Table of Contents - Neuropsychopharmacology
... because it does not involve any cognitive skills or cognition. It is an automated process. Psychologists do not even use the term “conditioning” to refer to learning because the change in response by associating two stimuli does not involve any cognitive process or conscious control of its learning. ...
... because it does not involve any cognitive skills or cognition. It is an automated process. Psychologists do not even use the term “conditioning” to refer to learning because the change in response by associating two stimuli does not involve any cognitive process or conscious control of its learning. ...
Lecture Powerpoint: Ch. 6
... learning in rats. Pay particular attention to the blue line. The rats in this group weren't reinforced until day 11; note the sudden drop in the number of their errors on receiving reinforcement. The rats were learning all along, even though they weren't showing it. (Source: Based on Tolman & Honzik ...
... learning in rats. Pay particular attention to the blue line. The rats in this group weren't reinforced until day 11; note the sudden drop in the number of their errors on receiving reinforcement. The rats were learning all along, even though they weren't showing it. (Source: Based on Tolman & Honzik ...
Redalyc.Transfer of latent inhibition of aversively conditioned
... lifetime). Although the available evidence from research in derived relational responding (e.g. Dougher et al., 1994; Roche & Barnes, 1997) together with evidence from prior studies on semantic conditioning (see Forsyth & Eifert, 1996), provide a promising avenue of empirical research on the etiolog ...
... lifetime). Although the available evidence from research in derived relational responding (e.g. Dougher et al., 1994; Roche & Barnes, 1997) together with evidence from prior studies on semantic conditioning (see Forsyth & Eifert, 1996), provide a promising avenue of empirical research on the etiolog ...
A reinforcement learning model of joy, distress, hope and fear.
... appraises based on the semantics of the state of the RL agent, such as if there is a wall or not, while in (Sequeira et al., 2014) appraisal is solely based on RL primitives. Furthermore, already in 1999 an exhaustive attempt has been made to investigate different ways in which both emotion and RL c ...
... appraises based on the semantics of the state of the RL agent, such as if there is a wall or not, while in (Sequeira et al., 2014) appraisal is solely based on RL primitives. Furthermore, already in 1999 an exhaustive attempt has been made to investigate different ways in which both emotion and RL c ...
The Role of Cognition in Classical and Operant Conditioning
... paradigms as exemplars of seemingly permanent solutions to particular scientific problems, exemplars that serve as models for subsequent research in the area. Classical and instrumental conditioning are paradigms in this sense of the term. They have provided models for study a variety of phenomena, ...
... paradigms as exemplars of seemingly permanent solutions to particular scientific problems, exemplars that serve as models for subsequent research in the area. Classical and instrumental conditioning are paradigms in this sense of the term. They have provided models for study a variety of phenomena, ...
Psy 101 Chapter 5 - Donna Vandergrift
... • Understand that your intelligence and thinking skills are not fixed but can change • Become passionate about learning and stretch your mind in challenging situations • Think about the growth mindsets of people ...
... • Understand that your intelligence and thinking skills are not fixed but can change • Become passionate about learning and stretch your mind in challenging situations • Think about the growth mindsets of people ...
Behavioral verification of associative learning in whisker
... direct function of the intensity of the UCS. For example, Morris and Bouton (2006) observed that the point in conditioning training at which freezing emerged and the asymptotic amount of freezing was directly related to the intensity of the UCS (footshock). Other studies indicate that performance in ...
... direct function of the intensity of the UCS. For example, Morris and Bouton (2006) observed that the point in conditioning training at which freezing emerged and the asymptotic amount of freezing was directly related to the intensity of the UCS (footshock). Other studies indicate that performance in ...
Chapter Five Learning
... Modifying Behavior • Important to establish a clear contingency between the desired behavior and the reinforcement • Contingency contracting involves an exchange of desirable reinforcers. ...
... Modifying Behavior • Important to establish a clear contingency between the desired behavior and the reinforcement • Contingency contracting involves an exchange of desirable reinforcers. ...
Classical Conditioning
... A. Studying the digestive process of dogs. He wanted to see how their stomach prepared to digest the food. B. We already knew that eating food causes saliva to secrete in the mouth. This is the initial breakdown of food. C. He noticed that just the sight or smell of food caused the dogs to salivate. ...
... A. Studying the digestive process of dogs. He wanted to see how their stomach prepared to digest the food. B. We already knew that eating food causes saliva to secrete in the mouth. This is the initial breakdown of food. C. He noticed that just the sight or smell of food caused the dogs to salivate. ...
