ppt
... a. When there is no ion flow across the membrane b. When the concentration gradient and electrical gradient are counterbalanced for a single ion c. When the concentration of all ions are equal on both sides When the concentration gradient for an ion is known, the equilibrium potentials can be cal ...
... a. When there is no ion flow across the membrane b. When the concentration gradient and electrical gradient are counterbalanced for a single ion c. When the concentration of all ions are equal on both sides When the concentration gradient for an ion is known, the equilibrium potentials can be cal ...
Neurophysiology Worksheet
... arrives at a presynaptic cell, it allows for extra cellular calcium ions to enter. This triggers the release of a neurotransmitters held within the presynaptic cell. These neurotransmitters enter the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the post synaptic cell. These post synaptic cell receptors a ...
... arrives at a presynaptic cell, it allows for extra cellular calcium ions to enter. This triggers the release of a neurotransmitters held within the presynaptic cell. These neurotransmitters enter the synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on the post synaptic cell. These post synaptic cell receptors a ...
Neurobiology of Consciousness Homework 1 Problem 1 Consider a
... Problem 1 Consider a motor neuron that receives excitatory input from afferent fibers of sensory neuron and inhibitory input coming from the motor cortex. Describe the electrical phenomena one can record from the cell body of the motor neuron. Discuss the role of motor neuron as an integrator of aff ...
... Problem 1 Consider a motor neuron that receives excitatory input from afferent fibers of sensory neuron and inhibitory input coming from the motor cortex. Describe the electrical phenomena one can record from the cell body of the motor neuron. Discuss the role of motor neuron as an integrator of aff ...
Nervous System - APBio
... Production of Action Potential • 1. Resting potential: Na+ gates closed, some K+ gates open (move out) and Na-K pump active • 2. stimulus Na+ channels open, causing depolarization • 3. When threshold is met, membrane is in rising phase • 4. The Na+ channels close and K+ channels open- falling phas ...
... Production of Action Potential • 1. Resting potential: Na+ gates closed, some K+ gates open (move out) and Na-K pump active • 2. stimulus Na+ channels open, causing depolarization • 3. When threshold is met, membrane is in rising phase • 4. The Na+ channels close and K+ channels open- falling phas ...
1. Cell body
... 1. A stimulus in the environment triggers a neuron 2. Dendrites receive the signal which then travels down to the axon of the first neuron. 3. When the signal reaches the end of the axon (axon terminal) , the axon releases chemicals called ...
... 1. A stimulus in the environment triggers a neuron 2. Dendrites receive the signal which then travels down to the axon of the first neuron. 3. When the signal reaches the end of the axon (axon terminal) , the axon releases chemicals called ...
Lecture 16
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
... Leaky integrate and fire neurons Encode each individual spike Time is represented exactly Each spike has an associated time The timing of recent incoming spikes determines whether a neuron will fire • Computationally expensive • Can we do almost as well without encoding every single spike? ...
Slide ()
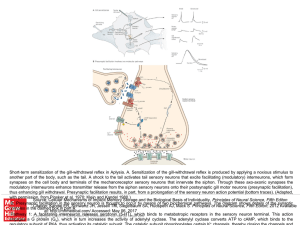
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - Coast Colleges Home Page
... Types of Conduction Continuous - Typical of Unmyelinated Neurons (Slower) - Steps as Previously Described (“transmission along a neuron”) Saltatory - Occurs along Myelinated Neurons - No Current where Myelin occurs - Action Potential Leaps from Node of Ranvier to Node - Faster! ...
... Types of Conduction Continuous - Typical of Unmyelinated Neurons (Slower) - Steps as Previously Described (“transmission along a neuron”) Saltatory - Occurs along Myelinated Neurons - No Current where Myelin occurs - Action Potential Leaps from Node of Ranvier to Node - Faster! ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Types of Conduction Continuous - Typical of Unmyelinated Neurons (Slower) - Steps as Previously Described (“transmission along a neuron”) Saltatory - Occurs along Myelinated Neurons - No Current where Myelin occurs - Action Potential Leaps from Node of Ranvier to Node - Faster! ...
... Types of Conduction Continuous - Typical of Unmyelinated Neurons (Slower) - Steps as Previously Described (“transmission along a neuron”) Saltatory - Occurs along Myelinated Neurons - No Current where Myelin occurs - Action Potential Leaps from Node of Ranvier to Node - Faster! ...
