A Level Maths - Further Maths FP1
... Be able to add, subtract, multiply and divide complex numbers given in the form: x + yj where x and y are real. Know that a complex number is zero if and only if both the real and imaginary parts are zero. Know that the complex roots of real polynomial equations with real coefficients occur in conju ...
... Be able to add, subtract, multiply and divide complex numbers given in the form: x + yj where x and y are real. Know that a complex number is zero if and only if both the real and imaginary parts are zero. Know that the complex roots of real polynomial equations with real coefficients occur in conju ...
Finite Difference Method The finite difference method is a means of
... in the above equation is the Fourier cell constant and must be smaller than 0.25 for the equation to remain stable. You must check your finite-element model for accuracy by comparing it to an analytical solution or reducing the time step and seeing that the result does not change. ...
... in the above equation is the Fourier cell constant and must be smaller than 0.25 for the equation to remain stable. You must check your finite-element model for accuracy by comparing it to an analytical solution or reducing the time step and seeing that the result does not change. ...
Factorization of C-finite Sequences - Institute for Algebra
... algebraic number α, specified by its minimal polynomial r, can we write α = βγ where β, γ are some other algebraic numbers with respective minimal polynomials p and q. Trivial decompositions are easy to find: For each r we obviously have r = r ⊗ (x − 1). Moreover, for every nonzero φ we have (x−φ)⊗( ...
... algebraic number α, specified by its minimal polynomial r, can we write α = βγ where β, γ are some other algebraic numbers with respective minimal polynomials p and q. Trivial decompositions are easy to find: For each r we obviously have r = r ⊗ (x − 1). Moreover, for every nonzero φ we have (x−φ)⊗( ...
Solving for x
... • Inverse operations are the same as opposite operations. • Addition and subtraction are inverse operations. • Multiplication and division are inverse operations. ...
... • Inverse operations are the same as opposite operations. • Addition and subtraction are inverse operations. • Multiplication and division are inverse operations. ...
4.1 Day 2 Notes
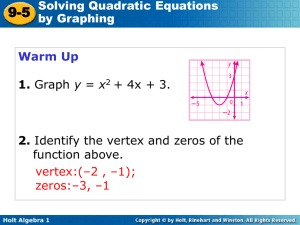
... Ex 6. Show that the height s above the ground of an object thrown upward from a point s0 feet above the ground with an initial velocity of v0 feet per second is given by the function s (t ) 16t 2 v0t s0 . (Recall, acceleration due to gravity is constant 32 ft/s 2 .) ...
... Ex 6. Show that the height s above the ground of an object thrown upward from a point s0 feet above the ground with an initial velocity of v0 feet per second is given by the function s (t ) 16t 2 v0t s0 . (Recall, acceleration due to gravity is constant 32 ft/s 2 .) ...
Review-Problems-for-Final-Exam-2
... 53. Completely factor the polynomial 54. Completely factor the polynomial ...
... 53. Completely factor the polynomial 54. Completely factor the polynomial ...