Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... Synapse - a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal but ...
... Synapse - a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal but ...
KKDP 3: The role of the neuron (dendrites, axon, myelin and
... dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of other neurons. When the dendrites receive information from other neurons, they pass it on to the neuron’s soma (cell body) where it is integrated. The soma may collect and integrate information from thousands of other neurons. Once the incoming informatio ...
... dozens, hundreds, or even thousands of other neurons. When the dendrites receive information from other neurons, they pass it on to the neuron’s soma (cell body) where it is integrated. The soma may collect and integrate information from thousands of other neurons. Once the incoming informatio ...
Slide ()
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
Slide ()
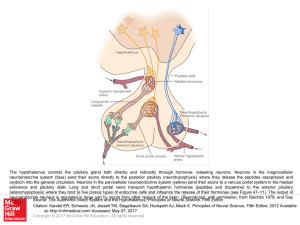
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
ntro to Nervous system study guide
... 1. What is the function of the nervous system? What other system has this same function? What is the difference between them? ...
... 1. What is the function of the nervous system? What other system has this same function? What is the difference between them? ...
List of vocabulary used in understanding the nervous
... e. Students know the roles of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation, thought, and response. An individual becomes aware of the environment through the sense organs and other body receptors (e.g., by allowing for touch, taste, and smell and by collecting information about temp ...
... e. Students know the roles of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons in sensation, thought, and response. An individual becomes aware of the environment through the sense organs and other body receptors (e.g., by allowing for touch, taste, and smell and by collecting information about temp ...
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (Ach) transmitter plays a role in
... Excitatory – excite the next cell into firing. Inhibitory – inhibit the next cell from firing. If excitatory signals exceed inhibitory signals the combined signals trigger an action potential. Threshold – the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse. *Increasing the level of sti ...
... Excitatory – excite the next cell into firing. Inhibitory – inhibit the next cell from firing. If excitatory signals exceed inhibitory signals the combined signals trigger an action potential. Threshold – the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse. *Increasing the level of sti ...
AP Biology Animal Form and Function
... another kind of gated channel opens, this time allowing the K+ on the inside to rush out of the cell. The movement of K+ out of the cell causes repolarization by restoring the original membrane polarization (a condition where it is once again more negative inside the cell) Unlike the resting potenti ...
... another kind of gated channel opens, this time allowing the K+ on the inside to rush out of the cell. The movement of K+ out of the cell causes repolarization by restoring the original membrane polarization (a condition where it is once again more negative inside the cell) Unlike the resting potenti ...
Nervous System
... As Na+ goes into cell, neuron goes from being polarized to depolarized When inside becomes positive, polarization is removed and the threshold is reached K+ ions move outside, Na+ ions stay inside membrane Refractory period returns everything ...
... As Na+ goes into cell, neuron goes from being polarized to depolarized When inside becomes positive, polarization is removed and the threshold is reached K+ ions move outside, Na+ ions stay inside membrane Refractory period returns everything ...
RAPID REVIEW The nervous system is made up of a complex
... neurotransmitter and has been linked with sleep, mood, and appetite. Low levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine have been found to cause Parkinson’s disease and increased levels of dopamine have been linked to the psychological disorder known as schizophrenia. Endorphin is a special neurotransmitte ...
... neurotransmitter and has been linked with sleep, mood, and appetite. Low levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine have been found to cause Parkinson’s disease and increased levels of dopamine have been linked to the psychological disorder known as schizophrenia. Endorphin is a special neurotransmitte ...
Nervous System Lecture Notes Page
... Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
... Repolarization Required before another Action Potential Sodium-Potassium Pump moves Na+ out & K+ in (Requires Energy) ...
Chapter Four
... outside of the membrane is positively charged (and the inside is negatively charged) because the axon contains ions. When the axon is resting, its ion channels are closed, so ions cannot move in or out of the axon. An action potential is caused by the opening of some ion channels in the membrane at ...
... outside of the membrane is positively charged (and the inside is negatively charged) because the axon contains ions. When the axon is resting, its ion channels are closed, so ions cannot move in or out of the axon. An action potential is caused by the opening of some ion channels in the membrane at ...
Nervous System
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
... Uses hormones that travel through the bloodstream. Takes longer to get there but lasts a long time ...
Slide 1
... spinal cord. The excitatory reticulospinal tract also operates as the muscle-tone excitatory system as well as the coerulospinal tract from the locus coeruleus (LC) and raphespinal tract from the raphe nuclei (RN). Signals from the SLR and those from the CLR activate the rhythm-generating system to ...
... spinal cord. The excitatory reticulospinal tract also operates as the muscle-tone excitatory system as well as the coerulospinal tract from the locus coeruleus (LC) and raphespinal tract from the raphe nuclei (RN). Signals from the SLR and those from the CLR activate the rhythm-generating system to ...
