Analog Devices
... The model library consists of analog models of off-the-shelf parts that can be used directly in circuits that are being developed. Refer to the Library Reference Manual for device models and in which library they can be found. The model library includes models implemented using the .MODEL statement ...
... The model library consists of analog models of off-the-shelf parts that can be used directly in circuits that are being developed. Refer to the Library Reference Manual for device models and in which library they can be found. The model library includes models implemented using the .MODEL statement ...
Particle Swarm for Attribute Selection in Bayesian Classification: An
... how well each particle (candidate solution) solves the problem at hand. The comparison phase identifies the best particles. The imitation phase produces new particle positions based on some of the best particles previously found. These three phases are repeated until a given stopping criterion is me ...
... how well each particle (candidate solution) solves the problem at hand. The comparison phase identifies the best particles. The imitation phase produces new particle positions based on some of the best particles previously found. These three phases are repeated until a given stopping criterion is me ...
Superconducting properties of vacuum in strong magnetic field
... Electroweak model and in Quantum Chromodynamics at zero temperature. In these phases the vacuum behaves as an anisotropic inhomogeneous superconductor which supports superconductivity along the axis of the magnetic field while in the transversal directions the superconductivity does not exist. The m ...
... Electroweak model and in Quantum Chromodynamics at zero temperature. In these phases the vacuum behaves as an anisotropic inhomogeneous superconductor which supports superconductivity along the axis of the magnetic field while in the transversal directions the superconductivity does not exist. The m ...
Global distribution of the effective aerosol hygroscopicity parameter
... The ability of aerosol particles to take up water vapour influences both their direct and indirect effects on climate. The aerosol water content controls the aerosol ambient radius – which in turn controls the ability of the particle to interact with solar radiation (direct effect). Also, it is the ...
... The ability of aerosol particles to take up water vapour influences both their direct and indirect effects on climate. The aerosol water content controls the aerosol ambient radius – which in turn controls the ability of the particle to interact with solar radiation (direct effect). Also, it is the ...
Neutrino oscillations II
... • We clearly know neutrinos oscillate Neutrinos have masses • It seems that there are three allowed regions of parameters (sin22 and m2) that the current data seem to point ...
... • We clearly know neutrinos oscillate Neutrinos have masses • It seems that there are three allowed regions of parameters (sin22 and m2) that the current data seem to point ...
eXtremely Fast Tr
... When a high-energy cosmic ray enters the atmosphere it loses its energy via interactions with the nuclei that make up the air. At high energies these interactions create particles. These new particles go on to create more particles, etc. This multiplication process is known as a particle cascade. Th ...
... When a high-energy cosmic ray enters the atmosphere it loses its energy via interactions with the nuclei that make up the air. At high energies these interactions create particles. These new particles go on to create more particles, etc. This multiplication process is known as a particle cascade. Th ...
accelerators for physics experiments: from diagnostics
... The LHC is a 27 km long superconducting accelerator, which CERN, the European highenergy particle physics research organisation, is presently being commissioned in a tunnel 80 m under ground level in the Geneva region. This machine forms the last link in an interconnected chain of several particle a ...
... The LHC is a 27 km long superconducting accelerator, which CERN, the European highenergy particle physics research organisation, is presently being commissioned in a tunnel 80 m under ground level in the Geneva region. This machine forms the last link in an interconnected chain of several particle a ...
Chapter 5: Magnetic Systems in
... where µz is the component of the magnetic moment in the direction of the magnetic field B. Because the magnetic moment has spin 1/2, it has two possible orientations. We write µz = sµ, where s = ±1. The association of the magnetic moment of a particle with its spin is an intrinsic quantum mechanical ...
... where µz is the component of the magnetic moment in the direction of the magnetic field B. Because the magnetic moment has spin 1/2, it has two possible orientations. We write µz = sµ, where s = ±1. The association of the magnetic moment of a particle with its spin is an intrinsic quantum mechanical ...
Tests of Irradiated Semiconductor Detectors for ATLAS Upgrade
... A proton is a subatomic stable particle. Its rest mass is 938.27 MeV/c2 [16] and its value of electrical charge is equal to the elementary charge3 . According to the Standard Model theory, protons are particles made up of three quarks (two up quarks and one down quark). Proton beams have found many ...
... A proton is a subatomic stable particle. Its rest mass is 938.27 MeV/c2 [16] and its value of electrical charge is equal to the elementary charge3 . According to the Standard Model theory, protons are particles made up of three quarks (two up quarks and one down quark). Proton beams have found many ...
