B42010712
... projections given new situations of interest and answer "what if" questions. so in this paper we tried to introduce a brief overview of ANN to help researchers in their way throw ANN. ...
... projections given new situations of interest and answer "what if" questions. so in this paper we tried to introduce a brief overview of ANN to help researchers in their way throw ANN. ...
The Nervous System
... The peripheral nervous system controls the functions of body tissues and organs. Somatic nerves transmit signals from the outer parts of the body to the brain. Autonomic nerves help to control the functions of internal organs, like the heart and stomach. ...
... The peripheral nervous system controls the functions of body tissues and organs. Somatic nerves transmit signals from the outer parts of the body to the brain. Autonomic nerves help to control the functions of internal organs, like the heart and stomach. ...
Lesson 7
... All Bobby wanted in the world was to be able to play wiffle ball with his friends. All Bobby’s neurotic mother wanted was for him to avoid injuries at all costs. Running the bases was going to be a ...
... All Bobby wanted in the world was to be able to play wiffle ball with his friends. All Bobby’s neurotic mother wanted was for him to avoid injuries at all costs. Running the bases was going to be a ...
Slide ()
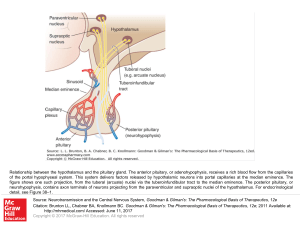
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
... Relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. The anterior pituitary, or adenohypophysis, receives a rich blood flow from the capillaries of the portal hypophyseal system. This system delivers factors released by hypothalamic neurons into portal capillaries at the median eminence. T ...
1 - Test Bank
... Chapter 2 1. In the structure of the neuron, the __________ sends information to other cells. a. axon b. dendrite c. soma d. myelin ANS: a LO=2.1 2. Which type of cell makes up 10 percent of the brain? a. glial cells b. neurons c. stem cells d. afferent cells ANS: b LO=2.1 3. Damaged nerve fibers in ...
... Chapter 2 1. In the structure of the neuron, the __________ sends information to other cells. a. axon b. dendrite c. soma d. myelin ANS: a LO=2.1 2. Which type of cell makes up 10 percent of the brain? a. glial cells b. neurons c. stem cells d. afferent cells ANS: b LO=2.1 3. Damaged nerve fibers in ...
File - Mrs. Walston Science
... The most important body structure between the body and the brain. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system, it it the pathway to the peripheral nervous sy ...
... The most important body structure between the body and the brain. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of neural signals between the brain and the rest of the body The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system, it it the pathway to the peripheral nervous sy ...
Human Neuroanatomy Grades 9-12
... to draw their own on a piece of paper. Label and discuss the functions of the parts listed above. Second, discuss the midbrain. The midbrain supports reflexes and other vital functions such as hunger. Draw the midbrain and label and discuss the parts above. Allow the students to draw it on their own ...
... to draw their own on a piece of paper. Label and discuss the functions of the parts listed above. Second, discuss the midbrain. The midbrain supports reflexes and other vital functions such as hunger. Draw the midbrain and label and discuss the parts above. Allow the students to draw it on their own ...
Physical features directly related to personality and metal processes
... degrees involved sitting examinations or writing of thesis. Methods from Physiology ...
... degrees involved sitting examinations or writing of thesis. Methods from Physiology ...
Presynaptic Questions
... Neurons can contain more than on NT; they frequently contain a peptide and one of the other types of NTs What ion is critical in vesicular release of NT? How might the role of this ion explain the proposed mechanism of the Lambert-Eaton Syndrome? Vesicular release of NTs is a Ca-dependent process o ...
... Neurons can contain more than on NT; they frequently contain a peptide and one of the other types of NTs What ion is critical in vesicular release of NT? How might the role of this ion explain the proposed mechanism of the Lambert-Eaton Syndrome? Vesicular release of NTs is a Ca-dependent process o ...
Psychiatry`s age of enlightenment
... cell-specific form of deep brain stimulation.19 Safe use of viral-mediated gene therapy in humans has already been established, and optogenetic manipulation of ex vivo human retinal tissue has been achieved.20 Furthermore, much effort is being directed toward developing an optogenetic toolbox design ...
... cell-specific form of deep brain stimulation.19 Safe use of viral-mediated gene therapy in humans has already been established, and optogenetic manipulation of ex vivo human retinal tissue has been achieved.20 Furthermore, much effort is being directed toward developing an optogenetic toolbox design ...
Slide 1
... Sensory- sensory receptors to CNS Motor- CNS to muscles Interneurons- Connections within CNS ...
... Sensory- sensory receptors to CNS Motor- CNS to muscles Interneurons- Connections within CNS ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... up a current that spreads out from the site of the action potential. Again, just like the graded potentials, it will decay with distance. However, if the current spreads to another site on the membrane containing voltage-gated Na+ channels and the current still has sufficient voltage to depolarize t ...
... up a current that spreads out from the site of the action potential. Again, just like the graded potentials, it will decay with distance. However, if the current spreads to another site on the membrane containing voltage-gated Na+ channels and the current still has sufficient voltage to depolarize t ...
