Experimental bases for a psychological theory of personality
... R2, R1, R1) whose execution sequence is different from the sequence that was reinforced in the previous trial (R1, R1, R2, R1). This is an alternative proposition to the previous hypothesis that states that the reinforcement program induces variability in some subjects. In this regard, the variabili ...
... R2, R1, R1) whose execution sequence is different from the sequence that was reinforced in the previous trial (R1, R1, R2, R1). This is an alternative proposition to the previous hypothesis that states that the reinforcement program induces variability in some subjects. In this regard, the variabili ...
Making Sense of Animal Conditioning
... costs money. The frequent delivery of reinforcers also disrupts behavior. Therefore, CRF is used to initially teach a response but a schedule of partial reinforcement is used as the response becomes stronger. In a partial reinforcement procedure (PRF), some instances of a response are not followed b ...
... costs money. The frequent delivery of reinforcers also disrupts behavior. Therefore, CRF is used to initially teach a response but a schedule of partial reinforcement is used as the response becomes stronger. In a partial reinforcement procedure (PRF), some instances of a response are not followed b ...
Stiahnuť prednášku - Nechodimnaprednasky.sk
... different forms of behaviorism, and that these forms differ in many important ways. The objective of the present tutorial is to promote an understanding of the differences between two of these forms of behaviorism – methodological behaviorism and radical behaviorism. It is sometimes said that La Met ...
... different forms of behaviorism, and that these forms differ in many important ways. The objective of the present tutorial is to promote an understanding of the differences between two of these forms of behaviorism – methodological behaviorism and radical behaviorism. It is sometimes said that La Met ...
Pavlov`s Contributions to Behavior Therapy
... dure could not only produce behaviors described as neurotic through the use of conditioning principles but also eliminate such behaviors through the systematic application of counterconditioning measures--an experimentally based paradigm for the study of anxiety responses appeared, laying the groun ...
... dure could not only produce behaviors described as neurotic through the use of conditioning principles but also eliminate such behaviors through the systematic application of counterconditioning measures--an experimentally based paradigm for the study of anxiety responses appeared, laying the groun ...
Learning
... The tendency to respond differently to two or more similar stimuli. In classical conditioning, it occurs when a stimulus similar to the condition stimulus (CS) fails to evoke a conditioned response ...
... The tendency to respond differently to two or more similar stimuli. In classical conditioning, it occurs when a stimulus similar to the condition stimulus (CS) fails to evoke a conditioned response ...
ACJ Article: Retrospective on Behavioral Approaches
... Watson (1924) also speculated about the relevance of classical conditioning to “thinking” and argued that “thinking” is simply “internal speech” (Watson, 1924, p. 239). He notes: “The behaviorist advances a natural science theory about thinking which makes it just as simple, and just as much a part ...
... Watson (1924) also speculated about the relevance of classical conditioning to “thinking” and argued that “thinking” is simply “internal speech” (Watson, 1924, p. 239). He notes: “The behaviorist advances a natural science theory about thinking which makes it just as simple, and just as much a part ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES To demonstrate mastery of this chapter
... studies have shown that animals as well as humans are cognitive time travelers. OBJECTIVE 6.12 – Explain the concept of stimulus control and describe the processes of generalization and discrimination as they relate to operant conditioning. OBJECTIVE 6.13 – Explain how punishers can be defined by th ...
... studies have shown that animals as well as humans are cognitive time travelers. OBJECTIVE 6.12 – Explain the concept of stimulus control and describe the processes of generalization and discrimination as they relate to operant conditioning. OBJECTIVE 6.13 – Explain how punishers can be defined by th ...
learning - Wofford
... Describe the basic elements of classical conditioning • Define the unconditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response Describe the basic elements of operant conditioning ...
... Describe the basic elements of classical conditioning • Define the unconditioned stimulus, unconditioned response, conditioned stimulus, and conditioned response Describe the basic elements of operant conditioning ...
Essentialism and Selectionism in Cognitive
... is a process that necessarily takes time: When contingencies of selection are stable over the duration of one's observations, species may appear to have essential properties, but Darwin showed that this appearance of stability is quite consistent with a selectionist account. When viewed over time, i ...
... is a process that necessarily takes time: When contingencies of selection are stable over the duration of one's observations, species may appear to have essential properties, but Darwin showed that this appearance of stability is quite consistent with a selectionist account. When viewed over time, i ...
Chapter 1
... • Empathy and Altruism: The Pure Motive for Helping He argues that pure altruism is most likely to come into play when we experience empathy for the person in need; that is, we are able to experience events and emotions the way that person experiences them. ...
... • Empathy and Altruism: The Pure Motive for Helping He argues that pure altruism is most likely to come into play when we experience empathy for the person in need; that is, we are able to experience events and emotions the way that person experiences them. ...
Interactive Training for Synthetic Characters
... surrounding world – need to be dealt with. Terzopoulos and Tu (1994) integrated learning into graphical creatures where the learning focused on locomotion for surviving in the simulated physical world. Relevant cues were already given and creatures were assumed to know what to learn and pay attentio ...
... surrounding world – need to be dealt with. Terzopoulos and Tu (1994) integrated learning into graphical creatures where the learning focused on locomotion for surviving in the simulated physical world. Relevant cues were already given and creatures were assumed to know what to learn and pay attentio ...
Behaviorism ppt
... Behaviorists believe that learning takes place as the result of a response that follows on a specific stimulus. By repeating the S-R cycle the organism (may it be an animal or human) is conditioned into repeating the response whenever the same stimulus is present. Behavior can be modified and learn ...
... Behaviorists believe that learning takes place as the result of a response that follows on a specific stimulus. By repeating the S-R cycle the organism (may it be an animal or human) is conditioned into repeating the response whenever the same stimulus is present. Behavior can be modified and learn ...