Abnormal Psychology Fifth Edition
... occur or does not exist. For example, you completely block a painful experience from your memory. PROJECTION Attributing one’s own feelings or thoughts to other people. For example, a husband argues that his wife is angry at him when, in fact, he is angry at her. REPRESSION Suppressing threatening m ...
... occur or does not exist. For example, you completely block a painful experience from your memory. PROJECTION Attributing one’s own feelings or thoughts to other people. For example, a husband argues that his wife is angry at him when, in fact, he is angry at her. REPRESSION Suppressing threatening m ...
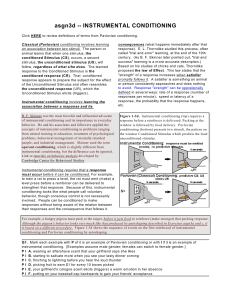
asgn3d -- INSTRUMENTAL CONDITIONING
... T F B. elicits (triggers) that response. T F C. becom es available on m aking that response. T F D. provides a signal to m ake that response. T F E. strengthens the im m ediately preceding response (whatever it m ay be). Q5. Richard Feynm an, the Nobel Prize winning physicist, was also known as an e ...
... T F B. elicits (triggers) that response. T F C. becom es available on m aking that response. T F D. provides a signal to m ake that response. T F E. strengthens the im m ediately preceding response (whatever it m ay be). Q5. Richard Feynm an, the Nobel Prize winning physicist, was also known as an e ...
Fundamentals of Phobias
... may take the form of a situationally bound or situationally predisposed panic attack. Note: In children, the anxiety may be expressed by crying, tantrums, freezing, or clinging C: The person recognizes that the fear is excessive or unreasonable. Note: In children, this feature may be absent D: The p ...
... may take the form of a situationally bound or situationally predisposed panic attack. Note: In children, the anxiety may be expressed by crying, tantrums, freezing, or clinging C: The person recognizes that the fear is excessive or unreasonable. Note: In children, this feature may be absent D: The p ...
Psychotherapies
... thoughts. • Exploring their thoughts & feelings in an accepting environment will lead the client to change their attitudes & behavior. • This approach very successful with dealing with client’s day-to-day concerns but not very successful in treating psychotic patients like those with severe schizoph ...
... thoughts. • Exploring their thoughts & feelings in an accepting environment will lead the client to change their attitudes & behavior. • This approach very successful with dealing with client’s day-to-day concerns but not very successful in treating psychotic patients like those with severe schizoph ...
FREE Sample Here - Find the cheapest test bank for your
... biological or social influences most clearly involve a debate over the issue of A. evolution versus natural selection. B. stage development versus continuous development. C. structuralism versus functionalism. D. behavior versus mental processes. E. nature versus nurture. Answer: E 40. Efforts to d ...
... biological or social influences most clearly involve a debate over the issue of A. evolution versus natural selection. B. stage development versus continuous development. C. structuralism versus functionalism. D. behavior versus mental processes. E. nature versus nurture. Answer: E 40. Efforts to d ...
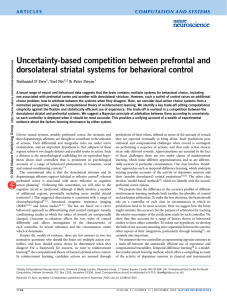
A Biologically Plausible Spiking Neuron Model of Fear Conditioning
... represented by LA will be increased (if a positive error signal is present for a sufficient duration, the value represented at LA will saturate at its maximum). It should be noted that the error signal used here only takes on values between 0 and 1. Because of this, it can only be used to drive acti ...
... represented by LA will be increased (if a positive error signal is present for a sufficient duration, the value represented at LA will saturate at its maximum). It should be noted that the error signal used here only takes on values between 0 and 1. Because of this, it can only be used to drive acti ...
Slide 1
... “the behavior is followed by a consequence, and the nature of the consequence modifies the organisms tendency to repeat the behavior in the future.” Imagine a rat in a cage. This is a special cage (called, in fact, a “Skinner box”) that has a bar or pedal on one wall that, when pressed, causes a lit ...
... “the behavior is followed by a consequence, and the nature of the consequence modifies the organisms tendency to repeat the behavior in the future.” Imagine a rat in a cage. This is a special cage (called, in fact, a “Skinner box”) that has a bar or pedal on one wall that, when pressed, causes a lit ...
PDF
... the tree-search controller. In the next phase of the experiment, the value of the food pellets is reduced, for instance by prefeeding the animal with them or by pairing them with illness to induce aversion. Then, animals are tested to see if they will continue to perform the actions previously assoc ...
