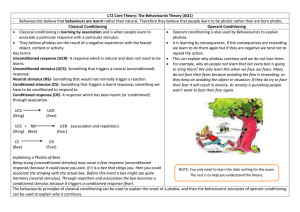
Lecture 4: Classical conditioning
... – But: when shown stimulus again, showed increased sensitization (looked at it more) ...
... – But: when shown stimulus again, showed increased sensitization (looked at it more) ...
Applications of Classical Conditioning
... to learn associations that help them adapt and survive. Contrary to what many before Garcia believed, some associations are learned more readily than others. ...
... to learn associations that help them adapt and survive. Contrary to what many before Garcia believed, some associations are learned more readily than others. ...
learning - Angelfire
... when they are not utilized. - Learning occurs then occurs with constant practice - However, correct practice or exercise in itself does not result in learning (example: practice or exercise without knowing the reasons for practicing or exercising does not improve learning) 4. Trial-and-error - is pr ...
... when they are not utilized. - Learning occurs then occurs with constant practice - However, correct practice or exercise in itself does not result in learning (example: practice or exercise without knowing the reasons for practicing or exercising does not improve learning) 4. Trial-and-error - is pr ...
Learning - Personal Pages
... boy to be afraid of rats by making a loud, startling-producing noise every time the boy was presented with a rat. The rat eventually produced a fear response in the boy, but also the presentation of rabbits and other animals (not previously fearful to the boy) also had the same effect. ...
... boy to be afraid of rats by making a loud, startling-producing noise every time the boy was presented with a rat. The rat eventually produced a fear response in the boy, but also the presentation of rabbits and other animals (not previously fearful to the boy) also had the same effect. ...
here
... Classical conditioning is learning by association and is when people learn to Operant conditioning is also used by Behaviourists to explain associate a particular response with a particular stimulus. phobias. They believe phobias are the result of a negative experience with the feared It is ...
... Classical conditioning is learning by association and is when people learn to Operant conditioning is also used by Behaviourists to explain associate a particular response with a particular stimulus. phobias. They believe phobias are the result of a negative experience with the feared It is ...
File
... o Social learning o Learned helplessness o Cognitive learning o Modeling o Cognitive map o Behavior modification o Latent learning What did Albert Bandura’s experiment show with the ‘Bobo doll?’ How did Edward Tolman discover the idea about cognitive maps and latent learning from his maze experi ...
... o Social learning o Learned helplessness o Cognitive learning o Modeling o Cognitive map o Behavior modification o Latent learning What did Albert Bandura’s experiment show with the ‘Bobo doll?’ How did Edward Tolman discover the idea about cognitive maps and latent learning from his maze experi ...
Unit 6 Jeopardy - Northern Highlands
... An organism may learn to respond not only to the CS, but also to other stimuli that are similar to the CS. ...
... An organism may learn to respond not only to the CS, but also to other stimuli that are similar to the CS. ...
learning
... reliably occurs when another stimulus (US) is about to appear. •First stimulus can be used to accurately predict the arrival of the US. Contiguity •When stimuli occur close together in time. •Appears that the CR is acquired only when the CS predicts what is going to follow. ...
... reliably occurs when another stimulus (US) is about to appear. •First stimulus can be used to accurately predict the arrival of the US. Contiguity •When stimuli occur close together in time. •Appears that the CR is acquired only when the CS predicts what is going to follow. ...
Behaviorism - Dr Matthew J Koehler
... – In studies where participants work on an interesting task like puzzles, the experimental group is given a reward when finished while the control group is not. – After the initial period, during a non-rewarded time participants are given a choice between continuing to work on the task or switching ...
... – In studies where participants work on an interesting task like puzzles, the experimental group is given a reward when finished while the control group is not. – After the initial period, during a non-rewarded time participants are given a choice between continuing to work on the task or switching ...
Chapter 5 Quiz
... 7. Your friend Madison became very ill a few hours after eating the fried chicken special in the college cafeteria. Now, Madison feels queasy whenever she smells fried chicken. Having read the learning chapter in your psychology class, you explain that: A) since Madison only experienced one pairing ...
