Initial practice problems. + + - O O O 2m 5m What is the net force on
... Suppose that sphere B1 is replaced by a second suspended sphere B2 that has the same mass, radius, and charge, but that is conducting. Equilibrium is again established when sphere A is 1.5 m from sphere B2 and their centers are at the same vertical height. State whether the equilibrium angle 2 will ...
... Suppose that sphere B1 is replaced by a second suspended sphere B2 that has the same mass, radius, and charge, but that is conducting. Equilibrium is again established when sphere A is 1.5 m from sphere B2 and their centers are at the same vertical height. State whether the equilibrium angle 2 will ...
Physics News from the AIP No 2, Term 1 2005
... To access the apps just go to the App Store or iTunes and search for "SparkVue" and elect to install. It's small and free so installs quickly. There's some preset experiment for x, y, z and x/y/z resultant accelerations. Note: For the safety of other passengers and those on the ground, Luna Park doe ...
... To access the apps just go to the App Store or iTunes and search for "SparkVue" and elect to install. It's small and free so installs quickly. There's some preset experiment for x, y, z and x/y/z resultant accelerations. Note: For the safety of other passengers and those on the ground, Luna Park doe ...
Role of stochastic processes in particle charging due to photoeffect
... elementary particles which create an electrical current through sunlit surface of the moon. They are knocked off of the surface soil, rise above the surface, and then fall back. Therefore, on average, on any unit of surface area there is a positive charge , equal in magnitude to the charge of photo ...
... elementary particles which create an electrical current through sunlit surface of the moon. They are knocked off of the surface soil, rise above the surface, and then fall back. Therefore, on average, on any unit of surface area there is a positive charge , equal in magnitude to the charge of photo ...
cp violation and the origins of matter
... at high energies does not respect some symmetry, like baryon number. At low energies we must include all local operators, including those that violate baryon number, an apparently disastrous result. But if the theory has an accidental symmetry, the only such operators are of dimension greater than f ...
... at high energies does not respect some symmetry, like baryon number. At low energies we must include all local operators, including those that violate baryon number, an apparently disastrous result. But if the theory has an accidental symmetry, the only such operators are of dimension greater than f ...
Particle Accelerators for High Energy Physics A Short History
... Here, F is the lens focal length and ` the lens separation. This separation matrix is a reasonable approximation to a dipole magnet for our purposes here. A similar matrix applies in the other transverse degree of freedom, with reversal of lens focusing character. Stability requires that M n remain ...
... Here, F is the lens focal length and ` the lens separation. This separation matrix is a reasonable approximation to a dipole magnet for our purposes here. A similar matrix applies in the other transverse degree of freedom, with reversal of lens focusing character. Stability requires that M n remain ...
Accelerator_course_english3 - Indico
... Introduction to Accelerators, 27 March 2009, Elena Wildner ...
... Introduction to Accelerators, 27 March 2009, Elena Wildner ...
Lecture 2: Chapter 16 Electric Charge and Electric Field
... • Insulators: electrons no free to move between atoms • Semiconductors - insulators that conduct in response to electric field • Objects can be charged by conduction or induction • The electric force is very strong compared to all other forces. ...
... • Insulators: electrons no free to move between atoms • Semiconductors - insulators that conduct in response to electric field • Objects can be charged by conduction or induction • The electric force is very strong compared to all other forces. ...
Year 9 Teacher Resource - Hadron Collider exhibition
... detection technology after they have explored and made inferences from the available detectors. It is important that the boxes never be opened to find out if the students were ‘right’, as the aim of the investigation is to find the best description of the nature of the particles (objects) inside the ...
... detection technology after they have explored and made inferences from the available detectors. It is important that the boxes never be opened to find out if the students were ‘right’, as the aim of the investigation is to find the best description of the nature of the particles (objects) inside the ...
IV. Colloidal Crystal
... of particles shows a similar trend but with shifted peak formation rate. A description of each region is given below. The optimum frequency increases as the particle size decreases (Table 1). However, frequency up to 10MHz was applied to 2nm particles but no Au nanowires could be formed. Later exper ...
... of particles shows a similar trend but with shifted peak formation rate. A description of each region is given below. The optimum frequency increases as the particle size decreases (Table 1). However, frequency up to 10MHz was applied to 2nm particles but no Au nanowires could be formed. Later exper ...
kovchegov
... At somewhat lower but still large momenta, QS < kT < kgeom , the BFKL evolution introduces anomalous dimension for gluon distributions: ...
... At somewhat lower but still large momenta, QS < kT < kgeom , the BFKL evolution introduces anomalous dimension for gluon distributions: ...
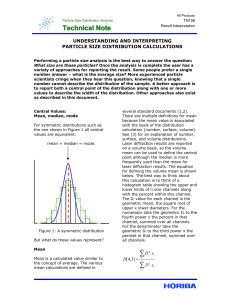
TN156 Understanding and Interpreting Particle Siz
... a volume, surface area, or number basis. Statistical calculations such as standard deviation and variance are available in either arithmetic or geometric forms, but are rarely used. The most common approach for expressing laser diffraction results is to report the D10, D50, and D90 values based on a ...
... a volume, surface area, or number basis. Statistical calculations such as standard deviation and variance are available in either arithmetic or geometric forms, but are rarely used. The most common approach for expressing laser diffraction results is to report the D10, D50, and D90 values based on a ...
Lecture 2
... ●The magnetic field and energy density of the deconfined matter reach very high values. ● Phenomenological analysis predicts disappearance of CME at the energy about the top SPS energy but too small effect at the LHC energy ● Actual calculations show no noticeable influence of the created electromag ...
... ●The magnetic field and energy density of the deconfined matter reach very high values. ● Phenomenological analysis predicts disappearance of CME at the energy about the top SPS energy but too small effect at the LHC energy ● Actual calculations show no noticeable influence of the created electromag ...
Unit 2 Particles and Waves
... something called exchange particles. Each force is mediated through an exchange particle or boson. Many theories postulate the existence of a further boson, called the Higgs boson (sometimes referred to as the ‘God particle’), which isn’t involved in forces but is what gives particles mass. Attempts ...
... something called exchange particles. Each force is mediated through an exchange particle or boson. Many theories postulate the existence of a further boson, called the Higgs boson (sometimes referred to as the ‘God particle’), which isn’t involved in forces but is what gives particles mass. Attempts ...
Electro-magnetically controlled acoustic metamaterials with adaptive
... considered in accelerators, plasma, or condense matter physics, there very light atomic or subatomic electrically charged particles move in a circle due to Lorentz force ...
... considered in accelerators, plasma, or condense matter physics, there very light atomic or subatomic electrically charged particles move in a circle due to Lorentz force ...
Electrostatics exam review
... Which graph represents the relationship between the magnitude of the electrostatic force on the electron and the magnitude of the electric field strength between the plates? ...
... Which graph represents the relationship between the magnitude of the electrostatic force on the electron and the magnitude of the electric field strength between the plates? ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.











![JLab 12 GeV upgrade (3) [C3]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022944901_1-077cfe868d2821e182d97c43c37805ed-300x300.png)