Slide 1
... • The spinal cord level. – more than just a conduit for signals from periphery of body to brain and vice versa. – cord contains: • walking circuits. • reflexes circuits. ...
... • The spinal cord level. – more than just a conduit for signals from periphery of body to brain and vice versa. – cord contains: • walking circuits. • reflexes circuits. ...
slides
... mapping position in the environment by path integration: ‘grid cells’ – neurons of the medial entorhinal cortex exhibit multiple firing fields in any given environment – such fields are arranged according to the nodes of a set of ‘tesselated’ triangles – grids, like head-direction tuning and place ...
... mapping position in the environment by path integration: ‘grid cells’ – neurons of the medial entorhinal cortex exhibit multiple firing fields in any given environment – such fields are arranged according to the nodes of a set of ‘tesselated’ triangles – grids, like head-direction tuning and place ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters
... different neurons allowing the message from one to be multiplied very quickly by sending it to many other neurons. ...
... different neurons allowing the message from one to be multiplied very quickly by sending it to many other neurons. ...
File - BHS AP Psychology
... travel within neurons during neural transmission and that in order to “fire” a neuron must meet the threshold to begin the action potential sending a chemical signal in a chain reaction down the neurons axon. __________ Point 7: Myelin Sheath: Students should explain that neural messages will be tra ...
... travel within neurons during neural transmission and that in order to “fire” a neuron must meet the threshold to begin the action potential sending a chemical signal in a chain reaction down the neurons axon. __________ Point 7: Myelin Sheath: Students should explain that neural messages will be tra ...
Objectives included for the test File
... by relay neurons, and from the CNS to effectors by motor neurons. Define resting potential and action potential (depolarization and repolarization). Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a non-myelinated neuron. Include the movement of Na+ and K+ ions to create a resting potential and an action p ...
... by relay neurons, and from the CNS to effectors by motor neurons. Define resting potential and action potential (depolarization and repolarization). Explain how a nerve impulse passes along a non-myelinated neuron. Include the movement of Na+ and K+ ions to create a resting potential and an action p ...
The basic unit of computation - Zador Lab
... more general models of network computation14–16, and it has been rigorously proven that such networks can implement a very rich class of computations17. Common to all these models is the notion that synapses do more than just provide a substrate for the long-lasting changes underlying learning and m ...
... more general models of network computation14–16, and it has been rigorously proven that such networks can implement a very rich class of computations17. Common to all these models is the notion that synapses do more than just provide a substrate for the long-lasting changes underlying learning and m ...
Nervous System Notes
... amplitude, action potentials are all-or-none 2. Duration – graded potentials are much longer (several milliseconds to several minutes) than action potentials (1/2 to 2 milliseconds) 3. Channels – graded use chemically, mechanically and light gated ion channels, action potentials use voltage gated ch ...
... amplitude, action potentials are all-or-none 2. Duration – graded potentials are much longer (several milliseconds to several minutes) than action potentials (1/2 to 2 milliseconds) 3. Channels – graded use chemically, mechanically and light gated ion channels, action potentials use voltage gated ch ...
Lecture Outline ()
... The Discovery of Neurotransmitters • Histological observations revealed a 20 to 40 nm gap between neurons (synaptic cleft) • Otto Loewi (1873-1961) first to demonstrate function of neurotransmitters at chemical synapse – flooded exposed hearts of 2 frogs with saline – stimulated vagus nerve of one ...
... The Discovery of Neurotransmitters • Histological observations revealed a 20 to 40 nm gap between neurons (synaptic cleft) • Otto Loewi (1873-1961) first to demonstrate function of neurotransmitters at chemical synapse – flooded exposed hearts of 2 frogs with saline – stimulated vagus nerve of one ...
Nolte – Chapter 1 (Introduction to the Nervous
... o Microfilaments anchor membrane molecules in place (receptor molecules at synapses) o Transport away from the soma is termed anterograde Kinesin moves things this way o Transport towards the soma is termed retrograde. Dynein moves things this way. o Transport can be slow or fast o Tubulin ...
... o Microfilaments anchor membrane molecules in place (receptor molecules at synapses) o Transport away from the soma is termed anterograde Kinesin moves things this way o Transport towards the soma is termed retrograde. Dynein moves things this way. o Transport can be slow or fast o Tubulin ...
CHAPTER 28 Nervous Systems
... – Sensory input: receptors-structures specialized to detect certain stimuli – Integration: through the spinal cord & brain – Motor output: effectors-respond to a stimulus such as muscles or glands ...
... – Sensory input: receptors-structures specialized to detect certain stimuli – Integration: through the spinal cord & brain – Motor output: effectors-respond to a stimulus such as muscles or glands ...
Neurotransmitters
... Dilaudid, Demerol, Codeine But can also cause pain if taken over a long period of time ...
... Dilaudid, Demerol, Codeine But can also cause pain if taken over a long period of time ...
Sensing the Environment
... Smells are detected by receptor neurons in our nose. Each receptor is sensitive to a different chemical ...
... Smells are detected by receptor neurons in our nose. Each receptor is sensitive to a different chemical ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 8. All cells have a membrane potential across their plasma membrane. What is the typical resting potential of a neuron? 9. Draw Figure 48.7. Label the outside cell, inside cell, Na+ ions, K+ ions, and the three proteins imbedded in the cell membrane. 10. How are the concentration gradients of Na+ an ...
