Peripheral nervous system
... • Na+ gates open first, before K+ gates • Na+ enters cell (depolarization) >> K+ exits cell (repolarization) >> possible undershoot if K+ channels stay open (hyperpolarization) • cannot combine w/ other action potentials • either occurs completely or none at all • can depolarize another area of the ...
... • Na+ gates open first, before K+ gates • Na+ enters cell (depolarization) >> K+ exits cell (repolarization) >> possible undershoot if K+ channels stay open (hyperpolarization) • cannot combine w/ other action potentials • either occurs completely or none at all • can depolarize another area of the ...
The Nervous System
... – causes partial depolarization bringing neuron closer to firing – one EPSP is probably too weak to trigger an action potential – EPSPs can be added together (summation) – results in firing of neuron ...
... – causes partial depolarization bringing neuron closer to firing – one EPSP is probably too weak to trigger an action potential – EPSPs can be added together (summation) – results in firing of neuron ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 20. At the beginning of an impulse, the ___ gates open. 21. Action Potential is another name for a (an) ___. 22. A(n) __ is an automatic response to a stimulus. 23 Subdivision of the PNS that regulates the activity of the heart and smooth muscle and of glands; also called the involuntary nervous sys ...
... 20. At the beginning of an impulse, the ___ gates open. 21. Action Potential is another name for a (an) ___. 22. A(n) __ is an automatic response to a stimulus. 23 Subdivision of the PNS that regulates the activity of the heart and smooth muscle and of glands; also called the involuntary nervous sys ...
1050927abstract
... place activity is formed or altered when animals learn to recognize new environments or experience any changes in familiar environments. Using whole-cell patch clamp in freely moving rats, we found that spatially homogenous current injection to a silent hippocampal neuron leads to spatially tuned su ...
... place activity is formed or altered when animals learn to recognize new environments or experience any changes in familiar environments. Using whole-cell patch clamp in freely moving rats, we found that spatially homogenous current injection to a silent hippocampal neuron leads to spatially tuned su ...
Excitatory_Inhibitory_Neural_Network_1
... Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected network comprised of a large number of excitatory ...
... Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected network comprised of a large number of excitatory ...
Maximum entropy modeling of multi-neuron firing patterns in V1
... Understanding the activity of a network of neurons is challenging due to the exponential growth in potential interactions as the network size increases. In the visual cortex, the firing activity of pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of the ...
... Understanding the activity of a network of neurons is challenging due to the exponential growth in potential interactions as the network size increases. In the visual cortex, the firing activity of pairs of neurons is correlated over a few tens of milliseconds, but the source and significance of the ...
ch 48 clicker questions
... conduction velocity for moving action potentials is likely seen in a) a large-diameter, nonmyelinated axon. b) a small-diameter, nonmyelinated axon. c) A myelinated axon. d) any of the above, as all neurons conduct action potentials at the same speed. ...
... conduction velocity for moving action potentials is likely seen in a) a large-diameter, nonmyelinated axon. b) a small-diameter, nonmyelinated axon. c) A myelinated axon. d) any of the above, as all neurons conduct action potentials at the same speed. ...
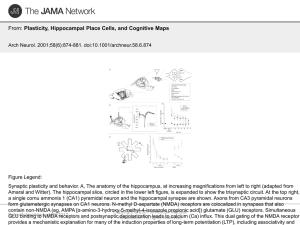
Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
... Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) pyramidal neuron and the hippocampal synapse are shown. Axons from CA3 pyramidal neurons form glutamatergic synapses on CA1 neuro ...
... Amaral and Witter). The hippocampal slice, circled in the lower left figure, is expanded to show the trisynaptic circuit. At the top right, a single cornu ammonis 1 (CA1) pyramidal neuron and the hippocampal synapse are shown. Axons from CA3 pyramidal neurons form glutamatergic synapses on CA1 neuro ...
Neuroscience & Behavior
... electrical signal called the Action Potential. Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell. When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons. ...
... electrical signal called the Action Potential. Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell. When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons. ...
Frontiers in , Ph.D. Pharmacology Proudly Presents
... The electrical properties of neurons depend not only on the types of ion channels and receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localiz ...
... The electrical properties of neurons depend not only on the types of ion channels and receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localiz ...
