A noun names a person, place, thing, or idea
... (I am happy. She appears lonely. They are all of the being verbs plus appear, look, feel, smell, taste, sound, remain, become, seem. ...
... (I am happy. She appears lonely. They are all of the being verbs plus appear, look, feel, smell, taste, sound, remain, become, seem. ...
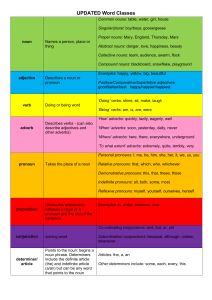
Word Class Chart - Elburton Primary School
... Positive/Comparative/Superlative adjectives: good/better/best happy/happier/happiest ‘Doing’ verbs: shine, sit, make, laugh ...
... Positive/Comparative/Superlative adjectives: good/better/best happy/happier/happiest ‘Doing’ verbs: shine, sit, make, laugh ...
TAM seminar I
... tigers, lioness, consumed, untimely, wholesome, gruesome, consumption, speaks, decorating, stopped, lovelier, strikingly a. Divide them into morphemes, noting any instances where you are unsure. b. Which of these morphemes are free and which are bound? c. Which of the morphemes can be identified as ...
... tigers, lioness, consumed, untimely, wholesome, gruesome, consumption, speaks, decorating, stopped, lovelier, strikingly a. Divide them into morphemes, noting any instances where you are unsure. b. Which of these morphemes are free and which are bound? c. Which of the morphemes can be identified as ...
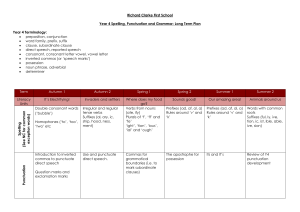
Year 4 SPAG Overview - Richard Clarke First School
... (because, due to, as a result of, next, then) ...
... (because, due to, as a result of, next, then) ...
Sentence components 1-subject: It is a noun or a pronoun which
... a- main verbs: they have meaning when they are alone. Main verbs are also classified into two types, transitive verbs such as (write, send, give, teach….etc.), and intransitive verbs such as (sleep, fly, sing, play…..etc.). ...
... a- main verbs: they have meaning when they are alone. Main verbs are also classified into two types, transitive verbs such as (write, send, give, teach….etc.), and intransitive verbs such as (sleep, fly, sing, play…..etc.). ...
Parts of Speech Notes - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Examples: dog, courage, soldier, Texas, sister, etc… Verbs Action verbs – show action, most common Linking verbs – show a state of being, or that something exists; it does not show action Helping verbs – used to make verb phrases, never stand alone Adjectives – modify nouns and pronouns; the ...
... Examples: dog, courage, soldier, Texas, sister, etc… Verbs Action verbs – show action, most common Linking verbs – show a state of being, or that something exists; it does not show action Helping verbs – used to make verb phrases, never stand alone Adjectives – modify nouns and pronouns; the ...
8 Parts of speech
... It was a beautiful day. Jenny was arguing with Paula, and she looked unhappy. ...
... It was a beautiful day. Jenny was arguing with Paula, and she looked unhappy. ...
Morphology - CSE, IIT Bombay
... Bound Base Morphemes • Occur only in a particular complex word • Do not have independent existence base (nonexistent) ...
... Bound Base Morphemes • Occur only in a particular complex word • Do not have independent existence base (nonexistent) ...
Morphology (CS 626-449)
... Bound Base Morphemes • Occur only in a particular complex word • Do not have independent existence base (nonexistent) ...
... Bound Base Morphemes • Occur only in a particular complex word • Do not have independent existence base (nonexistent) ...
Latin I Final Exam Study Guide (Final Exam is 20% of Course Grade
... o You will be given two nouns to decline. They will be from any of the following declensions: 1st, 2nd Masculine, 2nd Neuter, 3rd Masc/Fem, 3rd Neuter, 3rd Masc/Fem i-stem o You will be given one verb to conjugate in all 6 tenses for only one person & number e.g. "Conjugate mitto, mittere, misī, ...
