Week 1a Lecture Notes
... Integration of synaptic inputs, synaptic and cellular plasticity Methods of cognitive neuroscience, functional neuroimaging, EEG, TMS, MEG Data analysis methods, neural coding, computational neuroscience ...
... Integration of synaptic inputs, synaptic and cellular plasticity Methods of cognitive neuroscience, functional neuroimaging, EEG, TMS, MEG Data analysis methods, neural coding, computational neuroscience ...
File
... • ability of a cell to respond to inductive signals, determined by presence of receptors, transduction molecules, transcription factors • If a cell is incompetent to an inductive signal, will there be an effect? • No, because it does not have the machinery capable to induce the desired effect. • ...
... • ability of a cell to respond to inductive signals, determined by presence of receptors, transduction molecules, transcription factors • If a cell is incompetent to an inductive signal, will there be an effect? • No, because it does not have the machinery capable to induce the desired effect. • ...
Neurons and Networks. An Introduction to Behavioral Neuroscience, Second Edition Brochure
... solid foundation of understanding and knowledge required for further study. The new edition retains the features that made the first edition so attractive: consistent emphasis on results and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanati ...
... solid foundation of understanding and knowledge required for further study. The new edition retains the features that made the first edition so attractive: consistent emphasis on results and concepts that have stood the test of time; abundant high-quality illustrations; exceptionally clear explanati ...
Supporting Cells of the Nervous System
... 2) act as phagocytes to clean up worn-out neuron organelles. 3) Electrically insulate neurons by forming a myelin sheath. 4) increase the speed of the action potential (electrochemical message) in those cells that have a myelin sheath. ...
... 2) act as phagocytes to clean up worn-out neuron organelles. 3) Electrically insulate neurons by forming a myelin sheath. 4) increase the speed of the action potential (electrochemical message) in those cells that have a myelin sheath. ...
L11Nervous tissue strusture 11
... Neurons in the human Nervous systemmvary widely in their size and shape. However, all neurons have some features in common. A neuron consists of: 1. a cell body, called the soma, (Perikaryon) 2. with arms that reach out to connect to the network of other neurons in the brain. One arm, the dendrite, ...
... Neurons in the human Nervous systemmvary widely in their size and shape. However, all neurons have some features in common. A neuron consists of: 1. a cell body, called the soma, (Perikaryon) 2. with arms that reach out to connect to the network of other neurons in the brain. One arm, the dendrite, ...
1. nervous system
... is the neuron. The generic structure of a neuron is presented in figure 1-4. There are three basic types of neurons (Fig, 1-5). The multipolar neurons are characterized for having a highly branched dendritic terminal and a single axon capable of interacting with a very large number of other neurons. ...
... is the neuron. The generic structure of a neuron is presented in figure 1-4. There are three basic types of neurons (Fig, 1-5). The multipolar neurons are characterized for having a highly branched dendritic terminal and a single axon capable of interacting with a very large number of other neurons. ...
The Central Nervous System CNS
... sensory organ), the cell body (numbers of which sideby-side form gray matter) where the nucleus is found, and the axon which carries the impulse away from the cell. ...
... sensory organ), the cell body (numbers of which sideby-side form gray matter) where the nucleus is found, and the axon which carries the impulse away from the cell. ...
Lab 11 Nervous System I
... Lab 11 Nervous System I Laboratory Objectives Describe the organization of the nervous system. Identify the structure and function of the neuroglia. Identify the differences between glial cells in the central nervous system and in the peripheral nervous system. Identify the structures of a typical n ...
... Lab 11 Nervous System I Laboratory Objectives Describe the organization of the nervous system. Identify the structure and function of the neuroglia. Identify the differences between glial cells in the central nervous system and in the peripheral nervous system. Identify the structures of a typical n ...
Fridtjof Nansen Science Symposium 2011
... All animals and even unicellular organisms recognize other members of their species and interact with them, suggesting that ancient biological systems are involved in these recognition processes. Innate social behaviors emerge from neuronal circuits that interpret sensory information based on an ind ...
... All animals and even unicellular organisms recognize other members of their species and interact with them, suggesting that ancient biological systems are involved in these recognition processes. Innate social behaviors emerge from neuronal circuits that interpret sensory information based on an ind ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 2.1 Locomotor behavior in hydra
... FIGURE 2.18 Cajal’s (1909–1911) neural architecture drawing based on the Golgi method. It shows the organization of four major retinal neuron types (right) and connections between two gray matter regions: retina to optic tectum (superior colliculus; left). Applying the neuron doctrine and functional ...
... FIGURE 2.18 Cajal’s (1909–1911) neural architecture drawing based on the Golgi method. It shows the organization of four major retinal neuron types (right) and connections between two gray matter regions: retina to optic tectum (superior colliculus; left). Applying the neuron doctrine and functional ...
Physiology Unit Objectives and Assignments
... you could explain it to someone, mark the Green Light Box. If you kind of get it but still have some questions or need to a study a little more to memorize it, put an X in the Orange Light Box. If you do not understand the concept, have never heard of it, or are totally confused, put an X in the Red ...
... you could explain it to someone, mark the Green Light Box. If you kind of get it but still have some questions or need to a study a little more to memorize it, put an X in the Orange Light Box. If you do not understand the concept, have never heard of it, or are totally confused, put an X in the Red ...
