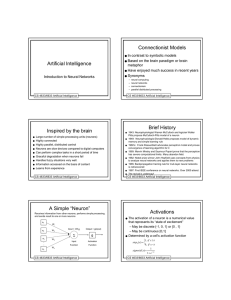
Artificial Intelligence Connectionist Models Inspired by the brain
... – May be discrete {-1, 0, 1} or {0 , 1} – May be continuous [0,1] Determined by a cell’s activation function 1, if x ≥ t stept ( x) = î 0, if x < t sigmoid ( x) = ...
... – May be discrete {-1, 0, 1} or {0 , 1} – May be continuous [0,1] Determined by a cell’s activation function 1, if x ≥ t stept ( x) = î 0, if x < t sigmoid ( x) = ...
Slide ()
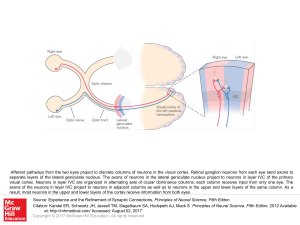
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
Unit 2: The body and the Brain
... 8. What is the purpose of the spinal cord (how does it relate to human behavior?) ...
... 8. What is the purpose of the spinal cord (how does it relate to human behavior?) ...
Axia College Material Appendix B Structures of the Nervous System
... This activity will increase your understanding of the different structures of the nervous system and brain. During the Web activity, you will view a variety of structures of the brain and nervous system and label each with the appropriate term. You will use this document to write a description for t ...
... This activity will increase your understanding of the different structures of the nervous system and brain. During the Web activity, you will view a variety of structures of the brain and nervous system and label each with the appropriate term. You will use this document to write a description for t ...
Netter`s Atlas of Neuroscience - 9780323265119 | US Elsevier
... in synaptic vesicles. When an action potential invades the terminal region, depolarization triggers Ca2+ influx into the terminal, causing numerous synaptic vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane, releasing their packets of neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter can b ...
... in synaptic vesicles. When an action potential invades the terminal region, depolarization triggers Ca2+ influx into the terminal, causing numerous synaptic vesicles to fuse with the presynaptic membrane, releasing their packets of neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter can b ...
Appendix 4 Mathematical properties of the state-action
... The heart of the ANNABELL model is the state-action association system, which is responsible for all decision processes, as described in Sect. “Global organization of the model”. This system is implemented as a neural network (state-action association neural network, abbreviated as SAANN) with input ...
... The heart of the ANNABELL model is the state-action association system, which is responsible for all decision processes, as described in Sect. “Global organization of the model”. This system is implemented as a neural network (state-action association neural network, abbreviated as SAANN) with input ...
chapter_12 - The Anatomy Academy
... detect changes in body and external environment information transmitted into brain or spinal cord lie between sensory and motor pathways in CNS 90% of our neurons are interneurons process, store and retrieve information ...
... detect changes in body and external environment information transmitted into brain or spinal cord lie between sensory and motor pathways in CNS 90% of our neurons are interneurons process, store and retrieve information ...
PSY103_Lecture_CH2_WordScript
... - How Neurons Communicate - Neurons are communication specialists in our brain and spinal cord; they use an electrochemical communication process. - An electrical impulse (called the action potential) travels down to the bottom of the axon where synaptic vesicles open and release chemicals called ne ...
... - How Neurons Communicate - Neurons are communication specialists in our brain and spinal cord; they use an electrochemical communication process. - An electrical impulse (called the action potential) travels down to the bottom of the axon where synaptic vesicles open and release chemicals called ne ...
document
... memory. Recurrent networks can have connections between nodes in any layer, which enables them to store data – a memory. Recurrent networks can be used to solve problems where the solution depends on previous inputs as well as current inputs ...
... memory. Recurrent networks can have connections between nodes in any layer, which enables them to store data – a memory. Recurrent networks can be used to solve problems where the solution depends on previous inputs as well as current inputs ...
Anikeeva
... We are developing minimally inavsive procedures for deep brain stimulation by coupling radiofrequency electromagnetic waves with nanoantennae interfaced with the neuronal cell membrane. Because of its weak interaction with biological molecules and deep tissue penetration, magnetic fields promise to ...
... We are developing minimally inavsive procedures for deep brain stimulation by coupling radiofrequency electromagnetic waves with nanoantennae interfaced with the neuronal cell membrane. Because of its weak interaction with biological molecules and deep tissue penetration, magnetic fields promise to ...
14.1 Nervous Control notes - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... Topic 14. COORDINATION & RESPONSE 14.1 Nervous control in humans Describe a nerve impulse - an electrical signal that passes along nerve cells called neurones Describe the human nervous system in terms of: – the central nervous system consisting of brain and spinal cord – the peripheral nervous syst ...
... Topic 14. COORDINATION & RESPONSE 14.1 Nervous control in humans Describe a nerve impulse - an electrical signal that passes along nerve cells called neurones Describe the human nervous system in terms of: – the central nervous system consisting of brain and spinal cord – the peripheral nervous syst ...