... 7. Your friend Madison became very ill a few hours after eating the fried chicken special in the college cafeteria. Now, Madison feels queasy whenever she smells fried chicken. Having read the learning chapter in your psychology class, you explain that: A) since Madison only experienced one pairing ...
Sensory Physiology
... Unlike other senses pain is coupled with behavioral and emotional responses ...
... Unlike other senses pain is coupled with behavioral and emotional responses ...
Sensory Physiology
... skeletal muscles and joints Visceral afferent fibers – carries impulses from organs within ventral body cavities Special sense afferent fibers – eyes, ears, taste, smell ...
... skeletal muscles and joints Visceral afferent fibers – carries impulses from organs within ventral body cavities Special sense afferent fibers – eyes, ears, taste, smell ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those considering more than one – This allows for parallel processing of the various inputs, and results in an internal, conscious image of the stimulus ...
... – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those considering more than one – This allows for parallel processing of the various inputs, and results in an internal, conscious image of the stimulus ...
Skeletal System
... – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those considering more than one – This allows for parallel processing of the various inputs, and results in an internal, conscious image of the stimulus ...
... – First to those restricted to the same modality and then to those considering more than one – This allows for parallel processing of the various inputs, and results in an internal, conscious image of the stimulus ...
Learning - McMurray VMC
... Neuroscientists discovered mirror neurons in the brains of animals and humans that are active during observational learning. Mirror Neurons: Frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or when observing another doing so. They enable imitation and empathy. ...
... Neuroscientists discovered mirror neurons in the brains of animals and humans that are active during observational learning. Mirror Neurons: Frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or when observing another doing so. They enable imitation and empathy. ...
PSYCHOLOGY
... problems; clarify clients goals; assist in meeting challenges School psychologists – testing; develop IEPs Educational – course planning and instructional methods ...
... problems; clarify clients goals; assist in meeting challenges School psychologists – testing; develop IEPs Educational – course planning and instructional methods ...
Psychology: Pavlov, Watson, Skinner
... especially children learn aggressive responses from observing others, either personally or through the media and environment. ...
... especially children learn aggressive responses from observing others, either personally or through the media and environment. ...
Sensation and Perception
... • Memory senses; they both have powerful connections to memory 6) Weber’s law determines • Absolute threshold • Focal length of the eye • Level of subliminal messages • Amplitude of sound waves • Just-noticeable difference ...
... • Memory senses; they both have powerful connections to memory 6) Weber’s law determines • Absolute threshold • Focal length of the eye • Level of subliminal messages • Amplitude of sound waves • Just-noticeable difference ...
Learning - s3.amazonaws.com
... learning processes: make connections between 2 or more events in the world respond to the effects of personal experiences observation of other people’s experiences ...
... learning processes: make connections between 2 or more events in the world respond to the effects of personal experiences observation of other people’s experiences ...
Lecture 26
... “Any relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs as a result of experience According to the behaviorists, learning can be defined as “the relatively permanent change in behavior brought about as a result of experience or practice.” Learning is the acquisition of knowledge, skill, or values t ...
... “Any relatively permanent change in behavior that occurs as a result of experience According to the behaviorists, learning can be defined as “the relatively permanent change in behavior brought about as a result of experience or practice.” Learning is the acquisition of knowledge, skill, or values t ...
Sensation
... a stimulus can be changed and the difference detected half the time. Example – Turn up the volume on the TV a very small ...
... a stimulus can be changed and the difference detected half the time. Example – Turn up the volume on the TV a very small ...
Behaviorism: Applied Logical Positivism
... perspective (reflexes, S-R pairs are molecular) Articulated an intervening variable theory of learning, not a stimulus-response theory Animals and humans engage in latent learning: build up knowledge of their environment from engaging the environment • rats running mazes—with and without rewards—dev ...
... perspective (reflexes, S-R pairs are molecular) Articulated an intervening variable theory of learning, not a stimulus-response theory Animals and humans engage in latent learning: build up knowledge of their environment from engaging the environment • rats running mazes—with and without rewards—dev ...
What is Psychology?
... – Reinforcers that are inherently related to the action being reinforced, such as enjoyment of the task and satisfaction of accomplishment. ...
... – Reinforcers that are inherently related to the action being reinforced, such as enjoyment of the task and satisfaction of accomplishment. ...