Neural Mechanism of Language
... viewpoint, the language relevant area is the brain in brain. If the cortex is called the second nature (1), language relevant area is the third nature. Specifically, neurons correspond to objects, attributes and motions, while connections correspond to associations and temporal relations. Therefore ...
... viewpoint, the language relevant area is the brain in brain. If the cortex is called the second nature (1), language relevant area is the third nature. Specifically, neurons correspond to objects, attributes and motions, while connections correspond to associations and temporal relations. Therefore ...
Chapter 5 - Metropolitan Community College
... Basic Brain Structures, cont. • Each neuron has a single axon (nerve fiber) that extends from it and meets the dendrites of other neurons at intersections called synapses - axons and dendrites don’t actually touch at synapses - electrical impulses trigger brain chemicals called neurotransmitters, w ...
... Basic Brain Structures, cont. • Each neuron has a single axon (nerve fiber) that extends from it and meets the dendrites of other neurons at intersections called synapses - axons and dendrites don’t actually touch at synapses - electrical impulses trigger brain chemicals called neurotransmitters, w ...
Lecture 7 (Jan 31): BRAIN DEVELOPMENT and EVOLUTION
... 1) Proliferation: Mitosis (division) of Neural Stem Cells in Ventricular Zone of Neural Tube. ...
... 1) Proliferation: Mitosis (division) of Neural Stem Cells in Ventricular Zone of Neural Tube. ...
Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... Resting state: Voltage-gated Na and K channels are closed; resting potential is maintained by ungated channels (not shown). ...
... Resting state: Voltage-gated Na and K channels are closed; resting potential is maintained by ungated channels (not shown). ...
A5: Neuropharamcology (student) - Ms De Souza`s Super Awesome
... The secondary messengers can persist for days and cause what is known as long-term potentiation (LTP), allowing new synapses to form in the hippocampus and other areas of the brain. ...
... The secondary messengers can persist for days and cause what is known as long-term potentiation (LTP), allowing new synapses to form in the hippocampus and other areas of the brain. ...
Nervous Tissue
... Lecture 2 Electrical Signals in Neurons • Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
... Lecture 2 Electrical Signals in Neurons • Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
A1985AUW1100002
... thought that, memory aside, the hippocampus offered several advantages. It has a cellular architecture that is remarkably conserved throughout mammals, and the main cetts, catted the pyramidal cells, are clustered in a discrete layer, an easy target for microelectrodes. These cells send their axons ...
... thought that, memory aside, the hippocampus offered several advantages. It has a cellular architecture that is remarkably conserved throughout mammals, and the main cetts, catted the pyramidal cells, are clustered in a discrete layer, an easy target for microelectrodes. These cells send their axons ...
Introduction to the Nervous System
... they are receiving, and respond by making changes to return the body to its set point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to generate sensory and motor output a- Sensory input (neuron) ...
... they are receiving, and respond by making changes to return the body to its set point. The nervous system uses a three step approach to generate sensory and motor output a- Sensory input (neuron) ...
Neuron Anatomy
... • Synchronization of the electrical activity of large populations of neurons; - e.g., the large populations of neurosecretory neurons that synthesize and release biologically active peptide neurotransmitters and hormones are extensively connected by electrical synapses. - e.g., Synchronization may b ...
... • Synchronization of the electrical activity of large populations of neurons; - e.g., the large populations of neurosecretory neurons that synthesize and release biologically active peptide neurotransmitters and hormones are extensively connected by electrical synapses. - e.g., Synchronization may b ...
CH. 2 (BIOLOGY)
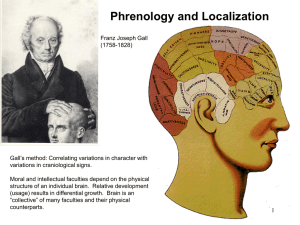
... A theory of personality formulated in the 18th and 19 centuries by German physician Franz Joesf Gall. It stated that specific abilities or personality traits are represented by specific areas of the brain. The size of these brain areas determines the degrees of the corresponding skill or trait. Alth ...
... A theory of personality formulated in the 18th and 19 centuries by German physician Franz Joesf Gall. It stated that specific abilities or personality traits are represented by specific areas of the brain. The size of these brain areas determines the degrees of the corresponding skill or trait. Alth ...
Slide ()
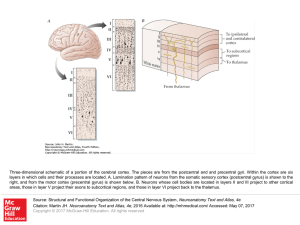
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
nervous5
... Some IPSPs result in no change in membrane potential by opening Chloride channels that stabilize membrane potential at resting value (Nernst Potential for Cl- = -70mV) or in cells that actively transport Cl- out. ...
... Some IPSPs result in no change in membrane potential by opening Chloride channels that stabilize membrane potential at resting value (Nernst Potential for Cl- = -70mV) or in cells that actively transport Cl- out. ...
sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
... b) Sensory neuron - starts with a sensory receptor (pressure, heat, light etc) - message travels towards CNS - cell body is outside CNS in Ganglia - long dendrite, short axon c) Association (inter) neuron - smaller than a & b above - entirely within CNS - both long and short axons and dendrites - co ...
... b) Sensory neuron - starts with a sensory receptor (pressure, heat, light etc) - message travels towards CNS - cell body is outside CNS in Ganglia - long dendrite, short axon c) Association (inter) neuron - smaller than a & b above - entirely within CNS - both long and short axons and dendrites - co ...