The Nervous System - School District of New Berlin
... The Synapse • A gap called a synapse or synaptic cleft separates the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron. • *Neurons do not touch. • Chemicals carry messages across the synapse. ...
... The Synapse • A gap called a synapse or synaptic cleft separates the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of the next neuron. • *Neurons do not touch. • Chemicals carry messages across the synapse. ...
9.1-9.4 Notes
... – Multipolar – Carry impulse out of CNS to the effectors – Stimulate muscle and glands to respond ...
... – Multipolar – Carry impulse out of CNS to the effectors – Stimulate muscle and glands to respond ...
chapter 2- neuroscience genetics and behavior
... CHAPTER 2- NEUROSCIENCE GENETICS AND BEHAVIOR Everything psychological is biological. This perspective is called biological psychologists or neuropsychologists. Phrenology -- Franz Gall early 1800’s-study of bumps on the head to determine character traits. Although this theory was false it did give ...
... CHAPTER 2- NEUROSCIENCE GENETICS AND BEHAVIOR Everything psychological is biological. This perspective is called biological psychologists or neuropsychologists. Phrenology -- Franz Gall early 1800’s-study of bumps on the head to determine character traits. Although this theory was false it did give ...
NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS TEST PREVIEW
... 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an impulse? 6. What is the pathway of an impulse from stimulus ...
... 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an impulse? 6. What is the pathway of an impulse from stimulus ...
Brain(annotated)
... predictable. Exact timing may depend on thermal fluctuations, or it may be due to the complexity of many neurons being wired together, or both. ...
... predictable. Exact timing may depend on thermal fluctuations, or it may be due to the complexity of many neurons being wired together, or both. ...
Multiscale Approach to Neural Tissue Modeling
... In the talk a multiscale model of neural tissue will be presented. The neural tissue is usually modeled in different areas. In the microscopic approach the tissue is modeled on a cellular or ion channels level. On the macroscopic level the tissue parameters are averaged over large domains representi ...
... In the talk a multiscale model of neural tissue will be presented. The neural tissue is usually modeled in different areas. In the microscopic approach the tissue is modeled on a cellular or ion channels level. On the macroscopic level the tissue parameters are averaged over large domains representi ...
11-Jun-15 1 - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... under conscious control & reflex arcs • Autonomic system: controls organ systems not under conscious control. ...
... under conscious control & reflex arcs • Autonomic system: controls organ systems not under conscious control. ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Refractory Period: a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired. Excitatory versus inhibitory Threshold: a level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse. All or none response: a neuron’s reaction of either firing (with a full strength response) or not firing. ...
... Refractory Period: a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired. Excitatory versus inhibitory Threshold: a level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse. All or none response: a neuron’s reaction of either firing (with a full strength response) or not firing. ...
N1 - Kůra mozku HE
... cells : 1.neurons and 2.glial cells • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vascul ...
... cells : 1.neurons and 2.glial cells • extracellular material is extremely reduced replaced by glial branched process • neurons receive stimuli and conduct nerve impulse via their processes • action potential transmission to the next cell through synapses (= intercellular contacts) • extensive vascul ...
to Psychology 3
... - nervous system tissue is composed of two types: gila and neurons 1. Glia: The Supporting System - glia cells exist throughout the nervous system and provide structural support and insulation for neurons - glia cells may supply nutrients, remove wastes, repair damage, or perform other non neural ta ...
... - nervous system tissue is composed of two types: gila and neurons 1. Glia: The Supporting System - glia cells exist throughout the nervous system and provide structural support and insulation for neurons - glia cells may supply nutrients, remove wastes, repair damage, or perform other non neural ta ...
Nervous System - Downey Unified School District
... • THEY TRAVEL DOWN THE AXON TO THE NERVE TERMINAL • OTHER NEUROTRANSMITTERS ARE SYNTHESIZED IN THE CYTOPLASM OF THE NERVE TERMINALS AND ARE STORED IN VESICLES • WHEN AN ACTION POTENTIAL PASSES ALONG THE MEMBRANE OF A SYNAPTIC KNOB IT INCREASES PERMEABILITY ALLOWING CALCIUM IONS IN BY OPENING CHANNEL ...
... • THEY TRAVEL DOWN THE AXON TO THE NERVE TERMINAL • OTHER NEUROTRANSMITTERS ARE SYNTHESIZED IN THE CYTOPLASM OF THE NERVE TERMINALS AND ARE STORED IN VESICLES • WHEN AN ACTION POTENTIAL PASSES ALONG THE MEMBRANE OF A SYNAPTIC KNOB IT INCREASES PERMEABILITY ALLOWING CALCIUM IONS IN BY OPENING CHANNEL ...
Central Nervous System - tvhs2011
... and interrupt messages throughout the body. It allows us to react to stimuli, sends chemicals that give us feelings, and enables our body to function. The nervous system consists mainly of two parts. These parts being the brain and the vertebrae also known as the spinal cord. Another major com ...
... and interrupt messages throughout the body. It allows us to react to stimuli, sends chemicals that give us feelings, and enables our body to function. The nervous system consists mainly of two parts. These parts being the brain and the vertebrae also known as the spinal cord. Another major com ...