George Mason University General Chemistry 212 Chapter 23
... rise steeply from left to right as the electrons become more difficult to remove from the poorly shielded increasing nuclear charge, i.e., no “d” electrons; thus, electrons held tighter to nucleus ● In the Transition metals, however, the first ionization energies increase relatively little because o ...
... rise steeply from left to right as the electrons become more difficult to remove from the poorly shielded increasing nuclear charge, i.e., no “d” electrons; thus, electrons held tighter to nucleus ● In the Transition metals, however, the first ionization energies increase relatively little because o ...
Coordination Compounds
... In theory, any species with a lone pair of electrons can behave as a Lewis base and donate a pair of electrons to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex or compound. The term ligand is often used to describe any species that exhibits this kind of chemistry and literally hundreds of liga ...
... In theory, any species with a lone pair of electrons can behave as a Lewis base and donate a pair of electrons to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex or compound. The term ligand is often used to describe any species that exhibits this kind of chemistry and literally hundreds of liga ...
Practical Problem I - Scheikundeolympiade
... number of moles of free fatty acid and ester present in 1.00 g of the sample. The iodine number shall be used to calculate the number of double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acid. Note: The candidate must be able to carry out the whole exam by using the delivered amount of unknown sample (12 mL). T ...
... number of moles of free fatty acid and ester present in 1.00 g of the sample. The iodine number shall be used to calculate the number of double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acid. Note: The candidate must be able to carry out the whole exam by using the delivered amount of unknown sample (12 mL). T ...
Document
... LP# 11. The reaction N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g) has a negative value of H. In what direction will the reaction shift if the temperature is increased? If the value of H is negative, the reaction is ______________. If a reaction is exothermic, it will NOT be favored by an increase in temperature. It ...
... LP# 11. The reaction N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g) has a negative value of H. In what direction will the reaction shift if the temperature is increased? If the value of H is negative, the reaction is ______________. If a reaction is exothermic, it will NOT be favored by an increase in temperature. It ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
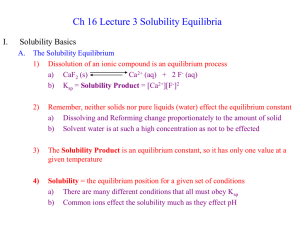
... Remember, neither solids nor pure liquids (water) effect the equilibrium constant a) Dissolving and Reforming change proportionately to the amount of solid b) Solvent water is at such a high concentration as not to be effected ...
... Remember, neither solids nor pure liquids (water) effect the equilibrium constant a) Dissolving and Reforming change proportionately to the amount of solid b) Solvent water is at such a high concentration as not to be effected ...
g moles molarity
... Example: When aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide and iron(III) nitrate are mixed, a red gelatinous precipitate forms. Calculate the mass of precipitate formed when 50.00 mL of 0.200 M NaOH and 30.00 mL of 0.125 M Fe(NO3)3 are mixed 1. Check for charge dense ions that can precipitate 2. Write a ne ...
... Example: When aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide and iron(III) nitrate are mixed, a red gelatinous precipitate forms. Calculate the mass of precipitate formed when 50.00 mL of 0.200 M NaOH and 30.00 mL of 0.125 M Fe(NO3)3 are mixed 1. Check for charge dense ions that can precipitate 2. Write a ne ...
3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 11, 13, 16, 17, 21, 22 Problems
... its normal boiling point is DvapH = 35.7 kJ/mol. The constant pressure molar heat capacities of the liquid and vapor are: Cp,m(l) = 138.7 J/mol-K and Cp,m(g) = 35.1 J/mol-K Consider the vaporization of one mole of superheated benzene at 100 oC. Calculate DSsys, DSsurr, and DSuniv for this process. S ...
... its normal boiling point is DvapH = 35.7 kJ/mol. The constant pressure molar heat capacities of the liquid and vapor are: Cp,m(l) = 138.7 J/mol-K and Cp,m(g) = 35.1 J/mol-K Consider the vaporization of one mole of superheated benzene at 100 oC. Calculate DSsys, DSsurr, and DSuniv for this process. S ...