... the tree-search controller. In the next phase of the experiment, the value of the food pellets is reduced, for instance by prefeeding the animal with them or by pairing them with illness to induce aversion. Then, animals are tested to see if they will continue to perform the actions previously assoc ...
EXTENDED PRIMARY AND HIGHER ORDER CONDITIONING OF
... this is attributable, as suggested by Bitterman (1960), to the difficulty of recording classical responses. Certainly, the tender membranes of the worm cannot be operated upon with the crude meehaneial devices so often required when working with a new species (i. e., one for which standard laborator ...
... this is attributable, as suggested by Bitterman (1960), to the difficulty of recording classical responses. Certainly, the tender membranes of the worm cannot be operated upon with the crude meehaneial devices so often required when working with a new species (i. e., one for which standard laborator ...
Intelligence, Learning, and Cognitive Psychology
... while crystallized intelligence are specific knowledge gained from applying fluid intelligence. ■ Crystallized intelligence involves the ability to use an accumulated body of general information to make judgments and solve problems. This kind of intelligence has to be specially learned and is theref ...
... while crystallized intelligence are specific knowledge gained from applying fluid intelligence. ■ Crystallized intelligence involves the ability to use an accumulated body of general information to make judgments and solve problems. This kind of intelligence has to be specially learned and is theref ...
Oppositional Defiant Disorder: Issues and interventions for positive
... suggest the impairments in executive functioning occur in correlation to a diagnosis of ADHD where ODD may also be present. Oosterlaan et al. (2005) pointed out the similarities between the diagnoses of ADHD and ODD along with their frequency to accompany one another in the diagnosis of a child. The ...
... suggest the impairments in executive functioning occur in correlation to a diagnosis of ADHD where ODD may also be present. Oosterlaan et al. (2005) pointed out the similarities between the diagnoses of ADHD and ODD along with their frequency to accompany one another in the diagnosis of a child. The ...
PsychAP Notes pt 12 The difference between Psychiatrists and
... parents praise them, it is positive reinforcement. Harry Potter again: look for the new conditioned stimulus and the new conditioned response. With the boggart, the new conditioned response is laughter. For Neville, the conditioned stimulus is the fear of Snape. The conditioned response is fear. Nat ...
... parents praise them, it is positive reinforcement. Harry Potter again: look for the new conditioned stimulus and the new conditioned response. With the boggart, the new conditioned response is laughter. For Neville, the conditioned stimulus is the fear of Snape. The conditioned response is fear. Nat ...
Lecture 11: Functionalism, the US brand of
... Johns Hopkins where he organized the first psychology laboratory Founded the American Journal of Psychology ...
... Johns Hopkins where he organized the first psychology laboratory Founded the American Journal of Psychology ...
Edwin Ray Guthrie (1886
... 1. Punishment needs to convey information, what the individual needs to do, e.g., dog chasing car. Pain during punishment is meaningless. 2. Punishment should produce an incompatible behavior to the unwanted behavior. 3. Punishment must be applied along with other stimuli, and it should be salient e ...
... 1. Punishment needs to convey information, what the individual needs to do, e.g., dog chasing car. Pain during punishment is meaningless. 2. Punishment should produce an incompatible behavior to the unwanted behavior. 3. Punishment must be applied along with other stimuli, and it should be salient e ...
Psychological behaviorism

Psychological behaviorism is a form of behaviorism - a major theory within psychology which holds that behaviors are learned through positive and negative reinforcements. The theory recommends that psychological concepts (such as personality, learning and emotion) are to be explained in terms of observable behaviors that respond to stimulus. Behaviorism was first developed by John B. Watson (1912), who coined the term ""behaviorism,"" and then B.F. Skinner who developed what is known as ""radical behaviorism."" Watson and Skinner rejected the idea that psychological data could be obtained through introspection or by an attempt to describe consciousness; all psychological data, in their view, was to be derived from the observation of outward behavior. Recently, Arthur W. Staats has proposed a psychological behaviorism - a ""paradigmatic behaviorist theory"" which argues that personality consists of a set of learned behavioral patterns, acquired through the interaction between an individual's biology, environment, cognition, and emotion. Holth also critically reviews psychological behaviorism as a ""path to the grand reunification of psychology and behavior analysis"".Psychological behaviorism’s theory of personality represents one of psychological behaviorism’s central differences from the preceding behaviorism’s; the other parts of the broader approach as they relate to each other will be summarized in the paradigm sections