THEORIES OF INSTRUCTION/LEARNING
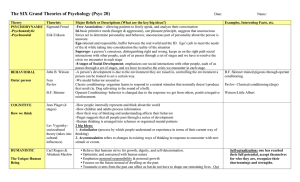
... B.F. Skinner is a name associated with behaviorism, a term ...
... B.F. Skinner is a name associated with behaviorism, a term ...
Ch 8 Jeopardy Answers
... schedules of reinforcement? An example of a secondary reinforcer. This is designed to weaken our tendency to do something. ...
... schedules of reinforcement? An example of a secondary reinforcer. This is designed to weaken our tendency to do something. ...
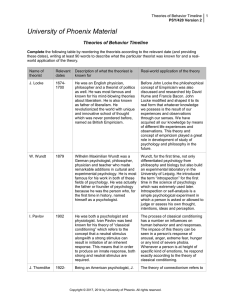
The SIX Grand Theories of Psychology (Psyc 20)
... -How their way of thinking and understanding affects their behavior -Piaget suggests that all people pass through a series of development -Human thinking is arranged into schemes or organized mental patterns 2 big Ideas: 1. Assimilation (process by which people understand or experience in terms of t ...
... -How their way of thinking and understanding affects their behavior -Piaget suggests that all people pass through a series of development -Human thinking is arranged into schemes or organized mental patterns 2 big Ideas: 1. Assimilation (process by which people understand or experience in terms of t ...
History, Theory, and Research Strategies
... experiences before and after birth Example: do children learn language rapidly because they are genetically predisposed to do so or because their parents teach them from an early age? ...
... experiences before and after birth Example: do children learn language rapidly because they are genetically predisposed to do so or because their parents teach them from an early age? ...
File
... long as the delivery is guaranteed. For example, if parents are inconsistent with punishment, children learn very quickly how to “get away with murder” with one parent and not the other. • Punishment may be imitated as a way of solving problems. Thus, a child might strike another at school as a way ...
... long as the delivery is guaranteed. For example, if parents are inconsistent with punishment, children learn very quickly how to “get away with murder” with one parent and not the other. • Punishment may be imitated as a way of solving problems. Thus, a child might strike another at school as a way ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint Pres.
... long as the delivery is guaranteed. For example, if parents are inconsistent with punishment, children learn very quickly how to “get away with murder” with one parent and not the other. • Punishment may be imitated as a way of solving problems. Thus, a child might strike another at school as a way ...
... long as the delivery is guaranteed. For example, if parents are inconsistent with punishment, children learn very quickly how to “get away with murder” with one parent and not the other. • Punishment may be imitated as a way of solving problems. Thus, a child might strike another at school as a way ...
using the principles of learning to understand everyday behavior
... – Reinforcement should be directly contingent on appropriate behavior. – Indiscriminate reinforcement to boost self-esteem doesn’t improve performance. – Reinforcement may teach children that educational activities should be performed for reward rather than for the intrinsic interest of the task. ...
... – Reinforcement should be directly contingent on appropriate behavior. – Indiscriminate reinforcement to boost self-esteem doesn’t improve performance. – Reinforcement may teach children that educational activities should be performed for reward rather than for the intrinsic interest of the task. ...
Classical Conditioning
... Watson & Rayner (1920 & 1921) began their research by testing Baby Albert to see their reactions to stimuli thought to be innately ...
... Watson & Rayner (1920 & 1921) began their research by testing Baby Albert to see their reactions to stimuli thought to be innately ...
psy420r2_theories_of_behavior_timeline_1
... biology. He was best and most reknowned for his discovery of “Nucleic acids” in 1962 alongwith other two scientists and was awarded a Nobel prize because of this discovery and its importance as nucleic acids are the components involved in the transfer of most important information in the living bein ...
... biology. He was best and most reknowned for his discovery of “Nucleic acids” in 1962 alongwith other two scientists and was awarded a Nobel prize because of this discovery and its importance as nucleic acids are the components involved in the transfer of most important information in the living bein ...
AP Psychology Unit VI: Learning Biological, Latent, Cognitive
... actions of models. Experiment was criticized by some on ethical grounds, for training children towards aggression. Bandura's results from the Bobo Doll Experiment changed the course of modern psychology, & were widely credited for helping shift the focus in academic psychology from pure behaviorism ...
... actions of models. Experiment was criticized by some on ethical grounds, for training children towards aggression. Bandura's results from the Bobo Doll Experiment changed the course of modern psychology, & were widely credited for helping shift the focus in academic psychology from pure behaviorism ...
Key Terms - Ms. Paras
... Unit 4: Learning and Behavior (7-9%) Reading Schedule: pg 229-239 due 11/3; pg 240-251 due 11/9; pg 252-263 due 11/14 Tentative Quest Date: 11/17 This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds ...
... Unit 4: Learning and Behavior (7-9%) Reading Schedule: pg 229-239 due 11/3; pg 240-251 due 11/9; pg 252-263 due 11/14 Tentative Quest Date: 11/17 This section of the course introduces students to differences between learned and unlearned behavior. The primary focus is exploration of different kinds ...
1.1 History and Perspective
... • Rehabilitation – help clients with mental retardation, developmental disabilities, and disabilities resulting from stroke or accidents adapt to their situations • School – assess and counsel students, consult with educators and parents, and perform ...
... • Rehabilitation – help clients with mental retardation, developmental disabilities, and disabilities resulting from stroke or accidents adapt to their situations • School – assess and counsel students, consult with educators and parents, and perform ...
Learning - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... • Think about gambling in Vegas – Imagine a slot machine that paid $0.92 on every trial – Compare that to a machine that pays an average of $0.92 for every dollar, but you win only once in a while • Which would you play for longer? ...