... 8. All cells have a membrane potential across their plasma membrane. What is the typical resting potential of a neuron? 9. Draw Figure 48.7. Label the outside cell, inside cell, Na+ ions, K+ ions, and the three proteins imbedded in the cell membrane. 10. How are the concentration gradients of Na+ an ...
Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Reading Guide 48.1
... 8. All cells have a membrane potential across their plasma membrane. What is the typical resting potential of a neuron? 9. Draw Figure 48.7. Label the outside cell, inside cell, Na+ ions, K+ ions, and the three proteins imbedded in the cell membrane. 10. How are the concentration gradients of Na+ an ...
... 8. All cells have a membrane potential across their plasma membrane. What is the typical resting potential of a neuron? 9. Draw Figure 48.7. Label the outside cell, inside cell, Na+ ions, K+ ions, and the three proteins imbedded in the cell membrane. 10. How are the concentration gradients of Na+ an ...
Nervous System
... visceral organs and fibers, and smaller somatic fibers. Thin myelin sheaths. Velocity: 15 m/s Group C: autonomic nervous system. Found in visceral organs and fibers, and smaller somatic fibers. Smallest diameter axon, and are unmyelinated. Velocity: 1 m/s. ...
... visceral organs and fibers, and smaller somatic fibers. Thin myelin sheaths. Velocity: 15 m/s Group C: autonomic nervous system. Found in visceral organs and fibers, and smaller somatic fibers. Smallest diameter axon, and are unmyelinated. Velocity: 1 m/s. ...
The brain is the body`s most complex organ. Neurons communicate
... The brain is organized to recognize sensations, initiate behaviors, and store and access memories that can last a lifetime. ...
... The brain is organized to recognize sensations, initiate behaviors, and store and access memories that can last a lifetime. ...
nervous system ppt
... their roles. This causes a massive flood of serotonin from the brain cells into the synapse. ...
... their roles. This causes a massive flood of serotonin from the brain cells into the synapse. ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... The electrical component of neural communication is captured in the action potential ...
... The electrical component of neural communication is captured in the action potential ...
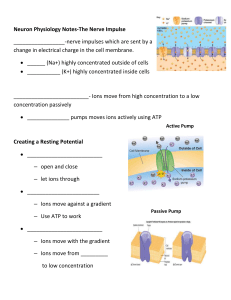
Neuron Physiology Notes
... 1) Neuron at “resting membrane potential” is polarized with a resting potential of (-70 mv) 2.) Neuron is stimulated by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters ...
... 1) Neuron at “resting membrane potential” is polarized with a resting potential of (-70 mv) 2.) Neuron is stimulated by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters ...
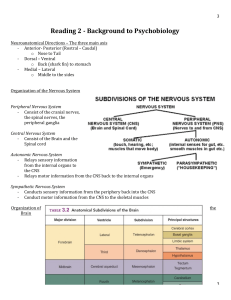
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matter mostly consist of axons o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnected (subcortical and cerebral cortex/different area ...
... - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matter mostly consist of axons o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnected (subcortical and cerebral cortex/different area ...
Neuron Structure
... FYI: Chocolate & the Nervous System • In 1502 Columbus seized the contents of a canoe and brought it back to Spain, this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as ...
... FYI: Chocolate & the Nervous System • In 1502 Columbus seized the contents of a canoe and brought it back to Spain, this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as ...
Nervous - Lamont High
... FYI: Chocolate & the Nervous System • In 1502 Columbus seized the contents of a canoe and brought it back to Spain, this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as ...
... FYI: Chocolate & the Nervous System • In 1502 Columbus seized the contents of a canoe and brought it back to Spain, this was cacao beans from the tree Cacao theobroma • Chocolate causes brain to produce natural opiates • Opiates produce feelings of euphoria, dull pain • 3 substances in choc act as ...
Nervous System Notes Outline
... 13. Name 3 structurally different neurons. 1. _______________ – one input (dendrite), one output (axon); eyes, nose, ears 2. _______________ – one output with 2 branches (fused dendrites and axon); most ___________ neurons of ________ 3. _______________ – many inputs (dendrites), one output (axon); ...
... 13. Name 3 structurally different neurons. 1. _______________ – one input (dendrite), one output (axon); eyes, nose, ears 2. _______________ – one output with 2 branches (fused dendrites and axon); most ___________ neurons of ________ 3. _______________ – many inputs (dendrites), one output (axon); ...
Nervous System - Downey Unified School District
... NERVOUS SYSTEM CONTINUED • 2. THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM IS THE SYSTEM THAT INFLUENCES THE FUNCTIONAL OF INTERNAL ORGANS. ANS HAS 2 BRANCHES: THE SYMPATHEIC NERVOUS SYSTEM IS ONE AND IS RESPONSIBLE FOR THE FIGHT-OR-FLIGHT RESPONSE IN THE BODY. THE SECOND IS THE PARASYMPATHEIC WHICH IS RESPONSIBLE ...
... NERVOUS SYSTEM CONTINUED • 2. THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM IS THE SYSTEM THAT INFLUENCES THE FUNCTIONAL OF INTERNAL ORGANS. ANS HAS 2 BRANCHES: THE SYMPATHEIC NERVOUS SYSTEM IS ONE AND IS RESPONSIBLE FOR THE FIGHT-OR-FLIGHT RESPONSE IN THE BODY. THE SECOND IS THE PARASYMPATHEIC WHICH IS RESPONSIBLE ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.