31.1 The Neuron
... open at the beginning of the axon and the internal cell environment become positive. This sends the nerve impulse down the axon to the axon terminals. ...
... open at the beginning of the axon and the internal cell environment become positive. This sends the nerve impulse down the axon to the axon terminals. ...
Threshold Stimulus
... propagation of the action potential • Blocks _______ channels • Sodium cannot flow into the cell, so threshold is not achieved ...
... propagation of the action potential • Blocks _______ channels • Sodium cannot flow into the cell, so threshold is not achieved ...
Slide ()
... A. Noradrenergic neurons (A groups) and adrenergic neurons (C groups) are located in the medulla and pons (shaded). The A2 and C2 groups in the Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available dorsal medulla ...
... A. Noradrenergic neurons (A groups) and adrenergic neurons (C groups) are located in the medulla and pons (shaded). The A2 and C2 groups in the Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available dorsal medulla ...
Slide ()
... A. Noradrenergic neurons (A groups) and adrenergic neurons (C groups) are located in the medulla and pons (shaded). The A2 and C2 groups in the Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available dorsal medulla ...
... A. Noradrenergic neurons (A groups) and adrenergic neurons (C groups) are located in the medulla and pons (shaded). The A2 and C2 groups in the Citation: Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM, Siegelbaum SA, Hudspeth AJ, Mack S. Principles of Neural Science, Fifth Editon; 2012 Available dorsal medulla ...
Abstract View ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERSION USING RECURRENT SPIKING NEURAL NETWORKS ;
... which would allow the transmission of information with large bandwidths despite the slow and imprecise characteristics of individual neurons and synapses. Simulations using integrate-and-fire neurons in simple networks, first with global inhibitory feedback and then with both inhibitory and excitato ...
... which would allow the transmission of information with large bandwidths despite the slow and imprecise characteristics of individual neurons and synapses. Simulations using integrate-and-fire neurons in simple networks, first with global inhibitory feedback and then with both inhibitory and excitato ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... The left hemisphere is usually called the categorical hemisphere. The left hemisphere contains the general interpretive and speech centers, and is specialized for language abilities as well as analytical and reasoning tasks. The other hemisphere, usually the right, is called the representational hem ...
... The left hemisphere is usually called the categorical hemisphere. The left hemisphere contains the general interpretive and speech centers, and is specialized for language abilities as well as analytical and reasoning tasks. The other hemisphere, usually the right, is called the representational hem ...
Chapter 39
... A. A synapse may occur between neurons or a neuron and a muscle cell 1. The neuron that ends at the synapse is the presynaptic neuron; the neuron that begins at a synapse is the postsynaptic neuron 2. Signals across synapses can be electrical or chemical a) Electrical synapses involve very close con ...
... A. A synapse may occur between neurons or a neuron and a muscle cell 1. The neuron that ends at the synapse is the presynaptic neuron; the neuron that begins at a synapse is the postsynaptic neuron 2. Signals across synapses can be electrical or chemical a) Electrical synapses involve very close con ...
Bump attractors and the homogeneity assumption
... • The input to the SAM cells are determined by a comparison of the output of the output cells to the output of the input cells ...
... • The input to the SAM cells are determined by a comparison of the output of the output cells to the output of the input cells ...
Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Action Potential: brief electrical charge that travels down an axon Refractory Period: period of inactivity after a neuron has fired Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse All-or-none response: neuron’s reaction of either firing (with full strength) or not firing at all ...
... Action Potential: brief electrical charge that travels down an axon Refractory Period: period of inactivity after a neuron has fired Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse All-or-none response: neuron’s reaction of either firing (with full strength) or not firing at all ...
Neurons
... • Neurons don’t touch – Synapse = millionth inch gap – In synapse = vesicles w/ neurotransmitters » Chemical messengers that transmit info ...
... • Neurons don’t touch – Synapse = millionth inch gap – In synapse = vesicles w/ neurotransmitters » Chemical messengers that transmit info ...
Answer Key
... 14. For you to be able to run, ________ must relay messages from your central nervous system to your leg muscles. A) interneurons B) agonists C) motor neurons D) sensory neurons E) the autonomic nervous system ...
... 14. For you to be able to run, ________ must relay messages from your central nervous system to your leg muscles. A) interneurons B) agonists C) motor neurons D) sensory neurons E) the autonomic nervous system ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.