Midterm Examination
... 1/ (20 pts) A 3-kg particle starts from rest at x = 0 and moves under the influence of a single force F = 6 + 4x - 3x2, where F is in newtons and x is in meters. (a) Find the work done by the force as the particle moves from x = 0 to x = 3 m. (b) Find the power delivered to the particle when it is a ...
... 1/ (20 pts) A 3-kg particle starts from rest at x = 0 and moves under the influence of a single force F = 6 + 4x - 3x2, where F is in newtons and x is in meters. (a) Find the work done by the force as the particle moves from x = 0 to x = 3 m. (b) Find the power delivered to the particle when it is a ...
PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 5 Angular momentum Nucleon magnetic moments
... in MeV: a1 ≈ 15.6, a2 ≈ 16.8, a3 ≈ 0.72, a4 ≈ 23.3, a5 ≈ 34 January 24, 2007 ...
... in MeV: a1 ≈ 15.6, a2 ≈ 16.8, a3 ≈ 0.72, a4 ≈ 23.3, a5 ≈ 34 January 24, 2007 ...
Midterm Examination
... 1/ (20 pts) A 3-kg particle starts from rest at x = 0 and moves under the influence of a single force F = 6 + 4x - 3x2, where F is in newtons and x is in meters. (a) Find the work done by the force as the particle moves from x = 0 to x = 3 m. (b) Find the power delivered to the particle when it is a ...
... 1/ (20 pts) A 3-kg particle starts from rest at x = 0 and moves under the influence of a single force F = 6 + 4x - 3x2, where F is in newtons and x is in meters. (a) Find the work done by the force as the particle moves from x = 0 to x = 3 m. (b) Find the power delivered to the particle when it is a ...
1 Dark Matter as a consequence of electric charge non
... with the gravitational field to be described below neutral particles survived inflation. These “early” neutral particles constitute what appears at present dark matter. For the sake of concreteness (cf. below) we will assume that these particles are thermal relics. Ordinary matter was produced after ...
... with the gravitational field to be described below neutral particles survived inflation. These “early” neutral particles constitute what appears at present dark matter. For the sake of concreteness (cf. below) we will assume that these particles are thermal relics. Ordinary matter was produced after ...
Klicker-questions, chapter 1 1. The figure shows the probability
... 4. The probability distribution for the position of a particle at time t is shown in the figure. At this time the position is measured and the value 0.73 is obtained. What is the most probable value to obtain the me position is measured again just a moment later? ...
... 4. The probability distribution for the position of a particle at time t is shown in the figure. At this time the position is measured and the value 0.73 is obtained. What is the most probable value to obtain the me position is measured again just a moment later? ...
CHAPTER 1: The Birth Of Modern Physics
... In a speech to the Royal Institution in 1900, Lord Kelvin himself described two “dark clouds on the horizon” of physics: ...
... In a speech to the Royal Institution in 1900, Lord Kelvin himself described two “dark clouds on the horizon” of physics: ...
Yr12 Physics Course Outline IMCC 2017
... the concept of ‘rest mass’. Describe time dilation. Atomic clock evidence of time dilation. Frame of reference. Relative motion. Limitations of Newton's laws (relatively low speeds). Relativity frames of reference, comparing speed. GPS only works if the clock on moving satellite is corrected for tim ...
... the concept of ‘rest mass’. Describe time dilation. Atomic clock evidence of time dilation. Frame of reference. Relative motion. Limitations of Newton's laws (relatively low speeds). Relativity frames of reference, comparing speed. GPS only works if the clock on moving satellite is corrected for tim ...
Heavy particle clustering in turbulent flows
... Optimal Stokes number for maximal clusterization No Reynolds dependence (as in Collins & Keswani 2004) Particles positions correlate with low values of acceleration ( prefer stay in hyperbolic regions) Maximum of clustering seems to be connected to ...
... Optimal Stokes number for maximal clusterization No Reynolds dependence (as in Collins & Keswani 2004) Particles positions correlate with low values of acceleration ( prefer stay in hyperbolic regions) Maximum of clustering seems to be connected to ...
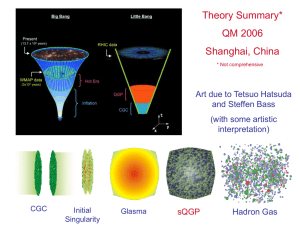
Rapporteur 4: Theory summary (30) Larry McLerran
... relationship to QCD No limit where theory is QCD Brian Greene: “data now emerging from the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at BNL appear to be more accurately described using string theory methods than with more traditional approaches” ...
... relationship to QCD No limit where theory is QCD Brian Greene: “data now emerging from the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at BNL appear to be more accurately described using string theory methods than with more traditional approaches” ...
Chapter28ReadingQuiz..
... electrons have a wave nature. light has a particle nature. a photon can be converted into an electron. electrons are the conductors in metals. ...
... electrons have a wave nature. light has a particle nature. a photon can be converted into an electron. electrons are the conductors in metals. ...
Proton - Common Sense Science
... analyze. Even worse, as Thomas states, “We know of no theoretical mechanism which could explain these data.” According to Shaevitz, however, forthcoming data from two Fermilab experiments may contest Thomas’s ideas.1 Shaevitz has the same attitude as most atomists who insist that more experiments wi ...
... analyze. Even worse, as Thomas states, “We know of no theoretical mechanism which could explain these data.” According to Shaevitz, however, forthcoming data from two Fermilab experiments may contest Thomas’s ideas.1 Shaevitz has the same attitude as most atomists who insist that more experiments wi ...
The cosmic connection
... every particle we know has a supersymmetric partner which is much more massive and interacts only weakly with regular matter. Supersymmetry solves deep problems in the mathematics of the Standard Model. It was developed for this reason, and not because it solves the dark matter problem. ...
... every particle we know has a supersymmetric partner which is much more massive and interacts only weakly with regular matter. Supersymmetry solves deep problems in the mathematics of the Standard Model. It was developed for this reason, and not because it solves the dark matter problem. ...
STEM Fair Introduction Beanium Isotopes Lab
... Neutrons are made of one “up” quark and two “down” quarks ...
... Neutrons are made of one “up” quark and two “down” quarks ...
What does LHC stand for
... Why does matter have mass? Can we find the Higgs boson, the particle which will explain mass? Matter and antimatter must have been produced in the same amounts at the time of the Big Bang, but from what we have observed so far, our Universe is made only of matter. Why? The LHC could help to provide ...
... Why does matter have mass? Can we find the Higgs boson, the particle which will explain mass? Matter and antimatter must have been produced in the same amounts at the time of the Big Bang, but from what we have observed so far, our Universe is made only of matter. Why? The LHC could help to provide ...
Year 8 Homework Task 8F-5 Compounds 5-7
... Followed the instructions for level 6, using detailed scientific knowledge and understanding, and also: Used symbols from the Periodic Table to write a symbol equation. ...
... Followed the instructions for level 6, using detailed scientific knowledge and understanding, and also: Used symbols from the Periodic Table to write a symbol equation. ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.