File
... that allow for a slow leakage of ions down their concentration gradients. K+ leaks out about 50x faster than Na+ leaks in promotion of negative resting potential (there are very few of these ‘open’ channels compared to the soon-to-be-mentioned ‘gates’ that open during an action potential). The pum ...
... that allow for a slow leakage of ions down their concentration gradients. K+ leaks out about 50x faster than Na+ leaks in promotion of negative resting potential (there are very few of these ‘open’ channels compared to the soon-to-be-mentioned ‘gates’ that open during an action potential). The pum ...
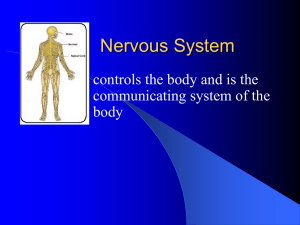
Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... coordination of muscle activity. • Pons: relays sensory info from the cerebellum to the cerebral cortex. • Medulla oblongata: the “primitive” brain; controls heart rate, respirations, ...
... coordination of muscle activity. • Pons: relays sensory info from the cerebellum to the cerebral cortex. • Medulla oblongata: the “primitive” brain; controls heart rate, respirations, ...
The neuroscience of depression: why does it matter?
... If they help to grow more neurons (via BDNF), they can improve information processing ...
... If they help to grow more neurons (via BDNF), they can improve information processing ...
Principles of Biology ______Lake Tahoe
... g. 6. neurotransmitter is broken down by an enzyme and channels close, ensuring brief and precise response to neurotransmitter h. only sending neurons have neurotransmitters to release at a synapse, only receiving neuron has receptor molecules ensuring that signal only travels one way. 11. a variety ...
... g. 6. neurotransmitter is broken down by an enzyme and channels close, ensuring brief and precise response to neurotransmitter h. only sending neurons have neurotransmitters to release at a synapse, only receiving neuron has receptor molecules ensuring that signal only travels one way. 11. a variety ...
Synapse
... • During rest, both the pre. and postsynaptic membrane have R.M.P is about -70 mV. • Stim. of presynaptic neuron → generation of AP → AP reaches the synaptic knob→ transient opening of the VGCa2+ channels Ca2+ influx → Ca2+ causes the vesicles to fuse with the knob membrane at active zones vesic ...
... • During rest, both the pre. and postsynaptic membrane have R.M.P is about -70 mV. • Stim. of presynaptic neuron → generation of AP → AP reaches the synaptic knob→ transient opening of the VGCa2+ channels Ca2+ influx → Ca2+ causes the vesicles to fuse with the knob membrane at active zones vesic ...
SV3 Neuroscience n Behavior Oct 5 09
... Describe the nervous system’s two major divisions, and identify the three types of neurons that transmit information through the system Identify the subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system, and describe their Functions Contrast the simplicity of the reflex pathways with the complexity of neura ...
... Describe the nervous system’s two major divisions, and identify the three types of neurons that transmit information through the system Identify the subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system, and describe their Functions Contrast the simplicity of the reflex pathways with the complexity of neura ...
Nervous System - Phoenix Union High School District
... d) oligodendrocytes- branched; connect thick nerve fibers; produce a myelin sheath around neurons. ...
... d) oligodendrocytes- branched; connect thick nerve fibers; produce a myelin sheath around neurons. ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness. Neurogenesis—the production of new neurons—has been shown to occur in early postnatal development, but recently, Princeton Psychologist Eliz ...
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness. Neurogenesis—the production of new neurons—has been shown to occur in early postnatal development, but recently, Princeton Psychologist Eliz ...
chapter 48
... There are three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems: o Sensory input sensory receptors take info from inside the body and the outside world and convey it to integration centers o Integration carried out in the CNS – input is interpreted and sends a signal so body can ...
... There are three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems: o Sensory input sensory receptors take info from inside the body and the outside world and convey it to integration centers o Integration carried out in the CNS – input is interpreted and sends a signal so body can ...
Slides Ch 2 - Department of Linguistics and English Language
... When monkeys watched person pick up food and eat, the same neurons fired ...
... When monkeys watched person pick up food and eat, the same neurons fired ...
Biology Option Review Section E
... rates of survival, as is the case with the Loggerhead turtles who are, after birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and travel immense distances when the time comes to lay their eggs, back to the ...
... rates of survival, as is the case with the Loggerhead turtles who are, after birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and travel immense distances when the time comes to lay their eggs, back to the ...
Neuroanatomy 18 [4-20
... => postcommisural fornix => medial and lateral mamillary nuclei, => precommisural fornix => lateral septal nuclues, => or anterior thalamic nucleus ...
... => postcommisural fornix => medial and lateral mamillary nuclei, => precommisural fornix => lateral septal nuclues, => or anterior thalamic nucleus ...
Limbic system
... Limbic system It appears to contribute to the characteristics of the individual and the continuation of human life. The limbic system is responsible for feeding behavior, “fight and flight reactions”, aggression, the formation of memories and the emotional life. The limbic system receives input fr ...
... Limbic system It appears to contribute to the characteristics of the individual and the continuation of human life. The limbic system is responsible for feeding behavior, “fight and flight reactions”, aggression, the formation of memories and the emotional life. The limbic system receives input fr ...
Chapter 12 Functional Organization of the Nervous System
... presynaptic terminal by monoamine oxidase (MAO). 3. The neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft. D. Receptor molecules in synapses 1. Receptors for neurotransmitters are specific. 2. A neurotransmitter can bind to several different receptor types a. Therefore a neurotransmitter can be st ...
