What is CDNF?
... • Conserved Dopamine Neurotrophic Factor • Growth factor known as a trophic factor • Stimulates the growth of neurons ...
... • Conserved Dopamine Neurotrophic Factor • Growth factor known as a trophic factor • Stimulates the growth of neurons ...
Chapter 31 The Nervous System
... myelin sheath: insulating membrane surrounding the axon in some neurons ...
... myelin sheath: insulating membrane surrounding the axon in some neurons ...
Motor Neuron
... – Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system – Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... – Found in neural pathways in the central nervous system – Connect sensory and motor neurons ...
UNIT II File
... Calibration: A test of a model with known input and output information that is used to adjust or estimate factors for which data are not available. Validation : Comparison of model results wit h numerical data independently derived from experiments or observations of the environment. ...
... Calibration: A test of a model with known input and output information that is used to adjust or estimate factors for which data are not available. Validation : Comparison of model results wit h numerical data independently derived from experiments or observations of the environment. ...
Back Propagation Weight Update Rule
... The algorithm should adjust the weights such that E2 is minimised. Back-propagation is such an algorithm that performs a gradient descent minimisation of E2. In order to minimise E2, its sensitivity to each of the weights must be calculated. In other words, we need to know what effect changing each ...
... The algorithm should adjust the weights such that E2 is minimised. Back-propagation is such an algorithm that performs a gradient descent minimisation of E2. In order to minimise E2, its sensitivity to each of the weights must be calculated. In other words, we need to know what effect changing each ...
Neuro Physiology 1
... Neurons have two characteristic structural and functional features: an excitable membrane, and synapses. Excitability means the ability of neurons to generate and propagate sterotypic electrical impulses (action potentials). This is a feature which is also shared with muscle and some endocrine cells ...
... Neurons have two characteristic structural and functional features: an excitable membrane, and synapses. Excitability means the ability of neurons to generate and propagate sterotypic electrical impulses (action potentials). This is a feature which is also shared with muscle and some endocrine cells ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... generating and propagating ACTION POTENTIALS (AP). Only cells with excitable membranes (like muscle cells and neurons) can generate APs. ...
... generating and propagating ACTION POTENTIALS (AP). Only cells with excitable membranes (like muscle cells and neurons) can generate APs. ...
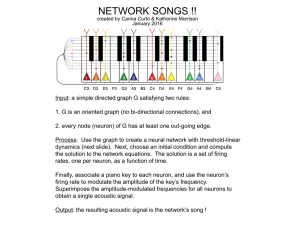
network songs - Personal.psu.edu
... the solution to the network equations. The solution is a set of firing rates, one per neuron, as a function of time. Finally, associate a piano key to each neuron, and use the neuron’s firing rate to modulate the amplitude of the key’s frequency. Superimpose the amplitude-modulated frequencies for a ...
... the solution to the network equations. The solution is a set of firing rates, one per neuron, as a function of time. Finally, associate a piano key to each neuron, and use the neuron’s firing rate to modulate the amplitude of the key’s frequency. Superimpose the amplitude-modulated frequencies for a ...
How Ca2+ triggers neurotransmitter release
... Molecular mechanisms of neurotransmitter release Thomas C. Südhof Thomas Südhof's research investigates how neurons in brain communicate with each other during synaptic transmission, which is the process that underlies all brain activity, from consciousness over memory to sensory perception and move ...
... Molecular mechanisms of neurotransmitter release Thomas C. Südhof Thomas Südhof's research investigates how neurons in brain communicate with each other during synaptic transmission, which is the process that underlies all brain activity, from consciousness over memory to sensory perception and move ...
Honors Thesis
... common” one is medication that addresses “the shortage of the brain chemical (neurotransmitter) dopamine” which is said to cause the symptoms of Parkinson’s." When medication does not work, brain surgery is an option. The safest, least harmful method of surgery is Deep Brain Stimulation, a.k.a. DBS. ...
... common” one is medication that addresses “the shortage of the brain chemical (neurotransmitter) dopamine” which is said to cause the symptoms of Parkinson’s." When medication does not work, brain surgery is an option. The safest, least harmful method of surgery is Deep Brain Stimulation, a.k.a. DBS. ...
AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... another kind of gated channel opens, this time allowing the K+ on the inside to rush out of the cell. The movement of K+ out of the cell causes repolarization by restoring the original membrane polarization (a condition where it is once again more negative inside the cell) Unlike the resting potenti ...