Experimental and Simulation Results for the Removal of H2S from
... used as a renewable fuel, biogas, whose energy comes only from methane, must be purified from carbon dioxide and other impurities such as water vapor, siloxanes and hydrogen sulfide. Purification of biogas for this application particularly requires the removal of hydrogen sulfide, which negatively a ...
... used as a renewable fuel, biogas, whose energy comes only from methane, must be purified from carbon dioxide and other impurities such as water vapor, siloxanes and hydrogen sulfide. Purification of biogas for this application particularly requires the removal of hydrogen sulfide, which negatively a ...
am 06 chemistry - University of Malta
... (c) Calculate a value for the equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at 1000 K, stating its units. Kp = pp2 NH3 pp N2 x pp3 H2 deduct ½ mark if square brackets are used ...
... (c) Calculate a value for the equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction at 1000 K, stating its units. Kp = pp2 NH3 pp N2 x pp3 H2 deduct ½ mark if square brackets are used ...
cellular discrimination processes in metal accumulating cells
... these ions before it was possible to evolve aerobic metabolism (Fridovich, 1978). The association between metal ions and cells is, however, a complicated one involving a wide range of redox and ligand-binding activities. Thus, the occurrence of ferric ions is limited under physiological conditions b ...
... these ions before it was possible to evolve aerobic metabolism (Fridovich, 1978). The association between metal ions and cells is, however, a complicated one involving a wide range of redox and ligand-binding activities. Thus, the occurrence of ferric ions is limited under physiological conditions b ...
Energetics - chemistryatdulwich
... size of ion: the smaller the ion , the larger the electrostatic attraction and the more energy is needed to sublime the ions. charge of the ion: the larger the charge, the greater the electrostatic attraction. The smaller the ionic radius and the greater the charge of the ion the greater the charg ...
... size of ion: the smaller the ion , the larger the electrostatic attraction and the more energy is needed to sublime the ions. charge of the ion: the larger the charge, the greater the electrostatic attraction. The smaller the ionic radius and the greater the charge of the ion the greater the charg ...
AP CHEMISTRY COURSE SYLLABUS
... with respect to the kind of textbook used, the range and depth of topics covered, the kind of laboratory work done, and the time and effort required. The aim of this course is to provide you with the conceptual framework, factual knowledge, and analytical skills necessary to deal critically with the ...
... with respect to the kind of textbook used, the range and depth of topics covered, the kind of laboratory work done, and the time and effort required. The aim of this course is to provide you with the conceptual framework, factual knowledge, and analytical skills necessary to deal critically with the ...
Chapter 4,5,6
... 3. A 0.500 L sample of H2SO4 solution was analyzed by taking a 100.0 mL portion and adding 50.0 mL of 0.213 M NaOH. After the reaction occurred, an excess of OH- ions remained in the solution. The excess base required 13.21 mL of 0.103 M HCl for neutralization. Calculate the molarity of the original ...
... 3. A 0.500 L sample of H2SO4 solution was analyzed by taking a 100.0 mL portion and adding 50.0 mL of 0.213 M NaOH. After the reaction occurred, an excess of OH- ions remained in the solution. The excess base required 13.21 mL of 0.103 M HCl for neutralization. Calculate the molarity of the original ...
Unit 10: Solutions Text Notes from Zumdahl, Zumdahl, DeCoste
... supersaturated = more solute is staying dissolved than should 22. What happens if you add a crystal of the solid to a supersaturated solution? solid will precipitate out until the solution reaches the saturation point 23. What must we do to describe a solution completely? specify the amounts of solu ...
... supersaturated = more solute is staying dissolved than should 22. What happens if you add a crystal of the solid to a supersaturated solution? solid will precipitate out until the solution reaches the saturation point 23. What must we do to describe a solution completely? specify the amounts of solu ...
lecture 9 nucl_electro_add_abs
... toward nucleophilic attack at carbon than is the CO trans to the weak ‐acid PPh3. Unfortunately, the amine formed can sometimes coordinate to the metal. A second problem with the method is that successive carbonyls become harder and harder to remove as the back bonding to the remaining CO group ...
... toward nucleophilic attack at carbon than is the CO trans to the weak ‐acid PPh3. Unfortunately, the amine formed can sometimes coordinate to the metal. A second problem with the method is that successive carbonyls become harder and harder to remove as the back bonding to the remaining CO group ...