Classical Conditioning
... o Classical Conditioning: Initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus Neutral stimulus begins triggering conditioned response o Operant Conditioning: The strengthening of a reinforced response o Neutral stimulus should come (.5 seconds) before the uncondition ...
... o Classical Conditioning: Initial stage, when one links a neutral stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus Neutral stimulus begins triggering conditioned response o Operant Conditioning: The strengthening of a reinforced response o Neutral stimulus should come (.5 seconds) before the uncondition ...
1 - QuizWiki
... test back, he said, "That's the last time I use a tape recorder to help me study!" Ihab's remark indicates that he experienced what behaviorists call A. classical conditioning. B. positive reinforcement. C. negative reinforcement. Correct ...
... test back, he said, "That's the last time I use a tape recorder to help me study!" Ihab's remark indicates that he experienced what behaviorists call A. classical conditioning. B. positive reinforcement. C. negative reinforcement. Correct ...
Pavlov and Skinner: Two lives in science ( an introduction to B. F.
... absence of a light. The rat comes to press the lever in the presence of the discriminative stimulus, the light, but not in its absence. As we shall see, at first the respondent and operant vocabularies overlapped: It took Skinner a long time to distinguish between the Pavlovian conditional stimulus ...
... absence of a light. The rat comes to press the lever in the presence of the discriminative stimulus, the light, but not in its absence. As we shall see, at first the respondent and operant vocabularies overlapped: It took Skinner a long time to distinguish between the Pavlovian conditional stimulus ...
Chapter 8: Conditioning and Learning
... In the example shown, a horn precedes a puff of air to the eye. Eventually the horn alone will produce an eye blink. In operant conditioning, a response that is followed by a reinforcing consequence becomes more likely to occur on future occasions. In the example shown, a dog learns to sit up when i ...
... In the example shown, a horn precedes a puff of air to the eye. Eventually the horn alone will produce an eye blink. In operant conditioning, a response that is followed by a reinforcing consequence becomes more likely to occur on future occasions. In the example shown, a dog learns to sit up when i ...
Chapter 8: Conditioning and Learning
... In the example shown, a horn precedes a puff of air to the eye. Eventually the horn alone will produce an eye blink. In operant conditioning, a response that is followed by a reinforcing consequence becomes more likely to occur on future occasions. In the example shown, a dog learns to sit up when i ...
... In the example shown, a horn precedes a puff of air to the eye. Eventually the horn alone will produce an eye blink. In operant conditioning, a response that is followed by a reinforcing consequence becomes more likely to occur on future occasions. In the example shown, a dog learns to sit up when i ...
Paper by Daniel Romer (2010) "Adolescent Risk Taking,Impulsivity
... 2000). Mischel et al. (1988) used a simpler task in which children as young as age 4 were given the task of waiting to receive a tempting treat such as a pair of marshmallows. Those children who could deny themselves one marshmallow in order to receive two at a later time were scored as exhibiting p ...
... 2000). Mischel et al. (1988) used a simpler task in which children as young as age 4 were given the task of waiting to receive a tempting treat such as a pair of marshmallows. Those children who could deny themselves one marshmallow in order to receive two at a later time were scored as exhibiting p ...
Learning
... learns to avoid food with a certain taste after a single experience, if eating it is followed by illness ...
... learns to avoid food with a certain taste after a single experience, if eating it is followed by illness ...
Neural Computation and Neuromodulation Underlying Social
... the complexity inherent in natural social interactions. Behavioral variability is even seen in isogenic animals raised under as similar conditions as possible. The degree of behavioral variability observed in a population of animals can be different depending on the particular genetic strain, sugges ...
... the complexity inherent in natural social interactions. Behavioral variability is even seen in isogenic animals raised under as similar conditions as possible. The degree of behavioral variability observed in a population of animals can be different depending on the particular genetic strain, sugges ...
Psychological Disorders
... of leaving one’s familiar surroundings because one might have a panic attack in public. • Generalized anxiety disorder - disorder in which a person has feelings of dread and impending doom along with physical symptoms of stress, which lasts six months or more. ...
... of leaving one’s familiar surroundings because one might have a panic attack in public. • Generalized anxiety disorder - disorder in which a person has feelings of dread and impending doom along with physical symptoms of stress, which lasts six months or more. ...
operant conditioning
... In Pavlov’s classical conditioning studies, the dog was restrained in a harness in the cubicle and isolated from all distractions. An experimenter observed the dog through a one-way mirror and, by remote control, presented the dog with food and other conditioning stimuli. A tube carried the saliva f ...
... In Pavlov’s classical conditioning studies, the dog was restrained in a harness in the cubicle and isolated from all distractions. An experimenter observed the dog through a one-way mirror and, by remote control, presented the dog with food and other conditioning stimuli. A tube carried the saliva f ...
View/Open - ESIRC - Emporia State University
... than terminal responses elicited in anticipation of a food reward. According to these authors, the commonality of the pecking response in pigeons favored an explanation based on elicitation rather than on accidental response contingencies. In addition, some researchers suggest that the occurrence of ...
... than terminal responses elicited in anticipation of a food reward. According to these authors, the commonality of the pecking response in pigeons favored an explanation based on elicitation rather than on accidental response contingencies. In addition, some researchers suggest that the occurrence of ...
