Transmission at the Synapse and the
... o There are 3 mechanisms of presynaptic inhibition: Activation of chloride channels in the PRE-synaptic neuron – that hyperpolarizes the excitatory nerve ending and thus reduced the magnitude of excitatory action potential; and that in turn reduces the amount of calcium that enters the excitatory ...
... o There are 3 mechanisms of presynaptic inhibition: Activation of chloride channels in the PRE-synaptic neuron – that hyperpolarizes the excitatory nerve ending and thus reduced the magnitude of excitatory action potential; and that in turn reduces the amount of calcium that enters the excitatory ...
The Nervous System
... Neurotransmitters diffuse from the end of one neuron to receptors on the next neuron. When they land on the specific receptor they allow gates to open that allow sodium to enter - this ignites the electro-chemical impulse to begin in the the next neuron. ...
... Neurotransmitters diffuse from the end of one neuron to receptors on the next neuron. When they land on the specific receptor they allow gates to open that allow sodium to enter - this ignites the electro-chemical impulse to begin in the the next neuron. ...
Part 1 (nerve impulses, ppt file)
... move across muscle cells, and does in the heart. You can detect the changes in potential caused by this depolarization wave by ...
... move across muscle cells, and does in the heart. You can detect the changes in potential caused by this depolarization wave by ...
Neurotransmitters
... other neurons. The greater the surface area, the greater the amount of information. Some ...
... other neurons. The greater the surface area, the greater the amount of information. Some ...
Neurons - Seung Lab
... Neurons have a resting potential. • Most of the time, the voltage of the inside of a neuron is negative relative to the outside. • A typical value for this “resting potential” is –70 mV. ...
... Neurons have a resting potential. • Most of the time, the voltage of the inside of a neuron is negative relative to the outside. • A typical value for this “resting potential” is –70 mV. ...
Ch 49 Pract Test Nervous System
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
... Which statement about the resting potential of a neuron is true? a. Sodium ions are in balance inside and outside the neuron’s membrane. b. There are many times more sodium ions outside the neuron’s membrane than inside. c. There are fewer potassium ions inside the neuron’s membrane than outside. d ...
We have seen how the Nervous System plays an important role in
... This needs A LOT of help. Good diagrams are a must for this topic!!! I’m not sure if this is too specific and needs to be more general, or if it is too general and needs to be more specific???????? We have seen how the nervous system plays an important role in reaction time, stability and balance, h ...
... This needs A LOT of help. Good diagrams are a must for this topic!!! I’m not sure if this is too specific and needs to be more general, or if it is too general and needs to be more specific???????? We have seen how the nervous system plays an important role in reaction time, stability and balance, h ...
Dynamic Equilibrium Review 1. Describe the structure and function
... How does this important to a neuron? The outside of the cell is more positive, relative to the inside. This assists in ion exchange (Na+ in, K+ out) that is the process of neuron firing. 3. How is both passive and active transport part of the function of a neuron? Sodium will rush in once the ion ch ...
... How does this important to a neuron? The outside of the cell is more positive, relative to the inside. This assists in ion exchange (Na+ in, K+ out) that is the process of neuron firing. 3. How is both passive and active transport part of the function of a neuron? Sodium will rush in once the ion ch ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... Synapses are junctions where signals are transmitted between Two neurons or between neurons and effector cells Electrical synapses ...
... Synapses are junctions where signals are transmitted between Two neurons or between neurons and effector cells Electrical synapses ...
Types of neurons
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
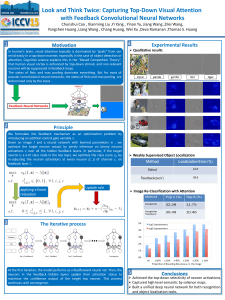
feedback-poster
... attention. Cognitive science explains this in the “Biased Competition Theory”, that human visual cortex is enhanced by top-down stimuli, and non-relevant neurons will be suppressed in feedback loops. The states of Relu and max pooling dominate everything. But for most of popular convolutional neural ...