Dual-porosity model of solute diffusion in biological tissue modified
... We model a block of tissue as composed of essentially two media, the extracellular and the intracellular. At their respective volume fractions, they occupy the same block of tissue, as is illustrated by Fig. 2. Tissue is modeled as comprising cells' interior volume that collectively forms the intrac ...
... We model a block of tissue as composed of essentially two media, the extracellular and the intracellular. At their respective volume fractions, they occupy the same block of tissue, as is illustrated by Fig. 2. Tissue is modeled as comprising cells' interior volume that collectively forms the intrac ...
Discrete Abelian Gauge Symmetries
... mental evidence of parity violation in weak processes motivated a chiral theory. The Standard Model with its three generations was able to yield a natural explanation for the observed CP violation due to the complex phase of the CKM matrix. Additionally, approximate global flavor symmetries of the S ...
... mental evidence of parity violation in weak processes motivated a chiral theory. The Standard Model with its three generations was able to yield a natural explanation for the observed CP violation due to the complex phase of the CKM matrix. Additionally, approximate global flavor symmetries of the S ...
arXiv:1210.1847v1 [hep-ph] 4 Oct 2012
... for several reasons. Primary among them is that in Minkowski space, a non-vanishing spatial lattice spacing generically breaks space-time symmetries in such a way that there are dimension-four Lorentz breaking operators in the Standard Model, requiring a large number of fine-tunings to restore Loren ...
... for several reasons. Primary among them is that in Minkowski space, a non-vanishing spatial lattice spacing generically breaks space-time symmetries in such a way that there are dimension-four Lorentz breaking operators in the Standard Model, requiring a large number of fine-tunings to restore Loren ...
Soot measurements in rich-premixed/diffusion flames using Laser
... decreases the soot fraction while a small increase is observed upon the addition of approximately 10% and 20% hydrogen. This effect deviates from the addition of hydrogen to methane. The influence of hydrogen on soot formation is a topic of study in literature and is at present poorly understood. ...
... decreases the soot fraction while a small increase is observed upon the addition of approximately 10% and 20% hydrogen. This effect deviates from the addition of hydrogen to methane. The influence of hydrogen on soot formation is a topic of study in literature and is at present poorly understood. ...
Physics in Our Lives (Jul 2005)
... stones called magnetite exhibit magnetic properties. Nothing seems to be common between them. Basic laws governing electromagnetic phenomena were formulated (Coulomb, Ampere, Faraday) in 19th century. Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction is a discovery of great importance, as thus made it poss ...
... stones called magnetite exhibit magnetic properties. Nothing seems to be common between them. Basic laws governing electromagnetic phenomena were formulated (Coulomb, Ampere, Faraday) in 19th century. Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction is a discovery of great importance, as thus made it poss ...
Unit 10: Dark Matter
... Units 1 and 2, the Standard Model describes these known particles and their interactions. But careful astronomical measurements, computer-based simulations, and nuclear theory calculations have all led us to believe that the particles described by the Standard Model account for only 4 percent of the ...
... Units 1 and 2, the Standard Model describes these known particles and their interactions. But careful astronomical measurements, computer-based simulations, and nuclear theory calculations have all led us to believe that the particles described by the Standard Model account for only 4 percent of the ...
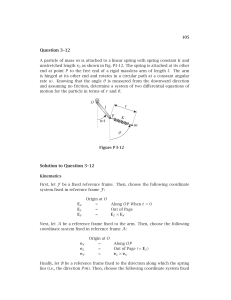
Question 3–12 Solution to Question 3–12
... Question 3–17 A particle of mass m is attached to an inextensible massless rope of length l as shown in Fig. P3-17. The rope is attached at its other end to point A located at the top of a fixed cylinder of radius R. As the particle moves, the rope wraps itself around the cylinder and never becomes ...
... Question 3–17 A particle of mass m is attached to an inextensible massless rope of length l as shown in Fig. P3-17. The rope is attached at its other end to point A located at the top of a fixed cylinder of radius R. As the particle moves, the rope wraps itself around the cylinder and never becomes ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.














![arXiv:1210.1847v1 [hep-ph] 4 Oct 2012](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016134331_1-89b462677ee8890a2a821c4d84b8db52-300x300.png)