Where does breathing start?
... The impulse to breathe, the inhale, is a reflex action that is generated in the lower brainstem. So one could say that the prime mover for breathing is the brain. But where does the stimulus for the reflex come from? It comes from the respiratory centres called medulla oblongata and the pons which a ...
... The impulse to breathe, the inhale, is a reflex action that is generated in the lower brainstem. So one could say that the prime mover for breathing is the brain. But where does the stimulus for the reflex come from? It comes from the respiratory centres called medulla oblongata and the pons which a ...
PDF - the Houpt Lab
... voluntary movement) or via smooth muscle and glands (autonomic nervous system). Neurons (nerve cells) Point to point communication across the body to coordinate responses Integrate electrical and chemical signals at dendrites & cell body; depending on inputs, neuron sends electrical and chemical sig ...
... voluntary movement) or via smooth muscle and glands (autonomic nervous system). Neurons (nerve cells) Point to point communication across the body to coordinate responses Integrate electrical and chemical signals at dendrites & cell body; depending on inputs, neuron sends electrical and chemical sig ...
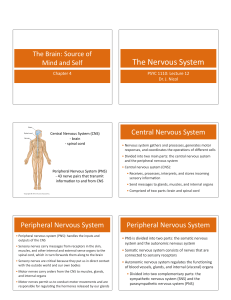
The Nervous System
... muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spinal cord, which in turn forwards them along to the brain • Sensory nerves are criJcal because they put us in direct contact with the ...
... muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spinal cord, which in turn forwards them along to the brain • Sensory nerves are criJcal because they put us in direct contact with the ...
Nervous System Notes
... – Pineal body: assists in biological clock (daily/seasonal/life cycles) by releasing melatonin – Choroid plexus: forms cerebrospinal fluid (there is also another one in the brainstem) ...
... – Pineal body: assists in biological clock (daily/seasonal/life cycles) by releasing melatonin – Choroid plexus: forms cerebrospinal fluid (there is also another one in the brainstem) ...
Spinal Cord
... Gray commissure connecting gray matter horns Posterior horns – interneurons Anterior horns – interneurons & somatic motor neurons Lateral horns – sympathetic nerve fibers ...
... Gray commissure connecting gray matter horns Posterior horns – interneurons Anterior horns – interneurons & somatic motor neurons Lateral horns – sympathetic nerve fibers ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... receptors for fine touch. These receptors are important in distinguishing the texture and shape of the stimulating agent. Tactile discs are associated with special tactile cells (Merkel cells), located in the stratum basale of the epidermis. ...
... receptors for fine touch. These receptors are important in distinguishing the texture and shape of the stimulating agent. Tactile discs are associated with special tactile cells (Merkel cells), located in the stratum basale of the epidermis. ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... receptors for fine touch. These receptors are important in distinguishing the texture and shape of the stimulating agent. Tactile discs are associated with special tactile cells (Merkel cells), located in the stratum basale of the epidermis. ...
... receptors for fine touch. These receptors are important in distinguishing the texture and shape of the stimulating agent. Tactile discs are associated with special tactile cells (Merkel cells), located in the stratum basale of the epidermis. ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience
... massive distention of the normal proximal colon develops secondarily. There is retention of fecal matter in the distended colon. The untreated disease has a mortality rate as high as 80%. Surgical removal of the aganglionic portion of the GI tract is an important part of the treatment regimen. ...
... massive distention of the normal proximal colon develops secondarily. There is retention of fecal matter in the distended colon. The untreated disease has a mortality rate as high as 80%. Surgical removal of the aganglionic portion of the GI tract is an important part of the treatment regimen. ...
Materialy/06/Lecture12- ICM Neuronal Nets 1
... = 40 – 100 mld. neurons, in artificial nets only tens till hundreds, it is enough for simulating of some functions ...
... = 40 – 100 mld. neurons, in artificial nets only tens till hundreds, it is enough for simulating of some functions ...
neural control of respiration
... Skeletal muscles provide the motive force for respiration. Unlike cardiac or smooth muscle, they have no rhythmic "beat" of their own; they depend entirely on the nervous system for a stimulus to contract. Two separate neural systems control respiration: (1) Voluntary control originates in cerebral ...
