Exam 2-SG suggested answers (2010)
... binocular neurons below the level of the cortex, while auditory pathways from from the two ears are extensively crossed, so cells at all levels above the cochlear nuclei are binaural, i.e. they receive inputs from both ears. 4. Photoreceptors that synapse onto ‘off’-center bipolars release depolariz ...
... binocular neurons below the level of the cortex, while auditory pathways from from the two ears are extensively crossed, so cells at all levels above the cochlear nuclei are binaural, i.e. they receive inputs from both ears. 4. Photoreceptors that synapse onto ‘off’-center bipolars release depolariz ...
Stereological estimates of neuronal loss in the primary motor cortex
... Introduction Whilst inflammatory demyelination (ID) is an important feature in the clinical and pathological diagnosis of MS, evidence suggests mechanisms other than ID may play an important role for the deterioration of function in people with progressive MS (pwPMS) (Trapp & Nave. Annu Rev Neurosci ...
... Introduction Whilst inflammatory demyelination (ID) is an important feature in the clinical and pathological diagnosis of MS, evidence suggests mechanisms other than ID may play an important role for the deterioration of function in people with progressive MS (pwPMS) (Trapp & Nave. Annu Rev Neurosci ...
Chapter 12-13 Summary
... A nerve impulse is an electrochemical event (initiated by various stimuli) that cause a change in neural plasma membrane permeability. This change allows sodium ions to enter the cell, causing depolarization. Once begun the action potential or nerve impulse continues over the entire surface of the a ...
... A nerve impulse is an electrochemical event (initiated by various stimuli) that cause a change in neural plasma membrane permeability. This change allows sodium ions to enter the cell, causing depolarization. Once begun the action potential or nerve impulse continues over the entire surface of the a ...
Biology 30: Unit A - County Central High School
... closely at the membrane, we see that there is a high concentration of sodium (Na+) outside the membrane and a high concentration of potassium (K+) inside the membrane ...
... closely at the membrane, we see that there is a high concentration of sodium (Na+) outside the membrane and a high concentration of potassium (K+) inside the membrane ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... How neurons communicate • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... How neurons communicate • Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential • Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell • When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
Chapter 16
... cholingeric (nicotinic or muscarinic), they generally excitatory (sm. muscles), but can be inhibitory (heart). – There are other neurotransmitters of ANS, such as, fatty acids like prostaglandins and peptides such as, gastrin, somatostatin, dopamine, etc… ...
... cholingeric (nicotinic or muscarinic), they generally excitatory (sm. muscles), but can be inhibitory (heart). – There are other neurotransmitters of ANS, such as, fatty acids like prostaglandins and peptides such as, gastrin, somatostatin, dopamine, etc… ...
The Nervous System
... • Typically, a single synaptic interaction will not create a graded depolarization strong enough to migrate to the axon hillock and induce the firing of an AP. – However, a graded depolarization will bring the neuronal VM closer to threshold. Thus, it’s often referred to as an excitatory postsynapti ...
... • Typically, a single synaptic interaction will not create a graded depolarization strong enough to migrate to the axon hillock and induce the firing of an AP. – However, a graded depolarization will bring the neuronal VM closer to threshold. Thus, it’s often referred to as an excitatory postsynapti ...
The nervous system
... Although the brain is only about 2% of the total body weight in humans, it receives 15-20% of the body's blood supply. Because brain cells will die if the supply of blood which carries oxygen is stopped, the brain has top priority for the blood. Even if other organs need blood, the body attempts to ...
... Although the brain is only about 2% of the total body weight in humans, it receives 15-20% of the body's blood supply. Because brain cells will die if the supply of blood which carries oxygen is stopped, the brain has top priority for the blood. Even if other organs need blood, the body attempts to ...
Neural Mechanism of Language
... model supported by existing evidences. Firstly, we briefly introduce this model in this paper, and then we explain the neural mechanism of language and reasoning with it. Moreover, we find that the position of an area determines its importance. Specifically, language relevant areas are in the capita ...
... model supported by existing evidences. Firstly, we briefly introduce this model in this paper, and then we explain the neural mechanism of language and reasoning with it. Moreover, we find that the position of an area determines its importance. Specifically, language relevant areas are in the capita ...
Nervous System - s3.amazonaws.com
... Threshold Level – minimum level of stimulus required to produce a response (action potential) Stimulus ...
... Threshold Level – minimum level of stimulus required to produce a response (action potential) Stimulus ...
Physiolgy of the nervous system
... - Propagation of nerve impulse is executed by repeating the conversion from polarization to depolarization in the next site of nerve. - the previous site is returned to the resting state (polarization). - Conductivity or transmission is exerted electrically alongside neuron and chemically when nerv ...
... - Propagation of nerve impulse is executed by repeating the conversion from polarization to depolarization in the next site of nerve. - the previous site is returned to the resting state (polarization). - Conductivity or transmission is exerted electrically alongside neuron and chemically when nerv ...
Spinal Cord
... Specific Ascending Pathways Stretch & fine touch impulses 1st order bundled in posterior tracts Pelvic level in gracilis Pectoral level in cuneatus Decussate in medulla into medial lemniscal tract Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st ...
