Principles of Evolution
... Lyell. Uniformitarianism states that the physical laws that now shape the earth have always done so, and that the past can be understood by studying the present. Both suggested that the Earth is very old. ...
... Lyell. Uniformitarianism states that the physical laws that now shape the earth have always done so, and that the past can be understood by studying the present. Both suggested that the Earth is very old. ...
Natural Selection Notes
... If the environment stays the same, then natural selection favors organisms with certain adaptations. Organisms with these adaptations (traits) survive and reproduce. Organisms that do not possess these traits may not survive long enough to reproduce. The population adjusts to the environment o ...
... If the environment stays the same, then natural selection favors organisms with certain adaptations. Organisms with these adaptations (traits) survive and reproduce. Organisms that do not possess these traits may not survive long enough to reproduce. The population adjusts to the environment o ...
Darwin Presents His Case
... Survival of the Fittest • Survival is not just staying alive • In evolutionary terms, survival means reproducing and passing adaptations on to the next generation ...
... Survival of the Fittest • Survival is not just staying alive • In evolutionary terms, survival means reproducing and passing adaptations on to the next generation ...
Lamarck
... Evolution is a theory • In science, this means there is overwhelming evidence to support it • Very slow, so hard to observe because humans don’t live very long –Evolution can take thousands or millions of years –Though, for some organisms we can see it ...
... Evolution is a theory • In science, this means there is overwhelming evidence to support it • Very slow, so hard to observe because humans don’t live very long –Evolution can take thousands or millions of years –Though, for some organisms we can see it ...
Biology Evolution Unit Review
... 10)What are the four principles of natural selection? List & explain each. (What four things have to occur for natural selection to take place?) (Pg. 421) -‐Variation: individuals in a population ...
... 10)What are the four principles of natural selection? List & explain each. (What four things have to occur for natural selection to take place?) (Pg. 421) -‐Variation: individuals in a population ...
How Populations Evolve
... Linnaeus also introduced a system for grouping species into a hierarchy of categories Beyond the grouping of species within genera, taxonomy extends to progressively broader categories of classification - family, orders, classes, phyla (singular, phylum), kingdoms, and domains Grouping organisms int ...
... Linnaeus also introduced a system for grouping species into a hierarchy of categories Beyond the grouping of species within genera, taxonomy extends to progressively broader categories of classification - family, orders, classes, phyla (singular, phylum), kingdoms, and domains Grouping organisms int ...
hssv0402t_powerpres
... Evolution by Natural Selection • Natural selection is the process by which individuals that have favorable variations and are better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully than less well adapted individuals do. • Darwin proposed that over many generations, natural selec ...
... Evolution by Natural Selection • Natural selection is the process by which individuals that have favorable variations and are better adapted to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully than less well adapted individuals do. • Darwin proposed that over many generations, natural selec ...
Welcome to Class
... Descent with Modification • through selective breeding able to dramatically change domestic species (dogs) • Over time/generations traits with reproductive advantages become more common • All species descended from one or a few original types of life ...
... Descent with Modification • through selective breeding able to dramatically change domestic species (dogs) • Over time/generations traits with reproductive advantages become more common • All species descended from one or a few original types of life ...
Ch 15 PPT
... • Finches had different types of beaks adapted to their type of food gathering • Mockingbirds had different traits suited for their niche! ...
... • Finches had different types of beaks adapted to their type of food gathering • Mockingbirds had different traits suited for their niche! ...
History of Psych
... Are abilities determined by our genes or our experiences? This is known as Nature vs. Nurture appears throughout modern psychology ...
... Are abilities determined by our genes or our experiences? This is known as Nature vs. Nurture appears throughout modern psychology ...
What is Cognitive Science?
... properties of the world, we would have to conclude that behavior is essentially stimulus-independent Every behavioral regularity (other than physical ones like falling) is cognitively penetrable ...
... properties of the world, we would have to conclude that behavior is essentially stimulus-independent Every behavioral regularity (other than physical ones like falling) is cognitively penetrable ...
BioFundamentals - Selection and drift
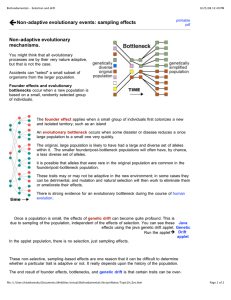
... The founder effect applies when a small group of individuals first colonizes a new and isolated territory, such as an island An evolutionary bottleneck occurs when some disaster or disease reduces a once large population to a small one very quickly. The original, large population is likely to have h ...