... Skeletal muscles provide the motive force for respiration. Unlike cardiac or smooth muscle, they have no rhythmic "beat" of their own; they depend entirely on the nervous system for a stimulus to contract. Two separate neural systems control respiration: (1) Voluntary control originates in cerebral ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... – Changes the probability of the postsynaptic neuron firing • Positive voltage shift – excitatory PSP • Negative voltage shift – inhibitory PSP ...
... – Changes the probability of the postsynaptic neuron firing • Positive voltage shift – excitatory PSP • Negative voltage shift – inhibitory PSP ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
... The spinal cord and the brain make up the central nervous system (CNS). The Spinal Cord The spinal cord extends from the base of the brain through a large opening in the skull and into the vertebral canal. Structure of the Spinal Cord The spinal nerves project from the cord between the vertebrae. Fl ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... neuron within the same ganglion 2. Ascends or descends the sympathetic chain to synapse in another chain ganglion 3. Passes through the chain ganglion and emerges without ...
... neuron within the same ganglion 2. Ascends or descends the sympathetic chain to synapse in another chain ganglion 3. Passes through the chain ganglion and emerges without ...
Notes - The Nervous System
... 4. The interneurons interpret the nerve impulses and decide on a response, you should answer the phone. 5. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the ...
... 4. The interneurons interpret the nerve impulses and decide on a response, you should answer the phone. 5. Impulses travel along motor neurons to the ...
File
... include the brain and spinal cord. 6. The peripheral nervous system uses specialized structures called _______________________________ to carry information. ...
... include the brain and spinal cord. 6. The peripheral nervous system uses specialized structures called _______________________________ to carry information. ...
1 - Kvalley Computers and Internet
... List the three different major types of neurons. What does each do? ...
... List the three different major types of neurons. What does each do? ...
The Mirror Mechanism: A Mechanism for Understanding Others
... the mirror mechanism in social cognition. I will discuss this issue and will show that, although there are several mechanisms through which one can understand the behaviour of others, the parieto-frontal mechanism is the only one that allows understanding others’ actions from the inside giving the o ...
... the mirror mechanism in social cognition. I will discuss this issue and will show that, although there are several mechanisms through which one can understand the behaviour of others, the parieto-frontal mechanism is the only one that allows understanding others’ actions from the inside giving the o ...
nervous_system_-_cns_and_pns_part_2_-_2015
... The Hypothalamus • Hypothalamus –Influence on the pituitary gland ...
... The Hypothalamus • Hypothalamus –Influence on the pituitary gland ...
Neurophysiology
... • Firing rate increases in single neurons • Spread of activation to a wider range of neurons-- “Density of Discharges” • Latency of Firing (shorter delay at higher ...
... • Firing rate increases in single neurons • Spread of activation to a wider range of neurons-- “Density of Discharges” • Latency of Firing (shorter delay at higher ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... receptors in peripheral body parts into the brain or spinal cord Interneuron-Transmits nerve impulses between neurons within the brain and spinal cord Motor Neurons- conduct nerve impulses from the brain or spinal cord out to effectors- muscle or glands. ...
... receptors in peripheral body parts into the brain or spinal cord Interneuron-Transmits nerve impulses between neurons within the brain and spinal cord Motor Neurons- conduct nerve impulses from the brain or spinal cord out to effectors- muscle or glands. ...
Nervous System I - Laurel County Schools
... receptors in peripheral body parts into the brain or spinal cord Interneuron-Transmits nerve impulses between neurons within the brain and spinal cord Motor Neurons- conduct nerve impulses from the brain or spinal cord out to effectors- muscle or glands. ...
... receptors in peripheral body parts into the brain or spinal cord Interneuron-Transmits nerve impulses between neurons within the brain and spinal cord Motor Neurons- conduct nerve impulses from the brain or spinal cord out to effectors- muscle or glands. ...
Congenital Malformation & Hydrocephalus
... Prenatal or perinatal insults may either cause: ◦ failure of normal CNS development ◦ tissue destruction ...
... Prenatal or perinatal insults may either cause: ◦ failure of normal CNS development ◦ tissue destruction ...
Malleable vs. Fixed Intelligence
... Neurons have three main parts: 1. The soma (a.k.a cell body) 2. The axon 3. The dendrites ...
... Neurons have three main parts: 1. The soma (a.k.a cell body) 2. The axon 3. The dendrites ...