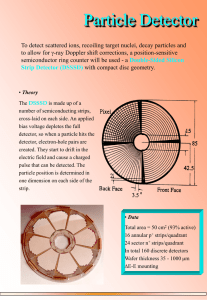
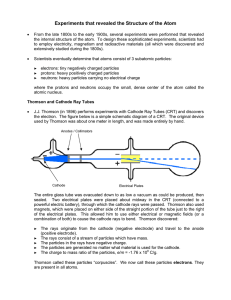
PowerPoint プレゼンテーション
... in supersymmetric model The Standard Model of elementary particle physics The best theory we know so far in describing elementary particle physics @ E=O(100 GeV) ...
... in supersymmetric model The Standard Model of elementary particle physics The best theory we know so far in describing elementary particle physics @ E=O(100 GeV) ...
Measuring Light Neutrino Families
... z 3l had N If Nv increases so does total decay width. ...
... z 3l had N If Nv increases so does total decay width. ...
03 Homework File
... Course title, week number and student’s name should appear on every sheet of the worked exercises, which should be securely bound together. Marked exercises will be returned in the box provided on the first floor the following week. The number of marks for each part is shown in []. Remember to use s ...
... Course title, week number and student’s name should appear on every sheet of the worked exercises, which should be securely bound together. Marked exercises will be returned in the box provided on the first floor the following week. The number of marks for each part is shown in []. Remember to use s ...
The Structure of Matter: The Basic Particle Model - ag
... model. From this application of the model there also follows the relativistic increase of mass at motion and the mass-energy equivalence. In addition Newton's law of motion is a consequence of the particle structure assumed in this model, and, as a further consequence of Newton's law, the law of ene ...
... model. From this application of the model there also follows the relativistic increase of mass at motion and the mass-energy equivalence. In addition Newton's law of motion is a consequence of the particle structure assumed in this model, and, as a further consequence of Newton's law, the law of ene ...
Elementary Particles in Physics
... subtle violation of these conservations laws has been observed. There is no understanding of the hierarchy of masses in Table 1 or why the observed neutrinos are so light. In addition to the leptons there exist hadrons (see Hadrons, Baryons, Hyperons, Mesons, Nucleon), which have strong interactions ...
... subtle violation of these conservations laws has been observed. There is no understanding of the hierarchy of masses in Table 1 or why the observed neutrinos are so light. In addition to the leptons there exist hadrons (see Hadrons, Baryons, Hyperons, Mesons, Nucleon), which have strong interactions ...
Modern physics 2330
... Q1 Indicate (√ ) for true statement and (× ) for false statement. 1- ( ) According to the special theory of relativity, interaction between objects in nature propagates with infinite speed. 2- ( ) An event is determined by the location where, and by the time at which occurs. 3- ( ) According to clas ...
... Q1 Indicate (√ ) for true statement and (× ) for false statement. 1- ( ) According to the special theory of relativity, interaction between objects in nature propagates with infinite speed. 2- ( ) An event is determined by the location where, and by the time at which occurs. 3- ( ) According to clas ...
Kaluza-Klein Theory
... (x+a) = exp( a d/dx ) (x) (per Taylor series; see footnote 1) (+z) = exp( [01-10]) () • in a sense, d/dx is translation; it’s the rule for how to go from here to there. similarly, [01-10] is how to rotate • generators of internal spaces correspond to bosons that act on their correspondi ...
... (x+a) = exp( a d/dx ) (x) (per Taylor series; see footnote 1) (+z) = exp( [01-10]) () • in a sense, d/dx is translation; it’s the rule for how to go from here to there. similarly, [01-10] is how to rotate • generators of internal spaces correspond to bosons that act on their correspondi ...
Observation of the Higgs Boson - Purdue Physics
... The Higgs Mechanism (1968) • Suppose the weak gauge bosons really were massless • Add another set of fields that they interact with which gives the same effect as mass: – A massless particle travels at the speed of light – Massless particles that “stick” to the Higgs field are slowed down – Photons ...
... The Higgs Mechanism (1968) • Suppose the weak gauge bosons really were massless • Add another set of fields that they interact with which gives the same effect as mass: – A massless particle travels at the speed of light – Massless particles that “stick” to the Higgs field are slowed down – Photons ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.