Psychobiology—Behavioral Problems Seeking Biological Solutions
... independent motility of eyes, head, and body in man; a fly has to move its body to change its view. He also points out that these similarities need not imply that visual motor control in fly and man have a common ancestor, but rather that visual processing itself has specific requirements (e.g., mai ...
... independent motility of eyes, head, and body in man; a fly has to move its body to change its view. He also points out that these similarities need not imply that visual motor control in fly and man have a common ancestor, but rather that visual processing itself has specific requirements (e.g., mai ...
Document
... He did not prefer the atmosphere that formal schooling produced, so instead of going to college he traveled around Europe, keeping a diary of his experiences After a year of doing this, he returned to Germany and enrolled in art school After several years, Erikson began to teach art and other subjec ...
... He did not prefer the atmosphere that formal schooling produced, so instead of going to college he traveled around Europe, keeping a diary of his experiences After a year of doing this, he returned to Germany and enrolled in art school After several years, Erikson began to teach art and other subjec ...
PERSONALITY Social-cognitive Psychoanalytic Humanism
... Rescorla’s research on predictability Garcia’s research of biological predispositions * easier to condition food aversions to taste rather than sight or sound * easiest to condition behaviors that promote survival Applications: Aversive conditioning—pairing a negative stimulus with a desired stimulu ...
... Rescorla’s research on predictability Garcia’s research of biological predispositions * easier to condition food aversions to taste rather than sight or sound * easiest to condition behaviors that promote survival Applications: Aversive conditioning—pairing a negative stimulus with a desired stimulu ...
File - R. Anthony James` Electronic Portfolio
... B F Skinner An Evaluation of Operant Conditioning and its Applications for instruction Anthony James EDTC 611 Learning and Cognition Spring 2006 ...
... B F Skinner An Evaluation of Operant Conditioning and its Applications for instruction Anthony James EDTC 611 Learning and Cognition Spring 2006 ...
Varieties of Thinking - World Academy of Art and Science
... Divides reality into smaller parts Aggregates the parts to reconstitute the whole Constructs concepts and conceptual systems out of the pieces Separates the observer from the object Concentrates by self-limitation and self-absorption Views reality from a single perspective and set of premises ...
... Divides reality into smaller parts Aggregates the parts to reconstitute the whole Constructs concepts and conceptual systems out of the pieces Separates the observer from the object Concentrates by self-limitation and self-absorption Views reality from a single perspective and set of premises ...
Learning and Behaviour- Core course of BSc
... a) People can learn through observing others. b) Learning doesn't always result in an immediate change. c) People set goals for themselves and strive to achieve their goals. d) People will learn something only if reinforcing or punishing consequences follow their behavior. e) As people develop, they ...
... a) People can learn through observing others. b) Learning doesn't always result in an immediate change. c) People set goals for themselves and strive to achieve their goals. d) People will learn something only if reinforcing or punishing consequences follow their behavior. e) As people develop, they ...
The cognitive revolution: a historical perspective
... mentalistic hypotheses about the cognitive processes responsible for the verbal behaviors we observe. The end of behaviorism Behaviorism was an exciting adventure for experimental psychology but by the mid-1950s it had become apparent that it could not succeed. As Chomsky remarked, defining psycholo ...
... mentalistic hypotheses about the cognitive processes responsible for the verbal behaviors we observe. The end of behaviorism Behaviorism was an exciting adventure for experimental psychology but by the mid-1950s it had become apparent that it could not succeed. As Chomsky remarked, defining psycholo ...
psychological foundations and research
... It is an academic elective that will introduce students to the history of Psychology, concepts, methodology, and vocabulary. Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. It is a unique science that often necessitates the use of special measurements and research methods. The c ...
... It is an academic elective that will introduce students to the history of Psychology, concepts, methodology, and vocabulary. Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes. It is a unique science that often necessitates the use of special measurements and research methods. The c ...
Psychological Perspectives
... Reaction Patterns: specific reactionsconditioned responses-past experiencepositive response = likes negative response = dislikes ...
... Reaction Patterns: specific reactionsconditioned responses-past experiencepositive response = likes negative response = dislikes ...
Chapter 5: Learning and Behavior A. Learning
... latent learning, the facilitation of learning after the stimuli that guide behavior have been experienced but without the behavior being reinforced in their presence 3. Perceptual learning is acquired by use of polysensory neurons (neurons that take inputs from more than one sense) to particular com ...
... latent learning, the facilitation of learning after the stimuli that guide behavior have been experienced but without the behavior being reinforced in their presence 3. Perceptual learning is acquired by use of polysensory neurons (neurons that take inputs from more than one sense) to particular com ...
Behavior Modification: Introduction and Implications
... the Veterans Administration. There is also a variety of other material, most of which relates to behavior modification projects conducted or funded by these departments. Accounts of four court cases in which individual rights were at issue are likewise included.5 The Subcommittee report, however, do ...
... the Veterans Administration. There is also a variety of other material, most of which relates to behavior modification projects conducted or funded by these departments. Accounts of four court cases in which individual rights were at issue are likewise included.5 The Subcommittee report, however, do ...
PERSONALITY THEORY AND ASSESSMENT
... and focuses on the importance of learned thoughts or cognitions as important variables in shaping personality patterns. One example is JULIAN ROTTER'S theory on LOCUS OF CONTROL. He proposes that it is our belief about a situation or experience that affects behavior. We either believe we are in cont ...
