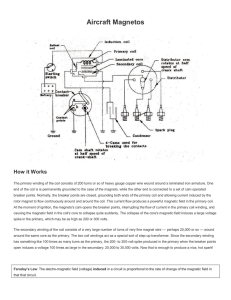
Earthquakes
... Secondary waves can’t be transmitted through liquid layers Primary waves are slowed and deflected by the outer core and speed up again when the reach the solid inner core ...
... Secondary waves can’t be transmitted through liquid layers Primary waves are slowed and deflected by the outer core and speed up again when the reach the solid inner core ...
Exam 1 - cloudfront.net
... (c) may be composed of either oceanic or continental lithosphere 30. The pulling forces that produce the most rapid plate velocities are concentrated at (a) ocean trenches (c) stable continental interiors ...
... (c) may be composed of either oceanic or continental lithosphere 30. The pulling forces that produce the most rapid plate velocities are concentrated at (a) ocean trenches (c) stable continental interiors ...
Solid E arth Sciences Section
... two of the greatest problems it faces are the forecast of large earthquakes and any accompanying tsunamis, and the development of disaster mitigation strategies to deal with them when they happen. A major task facing the discipline is to continue the cooperative research between seismologists and ge ...
... two of the greatest problems it faces are the forecast of large earthquakes and any accompanying tsunamis, and the development of disaster mitigation strategies to deal with them when they happen. A major task facing the discipline is to continue the cooperative research between seismologists and ge ...
Chapter 2
... – Rising hot rock in mantle melts to liquid magma – Buildup of magma causes overlying lithosphere to uplift and fracture; fractured lithosphere is then pulled outward and downward by gravity, aided by convection in mantle – Asthenosphere melts and rises to fill fractures, creating new oceanic lithos ...
... – Rising hot rock in mantle melts to liquid magma – Buildup of magma causes overlying lithosphere to uplift and fracture; fractured lithosphere is then pulled outward and downward by gravity, aided by convection in mantle – Asthenosphere melts and rises to fill fractures, creating new oceanic lithos ...
the electromagnetic environment of hospitals: how it is affected by
... Therefore, although the observed values were under 3 V/m in this measurement, because the distance between the measurement point and the nearest base station was 200 m, if the base station were nearer, the electric field intensity would be over the standard. The ASR antenna at Fukuoka International ...
... Therefore, although the observed values were under 3 V/m in this measurement, because the distance between the measurement point and the nearest base station was 200 m, if the base station were nearer, the electric field intensity would be over the standard. The ASR antenna at Fukuoka International ...
Electron Discovery (PowerPoint)
... charge-to-mass ratio of cathode rays by balancing an upward deflection from an electric field with a downward deflection from a magnetic (resulting in path b). Thomson argued that these “cathode rays” were tiny negatively charged particles and were constituents of atoms, not ions or atoms themselves ...
... charge-to-mass ratio of cathode rays by balancing an upward deflection from an electric field with a downward deflection from a magnetic (resulting in path b). Thomson argued that these “cathode rays” were tiny negatively charged particles and were constituents of atoms, not ions or atoms themselves ...
Lab 7: Electric Guitar and Faraday`s Law
... magnet), and determine the number of atoms affected by the outside magnetic field. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment that was induced on the string by the magnet. Did it reach saturation? What percentage of atoms are aligned? Do a quick calculation on how much industry is based o ...
... magnet), and determine the number of atoms affected by the outside magnetic field. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment that was induced on the string by the magnet. Did it reach saturation? What percentage of atoms are aligned? Do a quick calculation on how much industry is based o ...
Earthquakes
... • Tectonic plates move past each other causing stress-built up energy on a fault. Stress causes the rock to deform. – The amount of energy released depends on how much rock breaks and how far the blocks of rock move. ...
... • Tectonic plates move past each other causing stress-built up energy on a fault. Stress causes the rock to deform. – The amount of energy released depends on how much rock breaks and how far the blocks of rock move. ...
Lecture 18 - UConn Physics
... Example An instrument based on induced emf has been used to measure projectile speeds up to 6 km/s. A small magnet is imbedded in the projectile, as shown in Figure below. The projectile passes through two coils separated by a distance d. As the projectile passes through each coil a pulse of emf is ...
... Example An instrument based on induced emf has been used to measure projectile speeds up to 6 km/s. A small magnet is imbedded in the projectile, as shown in Figure below. The projectile passes through two coils separated by a distance d. As the projectile passes through each coil a pulse of emf is ...
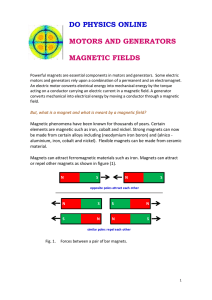
Electromagnetic Field Basics
... inductance, help stabilize power systems at these higher-frequency harmonics. The primary benefit here is lower inductance. Conceptually we can think of that resulting from the very wide surface area of the plane. This is a control for power system stability. Summary Changing electromagnetic fields ...
... inductance, help stabilize power systems at these higher-frequency harmonics. The primary benefit here is lower inductance. Conceptually we can think of that resulting from the very wide surface area of the plane. This is a control for power system stability. Summary Changing electromagnetic fields ...
Seismic Waves
... The P waves, also called primary or compressional waves are the fastest wave, traveling 5.5 km/second (3.3 miles/second or 12,000 miles/hour). They and are the first to arrive at a given location and can travel through solid and liquid layers of the earth. They alternately compresses and expands ma ...
... The P waves, also called primary or compressional waves are the fastest wave, traveling 5.5 km/second (3.3 miles/second or 12,000 miles/hour). They and are the first to arrive at a given location and can travel through solid and liquid layers of the earth. They alternately compresses and expands ma ...
PowerPoint
... reduction underground Larger caves induce smaller test mass perturbations The noise reduction is proportional to 1/r3 The longitudinal direction is more important =>elliptic cave ...
... reduction underground Larger caves induce smaller test mass perturbations The noise reduction is proportional to 1/r3 The longitudinal direction is more important =>elliptic cave ...
Convergent plate boundary - Department of Geology UPRM
... Effect of tectonics on rocks • Depends of physical conditions – Temperature & pressure – composition, time, fluids ...
... Effect of tectonics on rocks • Depends of physical conditions – Temperature & pressure – composition, time, fluids ...
Magnetotellurics

Magnetotellurics (MT) is an electromagnetic geophysical method for inferring the earth's subsurface electrical conductivity from measurements of natural geomagnetic and geoelectric field variation at the Earth's surface. Investigation depth ranges from 300m below ground by recording higher frequencies down to 10,000m or deeper with long-period soundings. Developed in the USSR and France during the 1950s, MT is now an international academic discipline and is used in exploration surveys around the world. Commercial uses include hydrocarbon (oil and gas) exploration, geothermal exploration, mining exploration, as well as hydrocarbon and groundwater monitoring. Research applications include experimentation to further develop the MT technique, long-period deep crustal exploration, and earthquake precursor prediction research.