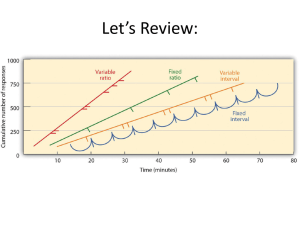
Practice in IDing Variables
... Dorothea Dix, Sigmund Freud, G. Stanley Hall, William James, Ivan Pavlov, Jean Piaget, Carl Rogers, B. F. Skinner, Margaret Floy Washburn, John B. Watson, Wilhelm Wundt). Overview: Psychology is an empirical discipline. Psychologists develop knowledge by doing research. Research provides guidance fo ...
... Dorothea Dix, Sigmund Freud, G. Stanley Hall, William James, Ivan Pavlov, Jean Piaget, Carl Rogers, B. F. Skinner, Margaret Floy Washburn, John B. Watson, Wilhelm Wundt). Overview: Psychology is an empirical discipline. Psychologists develop knowledge by doing research. Research provides guidance fo ...
Define: learning, reinforcement, response, antecedents, consequence
... Define: learning, reinforcement, response, antecedents, consequence Understand Classical Conditioning and all associated vocabulary Define informational view of Classical Conditioning Define extinction Define generalization Define discrimination Define phobia Understand operant conditioning and all ...
... Define: learning, reinforcement, response, antecedents, consequence Understand Classical Conditioning and all associated vocabulary Define informational view of Classical Conditioning Define extinction Define generalization Define discrimination Define phobia Understand operant conditioning and all ...
History of Psych
... Concerned with how mental processes are used by human and animals in adapting to their environment. Broadened psychology to include behavior as well as mental processes Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) emphasizes the role of unconscious mental forces & conflicts in determining behavior importance of ...
... Concerned with how mental processes are used by human and animals in adapting to their environment. Broadened psychology to include behavior as well as mental processes Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) emphasizes the role of unconscious mental forces & conflicts in determining behavior importance of ...
Week 8 Presentation
... Classical Conditioning When an unconditioned stimulus and its conditioned response are paired with a previously neutral stimulus, the neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus (learned stimulus) that evokes a conditioned response (learned response) ...
... Classical Conditioning When an unconditioned stimulus and its conditioned response are paired with a previously neutral stimulus, the neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus (learned stimulus) that evokes a conditioned response (learned response) ...
Lecture9-OperantCond..
... If you spend more time studying the material in PsychPortal, you will earn all the possible points. ...
... If you spend more time studying the material in PsychPortal, you will earn all the possible points. ...
Presentation
... stimulus to reverse the effects of the phobia. Conditioned taste aversion – when exposure to a noxious substance causes sickness and results in the individual associating the food with the sickness, making him or her avoid that food in the future ...
... stimulus to reverse the effects of the phobia. Conditioned taste aversion – when exposure to a noxious substance causes sickness and results in the individual associating the food with the sickness, making him or her avoid that food in the future ...
Learning Theories - School of Computing
... The teaching machine is merely a device for presenting the set of frames of which the program is composed. However, it is not supplementary but all-inclusive. The program will do all the teaching through a response/reward mechanism. Skinner also noted that the learning process should be divided into ...
... The teaching machine is merely a device for presenting the set of frames of which the program is composed. However, it is not supplementary but all-inclusive. The program will do all the teaching through a response/reward mechanism. Skinner also noted that the learning process should be divided into ...
iClicker Questions Section 6.2
... The organism learns an association between a behavior and a punishment. The organism learns an association between a behavior and a consequence. E. None of the above ...
... The organism learns an association between a behavior and a punishment. The organism learns an association between a behavior and a consequence. E. None of the above ...
Notes-Undergrad-Child-Psychopath-Wk1Day2
... Positive Reinforcement – a positively viewed stimulus follows a particular behavior and strengthens or increases the behavior. Negative Reinforcement – a negatively viewed stimulus is removed or avoided and strengthens or increases the behavior (e.g., carrying an umbrella); 2 primary types: avoidan ...
... Positive Reinforcement – a positively viewed stimulus follows a particular behavior and strengthens or increases the behavior. Negative Reinforcement – a negatively viewed stimulus is removed or avoided and strengthens or increases the behavior (e.g., carrying an umbrella); 2 primary types: avoidan ...
Learning Practice Exam 1. The most crucial ingredient in all learning
... more; more less; less more; less more; less less; more B. F. Skinner discounted the role of ________ in learning. negative reinforcement punishment cognitive processes secondary reinforcement effective parenting Mr. Schlenker has improved worker productivity at his furniture manufacturing plant by o ...
... more; more less; less more; less more; less less; more B. F. Skinner discounted the role of ________ in learning. negative reinforcement punishment cognitive processes secondary reinforcement effective parenting Mr. Schlenker has improved worker productivity at his furniture manufacturing plant by o ...
APPLIED LINGUISTICS LANE 622
... Rote-learned materials do not interact with cognition in a substantive ...
... Rote-learned materials do not interact with cognition in a substantive ...
Response - Macmillan Learning
... Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely ...
... Thorndike’s principle that behaviors followed by favorable consequences become more likely ...
reinforcement
... For this type of learning, the qualities of the intellect are very influential. The individual is confronted with a problem. For a while, the individual cannot make any progress in solving the problem. However, after a while, he/she suddenly recognizes the solution by reorganizing his/her perception ...
... For this type of learning, the qualities of the intellect are very influential. The individual is confronted with a problem. For a while, the individual cannot make any progress in solving the problem. However, after a while, he/she suddenly recognizes the solution by reorganizing his/her perception ...