... presynaptic terminal by monoamine oxidase (MAO). 3. The neurotransmitter diffuses out of the synaptic cleft. D. Receptor molecules in synapses 1. Receptors for neurotransmitters are specific. 2. A neurotransmitter can bind to several different receptor types a. Therefore a neurotransmitter can be st ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... memory and recognition of faces are among the various abilities that are regulated by which cerebral hemisphere? • A) the left hemisphere • B) the right hemisphere • C) Both hemispheres control these functions equally. • D) There is no research stating that either hemisphere dominates these skills. ...
... memory and recognition of faces are among the various abilities that are regulated by which cerebral hemisphere? • A) the left hemisphere • B) the right hemisphere • C) Both hemispheres control these functions equally. • D) There is no research stating that either hemisphere dominates these skills. ...
Neural Basis of Motor Control
... Remember, sodium has a positive charge, so the neuron becomes more positive and becomes depolarized. It takes longer for potassium channels to open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes ...
... Remember, sodium has a positive charge, so the neuron becomes more positive and becomes depolarized. It takes longer for potassium channels to open. When they do open, potassium rushes out of the cell, reversing the depolarization. Also at about this time, sodium channels start to close. This causes ...
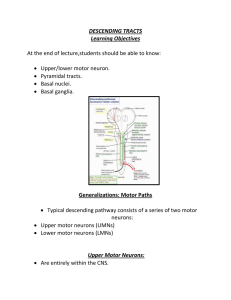
DESCENDING TRACTS Learning Objectives At the end of lecture
... Descends in anterior portion of lateral funiculus (column). Thought to mediate larger movements of trunk and limbs that do not require balance or fine movements of upper limbs. ...
... Descends in anterior portion of lateral funiculus (column). Thought to mediate larger movements of trunk and limbs that do not require balance or fine movements of upper limbs. ...
36.1: The Nervous System
... Controls and coordinates the body’s responses to changes in the environment HOW: Stimulus: a change in the external or internal environment which initiates an impulse Impulse~ an electro-chemical charge generated along a neuron Receptors~ structures specialized to detect certain stimuli Response~ a ...
... Controls and coordinates the body’s responses to changes in the environment HOW: Stimulus: a change in the external or internal environment which initiates an impulse Impulse~ an electro-chemical charge generated along a neuron Receptors~ structures specialized to detect certain stimuli Response~ a ...
Design of Intelligent Machines Heidi 2005
... They are significantly bigger than minicolumns, typically around 0.3-0.5 mm and have 4000-8000 neurons ...
... They are significantly bigger than minicolumns, typically around 0.3-0.5 mm and have 4000-8000 neurons ...
Chapter 6 - Sensory - Austin Community College
... Autonomic pathway consists of a two neuron chain: The first motor neuron called the preganglionic neuron, has its cell body in the CNS and its myelinated axon called the preganglionic fiber extends to autonomic ganglion. The second motor neuron called the postganglionic neuron has its soma in that a ...
... Autonomic pathway consists of a two neuron chain: The first motor neuron called the preganglionic neuron, has its cell body in the CNS and its myelinated axon called the preganglionic fiber extends to autonomic ganglion. The second motor neuron called the postganglionic neuron has its soma in that a ...
Function
... rich in dopamine and serotonin neurons part of two major dopamine pathways: the mesolimbic pathway - connects the VTA and the nucleus accumbens the mesocortical pathway - connects the VTA to cortical areas in the frontal lobes Function ...
... rich in dopamine and serotonin neurons part of two major dopamine pathways: the mesolimbic pathway - connects the VTA and the nucleus accumbens the mesocortical pathway - connects the VTA to cortical areas in the frontal lobes Function ...
Nerve Cells Images
... Phase contrast light microscopy image of neurons in the human cerebellum. The cerebellum is the posterior part of the brain that coordinates sensory inputs and muscular responses. The large cell bodies belong to Purkinje cells. This was a thick section, silver-stained and counterstained. Credit: Spi ...
... Phase contrast light microscopy image of neurons in the human cerebellum. The cerebellum is the posterior part of the brain that coordinates sensory inputs and muscular responses. The large cell bodies belong to Purkinje cells. This was a thick section, silver-stained and counterstained. Credit: Spi ...
1-The cell body
... called synapses. 3-The axon (Gr. axon, axis), which is a single long process ending at synapses specialized to generate and conduct nerve impulses to other cells (nerve, muscle, and gland cells). Axons may also receive information from other neurons, information that mainly modifies the transmission ...
... called synapses. 3-The axon (Gr. axon, axis), which is a single long process ending at synapses specialized to generate and conduct nerve impulses to other cells (nerve, muscle, and gland cells). Axons may also receive information from other neurons, information that mainly modifies the transmission ...
Biology 12 - Excretion
... A MOTOR neuron has a long axon and short dendrites. In the first part of the nerve impulse, the ion SODIUM moves to the inside of the neuron. The junction between one neuron and another is called a SYNAPSE. Each division of the autonomic nervous system controls the same organs, but they generally ha ...
... A MOTOR neuron has a long axon and short dendrites. In the first part of the nerve impulse, the ion SODIUM moves to the inside of the neuron. The junction between one neuron and another is called a SYNAPSE. Each division of the autonomic nervous system controls the same organs, but they generally ha ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.