961122 - NCTU Institute of Physics國立交通大學物理研究所
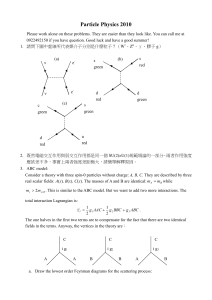
... Of the many possibilities for combining quarks with colour into colorless hadrons, only two configurations were found, till now… Because we cannot apply QCD at low Q2 since then g is large and the underlying theory is strongly coupling Quantum field theory which means no one can solve it analyticall ...
... Of the many possibilities for combining quarks with colour into colorless hadrons, only two configurations were found, till now… Because we cannot apply QCD at low Q2 since then g is large and the underlying theory is strongly coupling Quantum field theory which means no one can solve it analyticall ...
AP C Gauss` Law 26
... asymptotes, maxima or minima with numerical values or algebraic expressions as appropriate. i. The nuclear charge only q ...
... asymptotes, maxima or minima with numerical values or algebraic expressions as appropriate. i. The nuclear charge only q ...
Measuring the dynamics of single tethered DNA
... and its position is measured many times. From the gathered distribution one extracts the equilibrium state characteristics of the DNA. We developed a method for studying the dynamics of single DNAs, based on rapid frame-rate imaging. It is achieved by using gold nano particles as probes; the intense ...
... and its position is measured many times. From the gathered distribution one extracts the equilibrium state characteristics of the DNA. We developed a method for studying the dynamics of single DNAs, based on rapid frame-rate imaging. It is achieved by using gold nano particles as probes; the intense ...
Handout. Using the Fine Structure Constant to Push on the Standard
... o Renormalization yields a correction to the coupling constants which depends on energy. So, the coupling constants “run”, i.e. change with energy. o We expect that if the four forces are unified, the running coupling constants will converge at some high energy. (This is one of the motivations for s ...
... o Renormalization yields a correction to the coupling constants which depends on energy. So, the coupling constants “run”, i.e. change with energy. o We expect that if the four forces are unified, the running coupling constants will converge at some high energy. (This is one of the motivations for s ...
PDF Version
... particles other than neutrons—protons, in particular—may also be present in the neutron star because the exclusion principle on neutron does not apply to protons. Protons have positive charge, so neutron stars also need as many negatively charged particles to neutralize the proton charges. “If the i ...
... particles other than neutrons—protons, in particular—may also be present in the neutron star because the exclusion principle on neutron does not apply to protons. Protons have positive charge, so neutron stars also need as many negatively charged particles to neutralize the proton charges. “If the i ...
Radioactivity - Garbally Chemistry
... Alpha particles consists of two protons and two neutrons which is the same as the nucleus of Helium. The have low penetrating power and are stopped by a few centimeters of Air or a sheet of paper. Examples of elements which emit alpha particles is americium-241(smoke detectors). ...
... Alpha particles consists of two protons and two neutrons which is the same as the nucleus of Helium. The have low penetrating power and are stopped by a few centimeters of Air or a sheet of paper. Examples of elements which emit alpha particles is americium-241(smoke detectors). ...
Chapter 4 Assessment Key: 83, 85-89, 106
... 86. What is the primary factor determining whether a nucleus is stable or unstable? the neutron-to-proton ratio 87. Explain how energy loss and nuclear stability are related to radioactive decay. Radioactivity results when unstable nuclei emit energy in order to gain stability. 88. Explain what must ...
... 86. What is the primary factor determining whether a nucleus is stable or unstable? the neutron-to-proton ratio 87. Explain how energy loss and nuclear stability are related to radioactive decay. Radioactivity results when unstable nuclei emit energy in order to gain stability. 88. Explain what must ...
CLASSICAL MODEL OF A CHARGED PARTICLE WITH ANGULAR
... system which must be solved within the region occupied by the charge r :::::: r 0• At the origin of coordinates r = 0 the condition of regularity must be satisfied: the expansion for a quantity with index s starts with rs. At r = r 0 the components of the field and the static potential of the charge ...
