Chapter 4
... This equation says that all sodium chloride that enters the solution ends up as Na1 and Cl2 ions; there are no undissociated NaCl units in solution. Table 4.1 lists examples of strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. Ionic compounds, such as sodium chloride, potassium iodide (KI ...
... This equation says that all sodium chloride that enters the solution ends up as Na1 and Cl2 ions; there are no undissociated NaCl units in solution. Table 4.1 lists examples of strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. Ionic compounds, such as sodium chloride, potassium iodide (KI ...
aq - Haverford Alchemy
... Solution Chemistry • It is helpful to pay attention to exactly what species are present in a reaction mixture (i.e., solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution). • If we are to understand reactivity, we must be aware of just what is changing during the course of a reaction. Aqueous Reactions ...
... Solution Chemistry • It is helpful to pay attention to exactly what species are present in a reaction mixture (i.e., solid, liquid, gas, aqueous solution). • If we are to understand reactivity, we must be aware of just what is changing during the course of a reaction. Aqueous Reactions ...
PDF of article
... identify a water molecule (W1) coordinated by metal 1 and activated by Thr95 as the nucleophile (Pollack et al., 1994). The mechanism would proceed via inline displacement with inversion of configuration at phosphate and the metal ion at site 2 was proposed to assist in phosphate coordination and ch ...
... identify a water molecule (W1) coordinated by metal 1 and activated by Thr95 as the nucleophile (Pollack et al., 1994). The mechanism would proceed via inline displacement with inversion of configuration at phosphate and the metal ion at site 2 was proposed to assist in phosphate coordination and ch ...
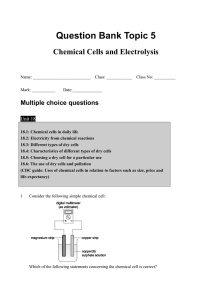
Question Bank Topic 5
... Which of the following statements concerning zinc-carbon cells are correct? (1) Used zinc-carbon cells can be disposed of in fire. (2) Zinc-carbon cells leak even though they are not in use. (3) The voltage of zinc-carbon cells drops rapidly over discharge. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2 ...
... Which of the following statements concerning zinc-carbon cells are correct? (1) Used zinc-carbon cells can be disposed of in fire. (2) Zinc-carbon cells leak even though they are not in use. (3) The voltage of zinc-carbon cells drops rapidly over discharge. A (1) and (2) only B (1) and (3) only C (2 ...
Epoxidation of α-pinene mediated by cobalt(III) catalysts
... Effect of Catalyst Concentration • The catalyst concentration was varied between 0.01mol% to 0.5mol%. • The reaction with the lowest amount of catalyst shows the highest conversion of 81.4% with a turnover frequency (TOF) of 105. ...
... Effect of Catalyst Concentration • The catalyst concentration was varied between 0.01mol% to 0.5mol%. • The reaction with the lowest amount of catalyst shows the highest conversion of 81.4% with a turnover frequency (TOF) of 105. ...
What Are the Mechanisms of Catalysis?
... concentration. (a) In specific acidbase catalysis, H+ or OHconcentration affects the reaction rate, kobs is pH-dependent, but buffers (which accept or donate H+/OH-) have no effect. (b) In general acid - base catalysis, in which an ionizable buffer may donate or accept a proton in the transition sta ...
... concentration. (a) In specific acidbase catalysis, H+ or OHconcentration affects the reaction rate, kobs is pH-dependent, but buffers (which accept or donate H+/OH-) have no effect. (b) In general acid - base catalysis, in which an ionizable buffer may donate or accept a proton in the transition sta ...
The effect of halide ions on nickel corrosion in perchloric acid solutions
... the population is estimated to be allergic to nickel. In fact the allergy is not caused by nickel itself but by the nickel salts that are formed under the effect of perspiration in contact with the piece of jewellery or watch. This phenomenon is always accompanied by the corrosion of the object. The ...
... the population is estimated to be allergic to nickel. In fact the allergy is not caused by nickel itself but by the nickel salts that are formed under the effect of perspiration in contact with the piece of jewellery or watch. This phenomenon is always accompanied by the corrosion of the object. The ...
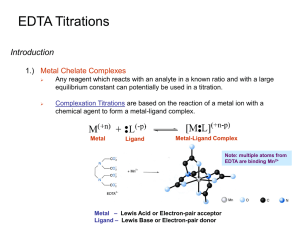
Chapter 12: EDTA Titrations - UNL
... Any reagent which reacts with an analyte in a known ratio and with a large equilibrium constant can potentially be used in a titration. ...
... Any reagent which reacts with an analyte in a known ratio and with a large equilibrium constant can potentially be used in a titration. ...