THE NEURON (Slides 4 to 14) • Based on the PowerPoint attached
... The firing is caused by an influx of sodium. It takes a few milliseconds to ‘fire’ sending an electrical impulse to the synapse, the threshold of excitation must be exceeded for the neuron to fire. The connections of the neurons to other neurons determine whether the neuron is likely to fire or not ...
... The firing is caused by an influx of sodium. It takes a few milliseconds to ‘fire’ sending an electrical impulse to the synapse, the threshold of excitation must be exceeded for the neuron to fire. The connections of the neurons to other neurons determine whether the neuron is likely to fire or not ...
Health - Nervous System Review
... 2. Sends messages from your brain and spinal cord to muscle cells 4. Eyes, ears, tongue, nose, and skin are examples of ___ organs. 5. Part of the brain that controls actions of muscles and maintains balance 6. Gap between two neurons 7. Nervous system that consists of a network of nerves branching ...
... 2. Sends messages from your brain and spinal cord to muscle cells 4. Eyes, ears, tongue, nose, and skin are examples of ___ organs. 5. Part of the brain that controls actions of muscles and maintains balance 6. Gap between two neurons 7. Nervous system that consists of a network of nerves branching ...
The Nervous System
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
neuron and nervous system
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
Document
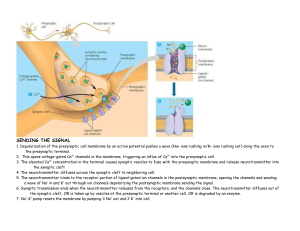
... a wave of Na+ in and K+ out through ion channels depolarizing the postsynaptic membrane sending the signal. 6. Synaptic transmission ends when the neurotransmitter releases from the receptors, and the channels close. The neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft, OR is taken up by vesicles ...
... a wave of Na+ in and K+ out through ion channels depolarizing the postsynaptic membrane sending the signal. 6. Synaptic transmission ends when the neurotransmitter releases from the receptors, and the channels close. The neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft, OR is taken up by vesicles ...
Neurons
... • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axons (carries info AWAY from the cell body.) • Some neurons are several FEET long! • A ...
... • BOTH are composed of neurons, or nerve cells, that transmit messages to different parts of the body. • Neurons have three main parts: cell body (produces energy), dendrites (DELIVERS info to the cell body), and axons (carries info AWAY from the cell body.) • Some neurons are several FEET long! • A ...
LTP
... One major mechanism of how neurons encode information is through their firing rate (number of AP’s per second). – Example: orientation selectivity. Another major mechanism is synchronization (AP’s occurring together in time). – Example: perceptual grouping. Synchrony could affect other neurons (e.g. ...
... One major mechanism of how neurons encode information is through their firing rate (number of AP’s per second). – Example: orientation selectivity. Another major mechanism is synchronization (AP’s occurring together in time). – Example: perceptual grouping. Synchrony could affect other neurons (e.g. ...
“Electrical Properties of Neuron”
... potentials or spikes or nerve impulses These action potentials are generated by means of influx and out flux of ions through the ion channels embedded in membrane Suitable electrical probe (electrode) and measurement instrumentation (amplifier and read-out) can measure these tiny potentials on t ...
... potentials or spikes or nerve impulses These action potentials are generated by means of influx and out flux of ions through the ion channels embedded in membrane Suitable electrical probe (electrode) and measurement instrumentation (amplifier and read-out) can measure these tiny potentials on t ...
Neuron PowerPoint
... In Greek, dendrites mean branches, hence, they are like extensive tree branches. The more branches, the more information a neuron can receive. ...
... In Greek, dendrites mean branches, hence, they are like extensive tree branches. The more branches, the more information a neuron can receive. ...
cms/lib/NY01001456/Centricity/Domain/535/nervous system tea
... rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and oxygen intake from lungs increase to give one more energy for a response. Controlled by the sympathetic division. 39. What is Cerebral Palsy? Birth defect often due to a temporary lack of oxygen that causes brain damage and results in a poorly controll ...
... rate, blood pressure, blood glucose levels, and oxygen intake from lungs increase to give one more energy for a response. Controlled by the sympathetic division. 39. What is Cerebral Palsy? Birth defect often due to a temporary lack of oxygen that causes brain damage and results in a poorly controll ...