PERSONALITY THEORY AND ASSESSMENT
... • Personality includes the unique pattern of psychological and behavioral characteristics that distinguishes each of us from everyone else. Personality characteristics are relatively stable and enduring, often developed in childhood and affect the way we think, act, feel and behave. Individual perso ...
... • Personality includes the unique pattern of psychological and behavioral characteristics that distinguishes each of us from everyone else. Personality characteristics are relatively stable and enduring, often developed in childhood and affect the way we think, act, feel and behave. Individual perso ...
Observational Learning
... – Have you ever been punished for something and learned just that you had to stop the behavior in a certain environment, but continued it elsewhere? ...
... – Have you ever been punished for something and learned just that you had to stop the behavior in a certain environment, but continued it elsewhere? ...
Many Ways of Knowing - National Catholic School of Social Service
... theories via 7 questions Focus on people's problems and groups’ problems and how these theories help us understand the problems and help them change Put it all together by applying to case examples ...
... theories via 7 questions Focus on people's problems and groups’ problems and how these theories help us understand the problems and help them change Put it all together by applying to case examples ...
Perspective Chart
... and a half years if one was to read 60 pages a day Also published four books in philosophy! At this time, psychology was not considered something separate from philosophy. In fact, Wundt rejected the idea when someone suggested it to him. ...
... and a half years if one was to read 60 pages a day Also published four books in philosophy! At this time, psychology was not considered something separate from philosophy. In fact, Wundt rejected the idea when someone suggested it to him. ...
Psychological Science, 3rd Edition
... By studying cats’ attempts to escape from a puzzle box, Thorndike was able to formulate his general theory of learning. ...
... By studying cats’ attempts to escape from a puzzle box, Thorndike was able to formulate his general theory of learning. ...
Document
... – In classical conditioning, a person or animal learns to associate a neutral stimulus (the conditioned stimulus, or CS) with a stimulus (the unconditioned stimulus, or US) that naturally produces a behavior (the unconditioned response, or UR). As a result of this association, the previously neutral ...
... – In classical conditioning, a person or animal learns to associate a neutral stimulus (the conditioned stimulus, or CS) with a stimulus (the unconditioned stimulus, or US) that naturally produces a behavior (the unconditioned response, or UR). As a result of this association, the previously neutral ...
07Learning
... • Negative reinforcement Increases behavior Remove an unwanted stimulus • E.g. Bill cleans up his room to ...
... • Negative reinforcement Increases behavior Remove an unwanted stimulus • E.g. Bill cleans up his room to ...
AP Psychology
... reinforcement. (see Why Reinforcers Work) 20. Define punishment and describe its role in operant conditioning. Discuss the disadvantages of and guidelines for using punishment. (see Punishment) 21. Discuss how operant conditioning can be used to treat problematic behavior. (see Some Applications of ...
... reinforcement. (see Why Reinforcers Work) 20. Define punishment and describe its role in operant conditioning. Discuss the disadvantages of and guidelines for using punishment. (see Punishment) 21. Discuss how operant conditioning can be used to treat problematic behavior. (see Some Applications of ...
Chapter 5 - IPFW.edu
... III. Processes and Phenomena of Classical Conditioning A. The stage of classical conditioning during which the CS and UCS are paired and the strength of the CR increases is called acquisition. B. Extinction is the process in which the strength of a CR decreases with repeated presentations of the CS ...
... III. Processes and Phenomena of Classical Conditioning A. The stage of classical conditioning during which the CS and UCS are paired and the strength of the CR increases is called acquisition. B. Extinction is the process in which the strength of a CR decreases with repeated presentations of the CS ...
Intro to course and What is learning?
... animals learned Focus on trial and error learning Did NOT have access to Pavlov’s work. Experimented with cats in a puzzle box ...
... animals learned Focus on trial and error learning Did NOT have access to Pavlov’s work. Experimented with cats in a puzzle box ...
Learning, Memory, Emotion and Language - Ping Pong
... acquisition of new information y Memory: the result of ...
... acquisition of new information y Memory: the result of ...
may - Suffolk County Community College
... crash of thunder. This best illustrates: A) operant conditioning. B) physiological psychology. C) observational learning. D) classical conditioning. 38. The researcher most closely associated with the study of classical conditioning is: A) Thorndike. B) Skinner. C) Bandura. D) Pavlov. 39. John B. Wa ...
... crash of thunder. This best illustrates: A) operant conditioning. B) physiological psychology. C) observational learning. D) classical conditioning. 38. The researcher most closely associated with the study of classical conditioning is: A) Thorndike. B) Skinner. C) Bandura. D) Pavlov. 39. John B. Wa ...
Psychological behaviorism

Psychological behaviorism is a form of behaviorism - a major theory within psychology which holds that behaviors are learned through positive and negative reinforcements. The theory recommends that psychological concepts (such as personality, learning and emotion) are to be explained in terms of observable behaviors that respond to stimulus. Behaviorism was first developed by John B. Watson (1912), who coined the term ""behaviorism,"" and then B.F. Skinner who developed what is known as ""radical behaviorism."" Watson and Skinner rejected the idea that psychological data could be obtained through introspection or by an attempt to describe consciousness; all psychological data, in their view, was to be derived from the observation of outward behavior. Recently, Arthur W. Staats has proposed a psychological behaviorism - a ""paradigmatic behaviorist theory"" which argues that personality consists of a set of learned behavioral patterns, acquired through the interaction between an individual's biology, environment, cognition, and emotion. Holth also critically reviews psychological behaviorism as a ""path to the grand reunification of psychology and behavior analysis"".Psychological behaviorism’s theory of personality represents one of psychological behaviorism’s central differences from the preceding behaviorism’s; the other parts of the broader approach as they relate to each other will be summarized in the paradigm sections