The Nervous System
... • Sensory neurons send messages about your body or environment to the spinal cord up to the brain for interpretation. ...
... • Sensory neurons send messages about your body or environment to the spinal cord up to the brain for interpretation. ...
The Nervous System - chemistrywithmrsmorton
... Neuron Function 1. Irritability: ability to respond to stimulus & convert to nerve impulse 2. Conductivity: transmit impulse to other neurons, muscles, or glands ...
... Neuron Function 1. Irritability: ability to respond to stimulus & convert to nerve impulse 2. Conductivity: transmit impulse to other neurons, muscles, or glands ...
THE BRAIN The brain can be divided into three main regions
... sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating sensory processes, such as vision and hearing. An important system of dopamine-releasing neurons that projects into various higher brain centers origin ...
... sense of equilibrium. One of the structures first depressed by alcohol. MIDBRAIN 1. The midbrain contains an area that is concerned with integrating sensory processes, such as vision and hearing. An important system of dopamine-releasing neurons that projects into various higher brain centers origin ...
Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the
... identify when exactly and in which type of neurons Runx1t1is expressed in the developing dorsal root ganglion. My results show that the expression of Runx1t1 is very strong during embryonic development, at a time when different types of neurons are being specified. In the future, we are planning to ...
... identify when exactly and in which type of neurons Runx1t1is expressed in the developing dorsal root ganglion. My results show that the expression of Runx1t1 is very strong during embryonic development, at a time when different types of neurons are being specified. In the future, we are planning to ...
Nerve Impulses - manorlakesscience
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...
... change in the charge across the axon membrane. A nerve impulse is a wave of electrical change (an action potential) that passes rapidly along an axon. After the nerve impulse has been transmitted – the distribution of ions across the cell membrane is restored. ...
Slide ()
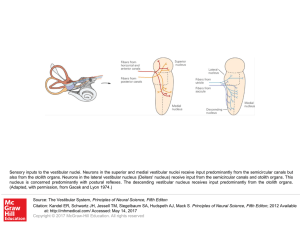
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
... Sensory inputs to the vestibular nuclei. Neurons in the superior and medial vestibular nuclei receive input predominantly from the semicircular canals but also from the otolith organs. Neurons in the lateral vestibular nucleus (Deiters' nucleus) receive input from the semicircular canals and otolith ...
2016-2017_1stSemester_Exam1_050117_final_solution
... inform neurons located in the……posterior horn.….... . The projecting neurons convey the information to the subcortical processing center via the crossed ………........ ……spinothalamic tract……………… . The organism protects itself from harmful stimuli by the ….…crossed flexor reflex……………………which is ……multi ...
... inform neurons located in the……posterior horn.….... . The projecting neurons convey the information to the subcortical processing center via the crossed ………........ ……spinothalamic tract……………… . The organism protects itself from harmful stimuli by the ….…crossed flexor reflex……………………which is ……multi ...
Acetylcholinesterase in Neuron Survival and
... hardly any Regeneration happens at CNS! Result = neuron loss, functional impairment for rest of the life Each year 10,000 new spinal cord injury occurs in USA ...
... hardly any Regeneration happens at CNS! Result = neuron loss, functional impairment for rest of the life Each year 10,000 new spinal cord injury occurs in USA ...
Biological Impact
... • Agonists mimic the neurotransmitter by binding to the receptor sites just as the neurotransmitters do and having the same effect on the receiving neuron. Agonists are used when it is believed that there is not enough neurotransmitter • Antagonists BLOCK the neurotransmitter by binding to the recep ...
... • Agonists mimic the neurotransmitter by binding to the receptor sites just as the neurotransmitters do and having the same effect on the receiving neuron. Agonists are used when it is believed that there is not enough neurotransmitter • Antagonists BLOCK the neurotransmitter by binding to the recep ...
For electrical signaling
... type of ion to pass through them) Some channels are not so selective, and in this case the potential E is estimated by the Goldman equation Reversal potentials takes a value intermediate between the equilibrium potentials of the individual ion types that it conducts ...
... type of ion to pass through them) Some channels are not so selective, and in this case the potential E is estimated by the Goldman equation Reversal potentials takes a value intermediate between the equilibrium potentials of the individual ion types that it conducts ...
NERVES
... Neurons also have gated ion channels, which open or close in response to three kinds of stimuli.. › Stretch-gated ion channels- are found in cells that sense stretch and open when the membrane is mechanically deformed › Ligand-gated ion channels are found at synapses and open or close when a specifi ...
... Neurons also have gated ion channels, which open or close in response to three kinds of stimuli.. › Stretch-gated ion channels- are found in cells that sense stretch and open when the membrane is mechanically deformed › Ligand-gated ion channels are found at synapses and open or close when a specifi ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.