... The founder effect applies when a small group of individuals first colonizes a new and isolated territory, such as an island An evolutionary bottleneck occurs when some disaster or disease reduces a once large population to a small one very quickly. The original, large population is likely to have h ...
EOY_ Psyhologists to know_ long list
... Robert Zajonc motivation; believes that we invent explanations to label feelings Rosenhan Psychopathology and Social Psychology; effects of labeling; Rosenhan and colleagues checked selves into mental hospitals with symptoms of hearing voices say "empty, dull and thud." Diagnosed with schizophrenia. ...
... Robert Zajonc motivation; believes that we invent explanations to label feelings Rosenhan Psychopathology and Social Psychology; effects of labeling; Rosenhan and colleagues checked selves into mental hospitals with symptoms of hearing voices say "empty, dull and thud." Diagnosed with schizophrenia. ...
theory and research
... • Macrosystem: A society’s overall cultural patterns such as dominant beliefs, ideologies, and economic and political systems • Chronosystem: The dimension of time: change and constancy in the person and the environment ...
... • Macrosystem: A society’s overall cultural patterns such as dominant beliefs, ideologies, and economic and political systems • Chronosystem: The dimension of time: change and constancy in the person and the environment ...
Artificial Selection
... Evolutionary theory deals mainly with how life changed after its origin. ...
... Evolutionary theory deals mainly with how life changed after its origin. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - History of Psychology
... viewed mind and body as interactive machines. Stated that the mind could follow body and vice versa. Proposed the idea of both voluntary and involuntary behavior. Ruled out areas other than the brain for mental functioning. ...
... viewed mind and body as interactive machines. Stated that the mind could follow body and vice versa. Proposed the idea of both voluntary and involuntary behavior. Ruled out areas other than the brain for mental functioning. ...
Evolution Part 1
... Darwin made extensive use of specimens and fossil evidence to explain his theory of evolution, but because DNA and genes had not yet been discovered, he was unable to explain why traits varied within individuals or how they were inherited. Victorian scientists found it difficult to test Darwin’s the ...
... Darwin made extensive use of specimens and fossil evidence to explain his theory of evolution, but because DNA and genes had not yet been discovered, he was unable to explain why traits varied within individuals or how they were inherited. Victorian scientists found it difficult to test Darwin’s the ...
Example - Harrison High School
... Darwin explained that if humans could change species by artificial selection, then perhaps nature could do the same thing over time. He concluded that this is how new species develop naturally over time…natural selective breeding. ...
... Darwin explained that if humans could change species by artificial selection, then perhaps nature could do the same thing over time. He concluded that this is how new species develop naturally over time…natural selective breeding. ...
History: Unit 7 - Behaviorism: Modern Applications
... In the real world, we are reinforced at varying rates and times, which Skinner called “schedules of reinforcement.” For example, slot machines provide intermittent reinforcement. You keep playing because you don’t know when you will receive a reward. Pay checks are fixed reinforcement because you re ...
... In the real world, we are reinforced at varying rates and times, which Skinner called “schedules of reinforcement.” For example, slot machines provide intermittent reinforcement. You keep playing because you don’t know when you will receive a reward. Pay checks are fixed reinforcement because you re ...
Principles of Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning, and
... Operant Conditioning, and Social Learning Psychology I Mrs. Hart ...
... Operant Conditioning, and Social Learning Psychology I Mrs. Hart ...
Evolution
... Variations among individuals are inherited traits. In every population, there is variation among the individuals. Some individual traits are better than others in a particular environment. ...
... Variations among individuals are inherited traits. In every population, there is variation among the individuals. Some individual traits are better than others in a particular environment. ...
PDF version
... organismic biology. The course presents the various taxonomic groups and their characteristics, while using the different groups to demonstrate general principles of organization of the body and its systems. The full course includes a lab module which serves for practical demonstration of principles ...
... organismic biology. The course presents the various taxonomic groups and their characteristics, while using the different groups to demonstrate general principles of organization of the body and its systems. The full course includes a lab module which serves for practical demonstration of principles ...