... another kind of gated channel opens, this time allowing the K+ on the inside to rush out of the cell. The movement of K+ out of the cell causes repolarization by restoring the original membrane polarization (a condition where it is once again more negative inside the cell) Unlike the resting potenti ...
Nerves Part 1 Powerpoint
... (CNS) • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
... (CNS) • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
Topic: Neurons Student learning outcome: Explain how neurons
... that the Hershey Kisses are neurotransmitters (perhaps acetylcholine, responsible for muscle movement). Begin by suggesting that you are the terminal branch of a nearby neuron and toss Hershey Kisses (neurotransmitters) in the direction of the dendrites and cell body (that is, into the synapse). The ...
... that the Hershey Kisses are neurotransmitters (perhaps acetylcholine, responsible for muscle movement). Begin by suggesting that you are the terminal branch of a nearby neuron and toss Hershey Kisses (neurotransmitters) in the direction of the dendrites and cell body (that is, into the synapse). The ...
the physiological approach
... Na+ channels inactivate (absolute refractory period) – completely unresponsive to a second stimulus Potassium flows out of the axon ...
... Na+ channels inactivate (absolute refractory period) – completely unresponsive to a second stimulus Potassium flows out of the axon ...
ANATOMICAL ORGANIZATION of the NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
... Branches off the cell body that carry information to the cell body. Usually several to many. Relatively short. Often branched. Have receptors for neurotransmitters. Conduct local potentials. ...
Chapter 17 Part A
... - sodium gates open (membrane suddenly permeable to Na+ ions) - charge inside changes to positive as Na+ ions flood interior - increases until rising voltage opposes inward flow of Na+ (peak of the graph) - repolarization from +40 mV to –65 mV - sodium gates close and potassium gates (in addition to ...
... - sodium gates open (membrane suddenly permeable to Na+ ions) - charge inside changes to positive as Na+ ions flood interior - increases until rising voltage opposes inward flow of Na+ (peak of the graph) - repolarization from +40 mV to –65 mV - sodium gates close and potassium gates (in addition to ...
N1 - Kůra mozku HE
... • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vasculature with variable amount of connec ...
... • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vasculature with variable amount of connec ...
11 - Karmayog .org
... This impulse is brought about by the movement of chemical ions either into or out of a neuron. - These ions have an electric charge this causes the flow of an electric current. - When it reaches a junction between two neurons (synapse). It causes the release of a neurotransmitters to stimulate the i ...
... This impulse is brought about by the movement of chemical ions either into or out of a neuron. - These ions have an electric charge this causes the flow of an electric current. - When it reaches a junction between two neurons (synapse). It causes the release of a neurotransmitters to stimulate the i ...
2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks
... sensory stimulus with a desired action is realized on a humonoid robot. The computational model of BTC circuit, incorporates two different levels of modeling: point neuorns and mass models. With the point neuron it is aimed to obtain a more realistic method to investigate the model in real time, whi ...
... sensory stimulus with a desired action is realized on a humonoid robot. The computational model of BTC circuit, incorporates two different levels of modeling: point neuorns and mass models. With the point neuron it is aimed to obtain a more realistic method to investigate the model in real time, whi ...
Lecture 7 Neurons
... – Allows for rapid movement of electrical impulses along axon – Nodes of Ranvier: gaps in myelin sheath where action potentials are transmitted – Multiple sclerosis is a breakdown of myelin sheath – Speed of neural impulse Ranges from 2 – 200+ mph ...
... – Allows for rapid movement of electrical impulses along axon – Nodes of Ranvier: gaps in myelin sheath where action potentials are transmitted – Multiple sclerosis is a breakdown of myelin sheath – Speed of neural impulse Ranges from 2 – 200+ mph ...
topic 6.5 Neurons
... – Allows for rapid movement of electrical impulses along axon – Nodes of Ranvier: gaps in myelin sheath where action potentials are transmitted – Multiple sclerosis is a breakdown of myelin sheath – Speed of neural impulse Ranges from 2 – 200+ mph ...
... – Allows for rapid movement of electrical impulses along axon – Nodes of Ranvier: gaps in myelin sheath where action potentials are transmitted – Multiple sclerosis is a breakdown of myelin sheath – Speed of neural impulse Ranges from 2 – 200+ mph ...