... o You will be given two nouns to decline. They will be from any of the following declensions: 1st, 2nd Masculine, 2nd Neuter, 3rd Masc/Fem, 3rd Neuter, 3rd Masc/Fem i-stem o You will be given one verb to conjugate in all 6 tenses for only one person & number e.g. "Conjugate mitto, mittere, misī, ...
Parts of speech
... The term “parts of speech” refers to the words that make up a sentence and the functions those words perform within the sentence. There are 8 parts of speech, but these 6 are the most important to recognize first: 1) noun 2) verb 3) preposition 4) adjective 5) adverb 6) article The same word can be ...
... The term “parts of speech” refers to the words that make up a sentence and the functions those words perform within the sentence. There are 8 parts of speech, but these 6 are the most important to recognize first: 1) noun 2) verb 3) preposition 4) adjective 5) adverb 6) article The same word can be ...
parts of speech here
... Articles (Determiners, Noun Markers) as Adjectives – a, an, the – Ex/ The dog is cute. ...
... Articles (Determiners, Noun Markers) as Adjectives – a, an, the – Ex/ The dog is cute. ...
Parts of speech
... [e.g., he {hablado} (I have {spoken}), habríamos {spoken} (we would have {studied})]. There are three conjugations of verbs: -ar [e.g., hablar, to speak], -er [e.g., comer, to eat], and -ir [e.g., vivir], each with typical sets of endings. The endings in Spanish indicate mood, for example indicative ...
... [e.g., he {hablado} (I have {spoken}), habríamos {spoken} (we would have {studied})]. There are three conjugations of verbs: -ar [e.g., hablar, to speak], -er [e.g., comer, to eat], and -ir [e.g., vivir], each with typical sets of endings. The endings in Spanish indicate mood, for example indicative ...
parts of speech - 220112012salinaunisel
... The first thing _____________ saw was a ___________________ standing beside a tree. He/She __________ over to the _______________. "What's your name?" asked ____________. The ...
... The first thing _____________ saw was a ___________________ standing beside a tree. He/She __________ over to the _______________. "What's your name?" asked ____________. The ...
Chapter 2 Parts of Speech
... The preposition connections its object(s) to some other word(s) in the sentence. A preposition and its object—usually a noun and a pronoun—with modifiers make up a prepositional phrase, which will function as an adjective or an adverb. ...
... The preposition connections its object(s) to some other word(s) in the sentence. A preposition and its object—usually a noun and a pronoun—with modifiers make up a prepositional phrase, which will function as an adjective or an adverb. ...
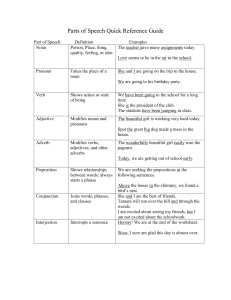
Parts of Speech Quick Reference Guide
... The wonderfully beautiful girl easily won the pageant. Today, we are getting out of school early. ...
... The wonderfully beautiful girl easily won the pageant. Today, we are getting out of school early. ...
Action Verb: Tells what the subject does. • Jeremy likes to run
... Adverb: words that modify, or describe, a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. • (verb) The snail moved slowly. • (adjective) The horse was already gigantic. • (adverb) The kingdom was far away. ...
... Adverb: words that modify, or describe, a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. • (verb) The snail moved slowly. • (adjective) The horse was already gigantic. • (adverb) The kingdom was far away. ...
THE QUESTIONS FOR FINAL EXAMINATION AT ROMANIAN
... 20. Liver - The Biggest Gland from the Human Body 21. The Excretory System 22. Urinary Apparatus – Kidneys ...
... 20. Liver - The Biggest Gland from the Human Body 21. The Excretory System 22. Urinary Apparatus – Kidneys ...