... Specific Ascending Pathways Stretch & fine touch impulses 1st order bundled in posterior tracts Pelvic level in gracilis Pectoral level in cuneatus Decussate in medulla into medial lemniscal tract Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st ...
The Nervous System
... Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Figure 48.10 Propagation of the action potential Figure 48.11 Saltatory conduction ...
... Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Figure 48.10 Propagation of the action potential Figure 48.11 Saltatory conduction ...
Document
... This changes the polarity slightly If the stimulus is strong enough to bring the inside to about -55 mv, a THRESHOLD has been reached. Once this occurs, the sodium channels immediately open wide and potassium channels close. ...
... This changes the polarity slightly If the stimulus is strong enough to bring the inside to about -55 mv, a THRESHOLD has been reached. Once this occurs, the sodium channels immediately open wide and potassium channels close. ...
Neurotransmitters
... the information about "heat" travels from your hand on the sensory neurons, to the Interneurons where it is brought to the appropriate brain region to process the information (now you know it is "hot") and make a decision about a corresponding action (too hot, let's move the hand). The information t ...
... the information about "heat" travels from your hand on the sensory neurons, to the Interneurons where it is brought to the appropriate brain region to process the information (now you know it is "hot") and make a decision about a corresponding action (too hot, let's move the hand). The information t ...
Test Question 1 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive
... AW: Signal strength represents H+ concentration. Signal frequency is determined by the specific local magnetic field strength. With frequency encoding or phase encoding the spatial origin of the signal can be determined in a 2-dimensional plane It is also possible to measure increased local neural a ...
... AW: Signal strength represents H+ concentration. Signal frequency is determined by the specific local magnetic field strength. With frequency encoding or phase encoding the spatial origin of the signal can be determined in a 2-dimensional plane It is also possible to measure increased local neural a ...
Nervous SystemHppt
... » As long as the nerve cell remains undisturbed or the charges do not change it will remain in a resting potential state. ...
... » As long as the nerve cell remains undisturbed or the charges do not change it will remain in a resting potential state. ...
Physiology
... response to a certain stimulus by coupling the stimulus to another intense (usually painful) stimulus (fig.2-1). The terminal which conducts the intense or painful stimulus is called a facilitator terminal which relays on the presynaptic sensory terminal. The facilitator terminal stimulates the pres ...
... response to a certain stimulus by coupling the stimulus to another intense (usually painful) stimulus (fig.2-1). The terminal which conducts the intense or painful stimulus is called a facilitator terminal which relays on the presynaptic sensory terminal. The facilitator terminal stimulates the pres ...
lec12
... • Every atomic vector and every association is stored in the clean-up memory. – The memory can take a degraded vector and return the closest stored vector, plus a goodness of fit. – It needs to be a matrix memory (or something similar) that can store many different vectors accurately. • Each time a ...
... • Every atomic vector and every association is stored in the clean-up memory. – The memory can take a degraded vector and return the closest stored vector, plus a goodness of fit. – It needs to be a matrix memory (or something similar) that can store many different vectors accurately. • Each time a ...
chapter29_Sections 6
... • Action potentials occur only at nodes, where there are gated ion channels and no myelin • After an action potential occurs at a node, positive ions diffuse quickly through the cytoplasm to the next node because myelin prevents them from leaking out across the membrane • Arrival of positive ions at ...
... • Action potentials occur only at nodes, where there are gated ion channels and no myelin • After an action potential occurs at a node, positive ions diffuse quickly through the cytoplasm to the next node because myelin prevents them from leaking out across the membrane • Arrival of positive ions at ...
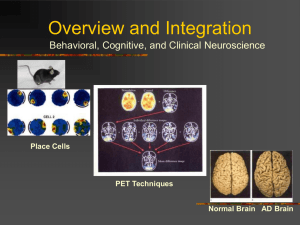
Overview and Integration
... Composite radioisotope brain scan for patients with each type of aphasia. Darker regions indicate areas where the lesions of many individual patients overlap. The isotope scans operate on the principle that the labeled compound can cross the blood-brain barrier in damaged tissue but not in healthy c ...
... Composite radioisotope brain scan for patients with each type of aphasia. Darker regions indicate areas where the lesions of many individual patients overlap. The isotope scans operate on the principle that the labeled compound can cross the blood-brain barrier in damaged tissue but not in healthy c ...
Your Name Here______________________________
... 15. Dopamine, histamine, norepinephrine and serotonin are in the class of neurotransmitters called a. neuropeptides b. amino acids c. neuromodulators d. monoamines 16. Immune protection of the CNS is in part based on the activity of a. astrocytes b. oligodendrocytes c. ependymal cells d. microglia ...
... 15. Dopamine, histamine, norepinephrine and serotonin are in the class of neurotransmitters called a. neuropeptides b. amino acids c. neuromodulators d. monoamines 16. Immune protection of the CNS is in part based on the activity of a. astrocytes b. oligodendrocytes c. ependymal cells d. microglia ...
File
... - Na+ gates on the axon open up and let Na+ flow in. -The inside of the neuron gains an positive charge and the outside gains a negative charge. -This is known as action potential. ...
... - Na+ gates on the axon open up and let Na+ flow in. -The inside of the neuron gains an positive charge and the outside gains a negative charge. -This is known as action potential. ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.