... and focuses on the importance of learned thoughts or cognitions as important variables in shaping personality patterns. One example is JULIAN ROTTER'S theory on LOCUS OF CONTROL. He proposes that it is our belief about a situation or experience that affects behavior. We either believe we are in cont ...
Chapter 6
... Long-term potentiation: Biological process involving physical changes that strengthen the synapses in groups of nerve cells; believed to be the neural basis of learning ...
... Long-term potentiation: Biological process involving physical changes that strengthen the synapses in groups of nerve cells; believed to be the neural basis of learning ...
Theory Application Paper Sarah Merve Ahmad Koç University
... I am going to analyze his behavior from two different perspectives. Firstly, I want to use Skinner's approach , If we look at this case with Skinner's glasses, the first thing that we should do is no to underestimate the importance of environment and we see that his behavior is mainly shaped by his ...
... I am going to analyze his behavior from two different perspectives. Firstly, I want to use Skinner's approach , If we look at this case with Skinner's glasses, the first thing that we should do is no to underestimate the importance of environment and we see that his behavior is mainly shaped by his ...
CHAPTER 6: LEARNING
... Offering of rewards – being positively reinforced Shaping – a way of teaching complex behaviors in which one first reinforces small steps in the right direction ...
... Offering of rewards – being positively reinforced Shaping – a way of teaching complex behaviors in which one first reinforces small steps in the right direction ...
Unit VI Learning Syllabus
... brought about by his or her repeated experiences in that situation provided that the behavioral change cannot be explained on the basis of native response tendencies, maturation, or temporary states of the subject (ex. fatigue, drugs). Types of learning we will study in this unit: 1. Classical Condi ...
... brought about by his or her repeated experiences in that situation provided that the behavioral change cannot be explained on the basis of native response tendencies, maturation, or temporary states of the subject (ex. fatigue, drugs). Types of learning we will study in this unit: 1. Classical Condi ...
Classical Conditioning
... principles of classical conditioning? • Learning of an association does not require repeated pairings of the stimulus and response. • The time delay is in hours and not seconds. ...
... principles of classical conditioning? • Learning of an association does not require repeated pairings of the stimulus and response. • The time delay is in hours and not seconds. ...
Limitations of Prompt-Based Training
... the environment and arranging certain contingencies that set the occasion for desirable behaviors. We manage the antecedent and consequence stimuli to achieve our behavioral objectives. It is important to arrange the relationship between the antecedents, behaviors and consequences as efficiently as ...
... the environment and arranging certain contingencies that set the occasion for desirable behaviors. We manage the antecedent and consequence stimuli to achieve our behavioral objectives. It is important to arrange the relationship between the antecedents, behaviors and consequences as efficiently as ...
UNIT I:
... Stage III: Pavlov decided to link both the presentation of meat and the ringing of a bell one after the other with an interval of 5 minutes. After repeatedly hearing the bell before getting the meat, the dog began to salivate as soon the bell rang. There is an association or link between meat and ri ...
... Stage III: Pavlov decided to link both the presentation of meat and the ringing of a bell one after the other with an interval of 5 minutes. After repeatedly hearing the bell before getting the meat, the dog began to salivate as soon the bell rang. There is an association or link between meat and ri ...
Chapter 7 Week 1
... "At last, they are getting along." He returns to work on his computerwithout saying anything to the kids. h) A spoiled child is being driven past a fast-food restaurant when he begins screaming that he must have some French fries or he just won’t survive. The parents surrender and buy the fries, at ...
... "At last, they are getting along." He returns to work on his computerwithout saying anything to the kids. h) A spoiled child is being driven past a fast-food restaurant when he begins screaming that he must have some French fries or he just won’t survive. The parents surrender and buy the fries, at ...
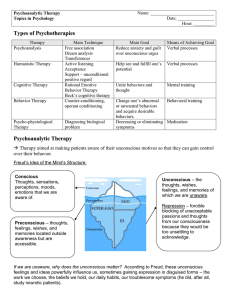
Psychoanalytic Therapy Notes
... Therapy aimed at making patients aware of their unconscious motives so that they can gain control over their behavior. Freud’s Idea of the Mind’s Structure: Conscious Thoughts, sensations, perceptions, moods, emotions that we are aware of. ...
... Therapy aimed at making patients aware of their unconscious motives so that they can gain control over their behavior. Freud’s Idea of the Mind’s Structure: Conscious Thoughts, sensations, perceptions, moods, emotions that we are aware of. ...
Words at Work: Learning terms like "positive punishment"
... signify something that increases the frequency of a behavior, and for punishment to be something that decreases it. It's not hard to label chunks of organic chicken, liberally handed out at the right time, as reinforcements. And it makes sense that correcting a dog with a choke collar every time he ...
... signify something that increases the frequency of a behavior, and for punishment to be something that decreases it. It's not hard to label chunks of organic chicken, liberally handed out at the right time, as reinforcements. And it makes sense that correcting a dog with a choke collar every time he ...
Learning: Classical and Operant Conditioning Chapter 7
... First step in self-control is to define the problem. People who have a very poor opinion of themselves would have to define the problem more concretely. Keep track of self-deprecating thoughts and remarks you make—may lead to a start in changing behavior. ...
... First step in self-control is to define the problem. People who have a very poor opinion of themselves would have to define the problem more concretely. Keep track of self-deprecating thoughts and remarks you make—may lead to a start in changing behavior. ...