... system which must be solved within the region occupied by the charge r :::::: r 0• At the origin of coordinates r = 0 the condition of regularity must be satisfied: the expansion for a quantity with index s starts with rs. At r = r 0 the components of the field and the static potential of the charge ...
Summary Notes Template
... perform a first-hand investigation or gather secondary information to observe radiation emitted from a nucleus using Wilson Cloud Chamber or similar detection device ...
... perform a first-hand investigation or gather secondary information to observe radiation emitted from a nucleus using Wilson Cloud Chamber or similar detection device ...
Fundamentals of Atomic Structure
... different elements are different in some fundamental way. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atomschanges in the way they ar ...
... different elements are different in some fundamental way. Chemical compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine with each other. A given compound always has the same relative numbers and types of atoms. Chemical reactions involve reorganization of the atomschanges in the way they ar ...
here - University of Kent
... when we want to describe nuclei as Skyrmions. Energies and allowed spin values of nuclei have so far almost exclusively been calculated by assuming that Skyrmions do not deform as they spin. We compute in the figure below how Skyrmions of various mass numbers B (see first row in figure) change their ...
... when we want to describe nuclei as Skyrmions. Energies and allowed spin values of nuclei have so far almost exclusively been calculated by assuming that Skyrmions do not deform as they spin. We compute in the figure below how Skyrmions of various mass numbers B (see first row in figure) change their ...
Formulae and Data Booklet - SCSA
... Note: the variable t refers to the 'time taken', sometimes referred to as the 'change in time' or Δt. ...
... Note: the variable t refers to the 'time taken', sometimes referred to as the 'change in time' or Δt. ...
PARTICLE PHYSICS
... nuclei as a result of nuclear instability. The fact that atoms seemed to spontaneously split apart also suggests they are not fundamental particles. ...
... nuclei as a result of nuclear instability. The fact that atoms seemed to spontaneously split apart also suggests they are not fundamental particles. ...
Anomaly driven signatures of new invisible physics
... possible because anomalous (i.e. gauge-variant) terms in the effective action have topological nature and are therefore scale independent. As a result, they are not suppressed even at energies much smaller than the masses of the particles producing these terms via loop effects. This gives hope to s ...
... possible because anomalous (i.e. gauge-variant) terms in the effective action have topological nature and are therefore scale independent. As a result, they are not suppressed even at energies much smaller than the masses of the particles producing these terms via loop effects. This gives hope to s ...
Impact of Large-Mixing-Angle Neutrino Oscillations
... Figure 4-2. In (i), only the quarks directly involved in the neutron decay reaction shown in Figure 4-1 are focused. In nature, it is known that not only the reaction (i), but also reactions (ii) and (iii) occur. All the reactions proceed from left to right. In (ii), a reaction is shown in which an ...
... Figure 4-2. In (i), only the quarks directly involved in the neutron decay reaction shown in Figure 4-1 are focused. In nature, it is known that not only the reaction (i), but also reactions (ii) and (iii) occur. All the reactions proceed from left to right. In (ii), a reaction is shown in which an ...
The Strangeness of Neutron Stars Neutron stars are the super
... cycles end in a supernova explosion. They provide a means to study the nature of matter at densities far beyond those attainable with terrestrial experiments. In the core of a neutron star the density is so extreme that atomic nuclei dissociate into their constituent baryons (neutrons and protons). ...
... cycles end in a supernova explosion. They provide a means to study the nature of matter at densities far beyond those attainable with terrestrial experiments. In the core of a neutron star the density is so extreme that atomic nuclei dissociate into their constituent baryons (neutrons and protons). ...
In Search of the God Particle
... Higgs particle and how would the CERN accelerator confirm its existence, thereby solving the riddle of the source of particle mass? What will become of the Standard Model of particle physics if this particle is not detected? Come join me on a journey through the things that engage the restless minds ...
... Higgs particle and how would the CERN accelerator confirm its existence, thereby solving the riddle of the source of particle mass? What will become of the Standard Model of particle physics if this particle is not detected? Come join me on a journey through the things that engage the restless minds ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.