... attention. Cognitive science explains this in the “Biased Competition Theory”, that human visual cortex is enhanced by top-down stimuli, and non-relevant neurons will be suppressed in feedback loops. The states of Relu and max pooling dominate everything. But for most of popular convolutional neural ...
Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
... preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not converge on single dendrites • Neurons with a highly tuned output signal receive input signals that are heterogeneous The results support a neuronal integration model involving summation of distributed inputs, rather than models that ...
... preference are widely dispersed over thedendritic tree and do not converge on single dendrites • Neurons with a highly tuned output signal receive input signals that are heterogeneous The results support a neuronal integration model involving summation of distributed inputs, rather than models that ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
... effectors (muscles or glands). The goal is usually to maintain stable conditions (especially internal) – Homeostasis. Motor neurons. - Somatic Nervous System (skeletal muscles) - Autonomic Nervous System (smooth muscles, glands) C. Neurons: Nerve cells. Unique structure – cell body with many extensi ...
Worksheet for Nervous Systems
... 32. In a neuron, an action potential can only be generated in the 33. The action potential is a non-graded, all or non event; meaning ___ 34. The action potential arises because the plasma membrane has ___ ____ ion channels. 35. Which two types of voltage-gated ion channels contribute to the action ...
... 32. In a neuron, an action potential can only be generated in the 33. The action potential is a non-graded, all or non event; meaning ___ 34. The action potential arises because the plasma membrane has ___ ____ ion channels. 35. Which two types of voltage-gated ion channels contribute to the action ...
The nervous system - Sonoma Valley High School
... by another neuron or the environment Action potential - When an impulse is sent the charge reverses inside the cell – it becomes positive Threshold – the amount of stimulus required to activate the neuron ...
... by another neuron or the environment Action potential - When an impulse is sent the charge reverses inside the cell – it becomes positive Threshold – the amount of stimulus required to activate the neuron ...
Neuron Function notes
... Nuclei = clusters of cell bodies INSIDE CNS Plexus = a complex network of nerves Comprised of nerves that are combinations of sensory and motor nerves Because of multiple branching, damage to a single root or spinal cord section DOES NOT lead to complete motor or sensory loss in the body part that i ...
... Nuclei = clusters of cell bodies INSIDE CNS Plexus = a complex network of nerves Comprised of nerves that are combinations of sensory and motor nerves Because of multiple branching, damage to a single root or spinal cord section DOES NOT lead to complete motor or sensory loss in the body part that i ...
The Brain and the Neuron (1)
... firing of a nerve cell • Resting potential: electric potential when neuron not firing (-70 millivolts) • Depolarization: neuron reduces resting potential by becoming positively charged • Action Potential: neuron fires when it reaches +30-40 millivolts ...
... firing of a nerve cell • Resting potential: electric potential when neuron not firing (-70 millivolts) • Depolarization: neuron reduces resting potential by becoming positively charged • Action Potential: neuron fires when it reaches +30-40 millivolts ...
Lesson 4 Section 9.2 Electrochemical Impulse
... o ATP fuels this o The membrane is now repolarized, or back to normal ...
... o ATP fuels this o The membrane is now repolarized, or back to normal ...
Threshold Stimulus
... potential • Blocks _______ channels • Sodium cannot flow into the cell, so threshold is not achieved ...
... potential • Blocks _______ channels • Sodium cannot flow into the cell, so threshold is not achieved ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... Similar in spirit to Fourier decomposition. Bumps = radial basis ...
... Similar in spirit to Fourier decomposition. Bumps = radial basis ...
Neurons - Holterman
... 4. The sodium-potassium pump pushes 3 Na and 2 K against their concentration gradients using 1 ATP. It restores and maintains the resting potential by pushing more Na out of neuron and pushing more K into neuron. (But overall, it pushes more positive charges out of the cell than it brings in.) 5. T ...
... 4. The sodium-potassium pump pushes 3 Na and 2 K against their concentration gradients using 1 ATP. It restores and maintains the resting potential by pushing more Na out of neuron and pushing more K into neuron. (But overall, it pushes more positive charges out of the cell than it brings in.) 5. T ...