Parts of Speech
... A verb phrase consists of at least one main verb and one or more helping verbs. Helping verbs: can, could, do, did, does, had, has, have, may, shall, should, will, would. The boy is leaving for Texas tomorrow. She should not have borrowed that necklace. ...
... A verb phrase consists of at least one main verb and one or more helping verbs. Helping verbs: can, could, do, did, does, had, has, have, may, shall, should, will, would. The boy is leaving for Texas tomorrow. She should not have borrowed that necklace. ...
Plural Nouns - Net Start Class
... them to mean more than one. class – classes radish – radishes beach – beaches box - boxes For most nouns that end in y, you would drop the y and add ies to the noun to change them to mean more than one. lady – ladies ...
... them to mean more than one. class – classes radish – radishes beach – beaches box - boxes For most nouns that end in y, you would drop the y and add ies to the noun to change them to mean more than one. lady – ladies ...
Year 2: To be introduced
... by compounding [for example, whiteboard, superman] Formation of adjectives using suffixes such as –ful, – less (A fuller list of suffixes can be found on page Error! Bookmark not defined. in the year 2 spelling section in English Appendix 1) Use of the suffixes –er, –est in adjectives and the use of ...
... by compounding [for example, whiteboard, superman] Formation of adjectives using suffixes such as –ful, – less (A fuller list of suffixes can be found on page Error! Bookmark not defined. in the year 2 spelling section in English Appendix 1) Use of the suffixes –er, –est in adjectives and the use of ...
study notes epi - Australia Plus TV
... check that word forms are used and formed correctly, for example • nouns formed from verbs (decide – decision) • adjectives formed from verbs (interest – interesting/interested) • adjectives formed from nouns (peace – peaceful) • nouns formed from adj ...
... check that word forms are used and formed correctly, for example • nouns formed from verbs (decide – decision) • adjectives formed from verbs (interest – interesting/interested) • adjectives formed from nouns (peace – peaceful) • nouns formed from adj ...
Inflection

In grammar, inflection or inflexion is the modification of a word to express different grammatical categories such as tense, mood, voice, aspect, person, number, gender and case. The inflection of verbs is also called conjugation, and the inflection of nouns, adjectives and pronouns is also called declension.An inflection expresses one or more grammatical categories with a prefix, suffix or infix, or another internal modification such as a vowel change. For example, the Latin verb ducam, meaning ""I will lead"", includes the suffix -am, expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense (future). The use of this suffix is an inflection. In contrast, in the English clause ""I will lead"", the word lead is not inflected for any of person, number, or tense; it is simply the bare form of a verb.The inflected form of a word often contains both a free morpheme (a unit of meaning which can stand by itself as a word), and a bound morpheme (a unit of meaning which cannot stand alone as a word). For example, the English word cars is a noun that is inflected for number, specifically to express the plural; the content morpheme car is unbound because it could stand alone as a word, while the suffix -s is bound because it cannot stand alone as a word. These two morphemes together form the inflected word cars.Words that are never subject to inflection are said to be invariant; for example, the English verb must is an invariant item: it never takes a suffix or changes form to signify a different grammatical category. Its categories can be determined only from its context.Requiring the inflections of more than one word in a sentence to be compatible according to the rules of the language is known as concord or agreement. For example, in ""the choir sings"", ""choir"" is a singular noun, so ""sing"" is constrained in the present tense to use the third person singular suffix ""s"".Languages that have some degree of inflection are synthetic languages. These can be highly inflected, such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, or weakly inflected, such as English. Languages that are so inflected that a sentence can consist of a single highly inflected word (such as many American Indian languages) are called polysynthetic languages. Languages in which each inflection conveys only a single grammatical category, such as Finnish, are known as agglutinative languages, while languages in which a single inflection can convey multiple grammatical roles (such as both nominative case and plural, as in Latin and German) are called fusional. Languages such as Mandarin Chinese that never use inflections are called analytic or isolating.