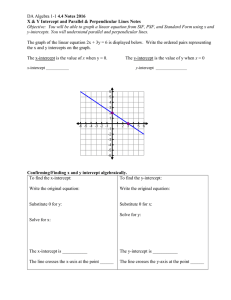
Chapter 8 - James Bac Dang
... • If you multiply the first row by (-1) and add it to the 2nd row, the result is (-2 0 0 -12) • What does this mean? -2x = -12, x=6 • By making an informed decision as to what variables to eliminate, we solved for a variable much more quickly! • Next, multiply row 1 by (-1) & add to 3rd row: (-2 2 0 ...
... • If you multiply the first row by (-1) and add it to the 2nd row, the result is (-2 0 0 -12) • What does this mean? -2x = -12, x=6 • By making an informed decision as to what variables to eliminate, we solved for a variable much more quickly! • Next, multiply row 1 by (-1) & add to 3rd row: (-2 2 0 ...
ALGEBRA 2 PRACTICE FINAL EXAM June 4 PART I
... 36. Solve the following equation and express the roots in simplest a + bi form. x 2 6x 13 0 37. Answer both parts a and b. a) Two men try to pull a pig out of a ditch. One man applies a force of 180 pounds while the other man applies a force of 220pounds. The resultant force is 280 pounds. Fin ...
... 36. Solve the following equation and express the roots in simplest a + bi form. x 2 6x 13 0 37. Answer both parts a and b. a) Two men try to pull a pig out of a ditch. One man applies a force of 180 pounds while the other man applies a force of 220pounds. The resultant force is 280 pounds. Fin ...