Chemistry 5560.002 and 556.003 (online sections) Inorganic
... of one to two times the “lecture” or lesson time on studying and working problems. Each student should therefore expect to spend an average of six to nine hours per week on this course (3 hours/week for the two online lessons and twice that amount or 6 hours/week for reading, studying, and working p ...
... of one to two times the “lecture” or lesson time on studying and working problems. Each student should therefore expect to spend an average of six to nine hours per week on this course (3 hours/week for the two online lessons and twice that amount or 6 hours/week for reading, studying, and working p ...
Document
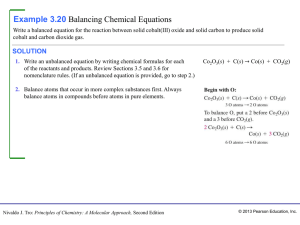
... CHECK The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydro ...
... CHECK The units of the answer are correct. The magnitude of the answer (25.8 g) is less than the initial mass of CO2 (37.8 g). This is reasonable because each carbon in CO2 has two oxygen atoms associated with it, while in C6H12O6 each carbon has only one oxygen atom associated with it and two hydro ...
Marshall Gibson Dalton Manuscript B706663E revised
... monomer concentration, as demonstrated by a linear correlation between ln{[LA]0/[LA]t} and reaction time (Figure 7). However, repeating this analysis over a range of initiator concentrations (1.4 – 3.5 x 10-2 mol l-1), revealed a non-first order dependence upon [3]. Examining the variation of rate w ...
... monomer concentration, as demonstrated by a linear correlation between ln{[LA]0/[LA]t} and reaction time (Figure 7). However, repeating this analysis over a range of initiator concentrations (1.4 – 3.5 x 10-2 mol l-1), revealed a non-first order dependence upon [3]. Examining the variation of rate w ...
TOPIC 11 Further equilibrium 11.1 Chemical equilibrium
... Acidic. NH4NO3 is a salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and a weak base (NH3). Alkaline. CH3CH2COOK is a salt of a weak acid (CH3CH2COOH) and a strong base (KOH). Neutral. NaNO3 is a salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and a strong base (NaOH). ...
... Acidic. NH4NO3 is a salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and a weak base (NH3). Alkaline. CH3CH2COOK is a salt of a weak acid (CH3CH2COOH) and a strong base (KOH). Neutral. NaNO3 is a salt of a strong acid (HNO3) and a strong base (NaOH). ...
SCH4U Exam Review
... 7. A 0.100 mol sample of formaldehyde vapour, CH2O, was placed in a heated 1.00 L vessel and some of it decomposed. The reaction is: CH2O(g) H2 (g) + CO(g) At equilibrium, the CH2O(g) concentration was 0.080 mol/L. Calculate Keq. ANS: 5.0x10-3 8. The equilibrium constant for the reaction: SO3 (g) ...
... 7. A 0.100 mol sample of formaldehyde vapour, CH2O, was placed in a heated 1.00 L vessel and some of it decomposed. The reaction is: CH2O(g) H2 (g) + CO(g) At equilibrium, the CH2O(g) concentration was 0.080 mol/L. Calculate Keq. ANS: 5.0x10-3 8. The equilibrium constant for the reaction: SO3 (g) ...
Corrosion and Corrosion Enhancers in Amine Systems
... because fewer molecules must come together at the reaction site. However, in amine solutions, the H2S concentration is low relative to HS- (Figure 1), and is dependent on pH, which can be affected by total acid gas and HSS concentrations. Sulfide on the other hand, is not likely to be in significan ...
... because fewer molecules must come together at the reaction site. However, in amine solutions, the H2S concentration is low relative to HS- (Figure 1), and is dependent on pH, which can be affected by total acid gas and HSS concentrations. Sulfide on the other hand, is not likely to be in significan ...
Complete Set
... increasing levels of CO2 will lead to increased dissolution of CaCO3 and critically affect the survival of life forms that rely on a carbonaceous skeleton. Calculate the concentrations of Ca2+ and CO32– in a saturated solution of CaCO3. (The Ksp of CaCO3 is 3.3 × 10–9.) The dissolution of CaCO3 foll ...
... increasing levels of CO2 will lead to increased dissolution of CaCO3 and critically affect the survival of life forms that rely on a carbonaceous skeleton. Calculate the concentrations of Ca2+ and CO32– in a saturated solution of CaCO3. (The Ksp of CaCO3 is 3.3 × 10–9.) The dissolution of CaCO3 foll ...
Definitions You SHould Know
... from the surroundings. The temperature decreases in an endothermic reaction. The products have weaker bonds than the reactants. Endothermic reactions have a +∆H value. The enthalpy of the products is higher than the reactants. The stability of the products is less than the reactants. ...
... from the surroundings. The temperature decreases in an endothermic reaction. The products have weaker bonds than the reactants. Endothermic reactions have a +∆H value. The enthalpy of the products is higher than the reactants. The stability of the products is less than the reactants. ...