... • Think about gambling in Vegas – Imagine a slot machine that paid $0.92 on every trial – Compare that to a machine that pays an average of $0.92 for every dollar, but you win only once in a while • Which would you play for longer? ...
theory and research
... • Theories are never set in stone; they are always open to change as a result of new findings? • People shape their world as it shapes them? • Cross-cultural research enables us to learn which aspects of development are universal and which are culturally influenced? • An experiment is the only way t ...
... • Theories are never set in stone; they are always open to change as a result of new findings? • People shape their world as it shapes them? • Cross-cultural research enables us to learn which aspects of development are universal and which are culturally influenced? • An experiment is the only way t ...
History and Approaches of Psychology
... • Task of psychology = analyze consciousness into its basic elements; study how elements are related – Focus on sensations (vision, hearing, touch), feelings, images, and perception ...
... • Task of psychology = analyze consciousness into its basic elements; study how elements are related – Focus on sensations (vision, hearing, touch), feelings, images, and perception ...
Chapter 7: Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, students
... Chapter 7: Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, students should be able to: ...
... Chapter 7: Learning Objectives After studying this chapter, students should be able to: ...
Intro to Learning and Learning Theories
... Way to understand individual people's different learning styles, and also an explanation of a cycle of experiential learning that applies to us all. Kolb includes this 'cycle of learning' as a central principle in his experiential learning theory. ...
... Way to understand individual people's different learning styles, and also an explanation of a cycle of experiential learning that applies to us all. Kolb includes this 'cycle of learning' as a central principle in his experiential learning theory. ...
Learning Theories and Adult Education
... Behaviorist theory rests on the belief that all forms of behavior (including learning) are composed of simple stimulus-response events that can be seen and measured. More complex learning is the gradual building up of larger and more complex patterns of stimulus and response. According to Behavioris ...
... Behaviorist theory rests on the belief that all forms of behavior (including learning) are composed of simple stimulus-response events that can be seen and measured. More complex learning is the gradual building up of larger and more complex patterns of stimulus and response. According to Behavioris ...
Behavioral Views of Learning Chapter 6 “We are by nature
... behavior and that learning is observable. Cognitivists learning as an internal process, cannot be observed directly….changes in behavior are a reflection of internal change ...
... behavior and that learning is observable. Cognitivists learning as an internal process, cannot be observed directly….changes in behavior are a reflection of internal change ...
556 04 Social Learning Theory
... observing others’ behavior and the outcomes of their behavior • Socialization: Process by which society teaches children to behave like the ideal adults of the society – One of the most powerful socialization forces is observational learning – Children learn to behave like others in their culture be ...
... observing others’ behavior and the outcomes of their behavior • Socialization: Process by which society teaches children to behave like the ideal adults of the society – One of the most powerful socialization forces is observational learning – Children learn to behave like others in their culture be ...
Introduction to Assistive Technology (AT)
... and accommodation of information. How information is presented is important. When information is introduced as an aid to problem solving, it functions as a tool rather than an isolated arbitrary fact. Learning should be whole, authentic, and "real": Piaget helps us to understand that meaning is cons ...
... and accommodation of information. How information is presented is important. When information is introduced as an aid to problem solving, it functions as a tool rather than an isolated arbitrary fact. Learning should be whole, authentic, and "real": Piaget helps us to understand that meaning is cons ...
Learning - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Discrimination: responding to only a specific stimuli Ch. 6 ...
... • Discrimination: responding to only a specific stimuli Ch. 6 ...
Learning Ch schedule-study guide
... operant conditioning, in which we learn to engage in behaviors that are rewarded and to avoid behaviors that are punished; and observational learning, in which we learn by observing and imitating others. The chapter also covers several important issues, including the generality of principles of lear ...
... operant conditioning, in which we learn to engage in behaviors that are rewarded and to avoid behaviors that are punished; and observational learning, in which we learn by observing and imitating others. The chapter also covers several important issues, including the generality of principles of lear ...
CHild Growth Notes on history and developmental theorists
... increases the behavior it follows. There are two kinds of reinforcers: – Positive reinforcers are favorable events or outcomes that are presented after the behavior. – Negative reinforcers involve the removal of an unfavorable events or outcomes after the display of a behavior. ...
... increases the behavior it follows. There are two kinds of reinforcers: – Positive reinforcers are favorable events or outcomes that are presented after the behavior. – Negative reinforcers involve the removal of an unfavorable events or outcomes after the display of a behavior. ...
Psychological behaviorism

Psychological behaviorism is a form of behaviorism - a major theory within psychology which holds that behaviors are learned through positive and negative reinforcements. The theory recommends that psychological concepts (such as personality, learning and emotion) are to be explained in terms of observable behaviors that respond to stimulus. Behaviorism was first developed by John B. Watson (1912), who coined the term ""behaviorism,"" and then B.F. Skinner who developed what is known as ""radical behaviorism."" Watson and Skinner rejected the idea that psychological data could be obtained through introspection or by an attempt to describe consciousness; all psychological data, in their view, was to be derived from the observation of outward behavior. Recently, Arthur W. Staats has proposed a psychological behaviorism - a ""paradigmatic behaviorist theory"" which argues that personality consists of a set of learned behavioral patterns, acquired through the interaction between an individual's biology, environment, cognition, and emotion. Holth also critically reviews psychological behaviorism as a ""path to the grand reunification of psychology and behavior analysis"".Psychological behaviorism’s theory of personality represents one of psychological behaviorism’s central differences from the preceding behaviorism’s; the other parts of the broader approach as they relate to each other will be summarized in the paradigm sections