CLASS #1: 9 Jan 2001
... arrangement, discovered by Bell and Magendie (thus the “Bell-Magendie Law”) creates a situation in which the dorsal part of the spinal cord has mainly sensory functions, whereas the ventral part has mainly motor functions. The cell soma for the the nerve fibers of the dorsal (sensory) division of ea ...
... arrangement, discovered by Bell and Magendie (thus the “Bell-Magendie Law”) creates a situation in which the dorsal part of the spinal cord has mainly sensory functions, whereas the ventral part has mainly motor functions. The cell soma for the the nerve fibers of the dorsal (sensory) division of ea ...
nerves
... Such clustering is absent in the cnidarians, the simplest animals with nervous systems. In cnidarians, a series of interconnected nerve cells form a diffuse nerve net that controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. ...
... Such clustering is absent in the cnidarians, the simplest animals with nervous systems. In cnidarians, a series of interconnected nerve cells form a diffuse nerve net that controls the contraction and expansion of the gastrovascular cavity. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... ATP E. Autonomic pathways control glands, smooth and cardiac _______ 1. The synapse between a postganglionic neuron and its target cell is called the _______________ junction a. Autonomic neuron axon terminals form bead-like strands called ________________, which lie across the target tissue b. Neur ...
... ATP E. Autonomic pathways control glands, smooth and cardiac _______ 1. The synapse between a postganglionic neuron and its target cell is called the _______________ junction a. Autonomic neuron axon terminals form bead-like strands called ________________, which lie across the target tissue b. Neur ...
A2.2.1.TheNeuron
... octopus has on average 300 billion neurons in its brain. Your neurons vary greatly in size, from as small as 4 microns to as large as nearly one meter. But, if you were to line up all the neurons in your body in a straight line, the line would be about 600 miles long. Communication within and betwee ...
... octopus has on average 300 billion neurons in its brain. Your neurons vary greatly in size, from as small as 4 microns to as large as nearly one meter. But, if you were to line up all the neurons in your body in a straight line, the line would be about 600 miles long. Communication within and betwee ...
Chapter 9 Lesson Two-Nervous System
... The central nervous system (CNS) The peripheral nervous system (PNS) central nervous system Made up of the brain and the spinal cord ...
... The central nervous system (CNS) The peripheral nervous system (PNS) central nervous system Made up of the brain and the spinal cord ...
the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
... the brain of subjects while they were shown a series of letter navons. A letter navon is a large letter composed of smaller letters as shown in the side box. The researchers soon found out that while the subjects concentrated on the small F's, the left hemisphere showed greater activity; when they f ...
... the brain of subjects while they were shown a series of letter navons. A letter navon is a large letter composed of smaller letters as shown in the side box. The researchers soon found out that while the subjects concentrated on the small F's, the left hemisphere showed greater activity; when they f ...
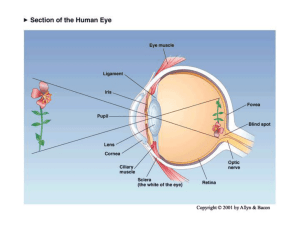
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... several different places in the brain • Each place in our visual field is represented by the activity of particular neurons in several different parts of our visual system • This map of the retina is represented and maintained in the LGN, primary visual cortex (V1), and other visual processing areas ...
... several different places in the brain • Each place in our visual field is represented by the activity of particular neurons in several different parts of our visual system • This map of the retina is represented and maintained in the LGN, primary visual cortex (V1), and other visual processing areas ...
Neurons - Noba Project
... pressure work collectively to facilitate electrochemical communication. 3. Define resting membrane potential, excitatory postsynaptic potentials, inhibitory postsynaptic potentials, and action potentials. 4. Explain the features of axonal and synaptic communication in neurons. ...
... pressure work collectively to facilitate electrochemical communication. 3. Define resting membrane potential, excitatory postsynaptic potentials, inhibitory postsynaptic potentials, and action potentials. 4. Explain the features of axonal and synaptic communication in neurons. ...
Payton
... CLASS THREE The Brain: Part One Todays Plan: 1. giving directions inside your brain 2. meninges and blood vessels 3. the cerebrospinal fluid and the ventricles 4. a development view 5. the forebrain (mammalian) Brain Diversity • brains are different shapes and size • all end with a little "tub"(aka ...
... CLASS THREE The Brain: Part One Todays Plan: 1. giving directions inside your brain 2. meninges and blood vessels 3. the cerebrospinal fluid and the ventricles 4. a development view 5. the forebrain (mammalian) Brain Diversity • brains are different shapes and size • all end with a little "tub"(aka ...
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA
... The T-type Ca2+ current of thalamocortical neurons (TC) plays a key role in different non-REM sleep waves, including slow (< 1Hz) oscillations, sleep spindles and delta oscillations (Crunelli et al., 2005). In particular, the transient opening of T-type Ca2+ channels gives rise to low threshold Ca2+ ...
... The T-type Ca2+ current of thalamocortical neurons (TC) plays a key role in different non-REM sleep waves, including slow (< 1Hz) oscillations, sleep spindles and delta oscillations (Crunelli et al., 2005). In particular, the transient opening of T-type Ca2+ channels gives rise to low threshold Ca2+ ...