two hemispheres have different functions even though they appear identical c. A ...
... d. Each contain a lateral ventricle (CSF) 2. Three main points about cerebral hemispheres: a. Each cerebral hemisphere receives sensory information from and sends motor information to the opposite side of the body b. The two hemispheres have different functions even though they appear identical c. A ...
doc nervous system notes
... neurons; cling to neurons and neighboring capillaries to provide nutrients to neurons; help form the Blood-Brain Barrier by forming tight junctions between endothelial cells that lines the capillaries; provides proper environment for nerve impulse conduction (monitor calcium and potassium concentrat ...
... neurons; cling to neurons and neighboring capillaries to provide nutrients to neurons; help form the Blood-Brain Barrier by forming tight junctions between endothelial cells that lines the capillaries; provides proper environment for nerve impulse conduction (monitor calcium and potassium concentrat ...