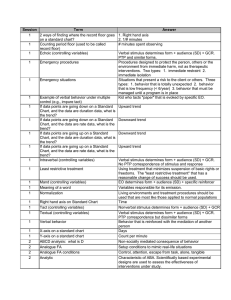
Session
... A reinforcer that is produced by the behavior without the participation of other people. For example, echolalia produces sounds that may maintain the behavior. It can be positive or negative reinforcement. Characteristic of ABA. Behavior is the focus, not a hypothetical entity. 1. Functional analysi ...
... A reinforcer that is produced by the behavior without the participation of other people. For example, echolalia produces sounds that may maintain the behavior. It can be positive or negative reinforcement. Characteristic of ABA. Behavior is the focus, not a hypothetical entity. 1. Functional analysi ...
Classical conditioning
... Behaviorism is a school of psychology that views all behaviors as learned. Classical conditioning is a form of behaviorism in which a specific stimulus produces a predictable response. The most common example is when dogs smell food that causes them to salivate. When a bell is rung at every meal, th ...
... Behaviorism is a school of psychology that views all behaviors as learned. Classical conditioning is a form of behaviorism in which a specific stimulus produces a predictable response. The most common example is when dogs smell food that causes them to salivate. When a bell is rung at every meal, th ...
Operant Conditioning
... steps, leading to a desired complex behavior – Successive approximation: small steps, one after another, that lead to a particular goal behavior ...
... steps, leading to a desired complex behavior – Successive approximation: small steps, one after another, that lead to a particular goal behavior ...
PPT
... Can Rewards Undermine Behavior Control? when children are extrinsically reinforced for a preferred behavior they may become less likely to engage in that behavior when those reinforcers are not available • the effect is not that widespread • the effect seems to be limited to certain types of behavi ...
... Can Rewards Undermine Behavior Control? when children are extrinsically reinforced for a preferred behavior they may become less likely to engage in that behavior when those reinforcers are not available • the effect is not that widespread • the effect seems to be limited to certain types of behavi ...
Classical Conditioning
... A child gets a "talking to" for teasing her baby brother. A puppy gets slapped with a newspaper for jumping up on a neighbor. A rat is blasted with bright lights and noise after choosing the wrong door. Punishment by removal: A child is not allowed to watch Nickelodeon for one week because she screa ...
... A child gets a "talking to" for teasing her baby brother. A puppy gets slapped with a newspaper for jumping up on a neighbor. A rat is blasted with bright lights and noise after choosing the wrong door. Punishment by removal: A child is not allowed to watch Nickelodeon for one week because she screa ...
Reinforcement - Karl Pribram
... subject to alteration bY-.§jgnals of mismatch; (i.e., a partial match); it leads to "exRectancies" of the environment by the organism. Such a process has been stated mathematically (MacKey. 1956),;. its implications for psychology (e.g., in percep~ readiness) have been detailed (Bruner, 1957). Here ...
... subject to alteration bY-.§jgnals of mismatch; (i.e., a partial match); it leads to "exRectancies" of the environment by the organism. Such a process has been stated mathematically (MacKey. 1956),;. its implications for psychology (e.g., in percep~ readiness) have been detailed (Bruner, 1957). Here ...
Learning
... If a behavior is followed by a positive state of affairs, the response becomes stronger (reward training). The term “Reinforcement” is used to refer to any stimulus which has the capability to strengthen behavior If a behavior is followed by a negative state of affairs, the response becomes weaker ( ...
... If a behavior is followed by a positive state of affairs, the response becomes stronger (reward training). The term “Reinforcement” is used to refer to any stimulus which has the capability to strengthen behavior If a behavior is followed by a negative state of affairs, the response becomes weaker ( ...
Number 3 • April 1997 - Institute for Applied Behavior Analysis
... being removed or rewards offered to placate Desmond. Attempts to manage Desmond when he was having a tantrum tended to lead to his behavior deteriorating sharply. It is possible to speculate that this in turn had led to the relatively high levels of noncompliance that Desmond exhibited at other time ...
... being removed or rewards offered to placate Desmond. Attempts to manage Desmond when he was having a tantrum tended to lead to his behavior deteriorating sharply. It is possible to speculate that this in turn had led to the relatively high levels of noncompliance that Desmond exhibited at other time ...
A weakening of a behavior is to ______, as a
... Full file at http://testbanksolutions.org/Test-Bank-for-Introduction-to-Learning-and-Behavior,4th-Edition-Russell-A.-Powell,-P.-Lynne-Honey,-Diane-G.-Symbaluk 20. “I am able to control only some of my behaviors.” This statement best exemplifies _____ theory of human behavior. a) Descartes’ b) Plato ...
... Full file at http://testbanksolutions.org/Test-Bank-for-Introduction-to-Learning-and-Behavior,4th-Edition-Russell-A.-Powell,-P.-Lynne-Honey,-Diane-G.-Symbaluk 20. “I am able to control only some of my behaviors.” This statement best exemplifies _____ theory of human behavior. a) Descartes’ b) Plato ...
A weakening of a behavior is to ______, as a
... Full file at http://TestMango.eu/Test-Bank-for-Introduction-to-Learning-and-Behavior-4thEdition-Powell 20. “I am able to control only some of my behaviors.” This statement best exemplifies _____ theory of human behavior. a) Descartes’ b) Plato’s c) Locke’s d) Titchener’s > A 8 21. “A person is both ...
... Full file at http://TestMango.eu/Test-Bank-for-Introduction-to-Learning-and-Behavior-4thEdition-Powell 20. “I am able to control only some of my behaviors.” This statement best exemplifies _____ theory of human behavior. a) Descartes’ b) Plato’s c) Locke’s d) Titchener’s > A 8 21. “A person is both ...