Objectives:
... Has ability to discern and express even subtle social-emotional nuances such as friendliness, fear, affection, distrust, anger, etc., and at a more basic level, determine if something might be good to eat. ...
... Has ability to discern and express even subtle social-emotional nuances such as friendliness, fear, affection, distrust, anger, etc., and at a more basic level, determine if something might be good to eat. ...
Classical Conditioning
... Thorndike (1898) insisted that it was “unnecessary to invoke reasoning” to explain how the learning took place. Thorndike’s law of effect formed the conceptual starting point for B. F. Skinner’s work in operant conditioning. ...
... Thorndike (1898) insisted that it was “unnecessary to invoke reasoning” to explain how the learning took place. Thorndike’s law of effect formed the conceptual starting point for B. F. Skinner’s work in operant conditioning. ...
Learning - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... specific objects, such as flowers or elephants, as you see here. Each step along this training process is accomplished by the relationship between the behavior (such as making a stroke) and some reward for it. Behaviors that are not desired (such as flicking the paint all over the canvas) are not re ...
... specific objects, such as flowers or elephants, as you see here. Each step along this training process is accomplished by the relationship between the behavior (such as making a stroke) and some reward for it. Behaviors that are not desired (such as flicking the paint all over the canvas) are not re ...
Chapter outline Chapter objectives
... 1. Read the outline for the chapter. Survey the topics for your chapter. This can be found on my website or the table of contents. 2. Read chapter objectives as shown below. The chapter objectives can also be found on the publisher’s website. 3. Read the corresponding section(s). 4. Make a detailed ...
... 1. Read the outline for the chapter. Survey the topics for your chapter. This can be found on my website or the table of contents. 2. Read chapter objectives as shown below. The chapter objectives can also be found on the publisher’s website. 3. Read the corresponding section(s). 4. Make a detailed ...
Modeling Function of Nectar Foraging of Honeybees using Operant
... the type of responses of the environment that change the probability of the behavior being repeated: neutral operant (if the responses do not change the probability of the behavior being repeated), reinforces (if the responses increase the probability of the behavior being repeated and these reinfor ...
... the type of responses of the environment that change the probability of the behavior being repeated: neutral operant (if the responses do not change the probability of the behavior being repeated), reinforces (if the responses increase the probability of the behavior being repeated and these reinfor ...
Educational Psychology Lesson 08 NATURE AND THEORIES OF
... 3. Concept learning. A concept in the form of a mental image denotes a generalized idea about things, persons or events. For example, our concept of 'tree' IS a mental images that up the similarities or common properties of all the different trees we know. We will call a thing 'tree' when it has som ...
... 3. Concept learning. A concept in the form of a mental image denotes a generalized idea about things, persons or events. For example, our concept of 'tree' IS a mental images that up the similarities or common properties of all the different trees we know. We will call a thing 'tree' when it has som ...
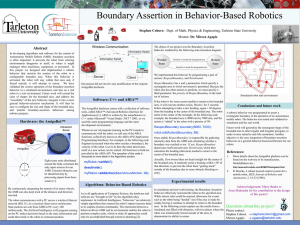
Poster title - Tarleton State University
... In developing algorithms and software for the control of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR), boundary assertion is often important: it prevents the robot from entering environments dangerous to itself, or where it might endanger other machinery, equipment, or personnel. In this project we designed and i ...
... In developing algorithms and software for the control of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR), boundary assertion is often important: it prevents the robot from entering environments dangerous to itself, or where it might endanger other machinery, equipment, or personnel. In this project we designed and i ...
Discontinuity in evolution: how different levels of organization imply
... its fitness. Only less than 1% of successful Os were not affected by mutations in the functional part of the genotype. On the other hand, almost 50% of the same Os did not differ at the functional nervous system level; 80% did not differ at the potential behavior level, and almost 90% did not differ ...
... its fitness. Only less than 1% of successful Os were not affected by mutations in the functional part of the genotype. On the other hand, almost 50% of the same Os did not differ at the functional nervous system level; 80% did not differ at the potential behavior level, and almost 90% did not differ ...
how different levels of organization imply pre
... its fitness. Only less than 1% of successful Os were not affected by mutations in the functional part of the genotype. On the other hand, almost 50% of the same Os did not differ at the functional nervous system level; 80% did not differ at the potential behavior level, and almost 90% did not differ ...
... its fitness. Only less than 1% of successful Os were not affected by mutations in the functional part of the genotype. On the other hand, almost 50% of the same Os did not differ at the functional nervous system level; 80% did not differ at the potential behavior level, and almost 90% did not differ ...
Emergence of Sense-Making Behavior by the Stimulus Avoidance
... spontaneously without having any explicit reward or evaluation function. We call this a “learning by stimulation avoidance” (LSA) principle. LSA assures a homeostatic property as it sustains stability and variation simultaneously. Shahaf and Marom (2001) demonstrated that cultured neuronal cells can ...
... spontaneously without having any explicit reward or evaluation function. We call this a “learning by stimulation avoidance” (LSA) principle. LSA assures a homeostatic property as it sustains stability and variation simultaneously. Shahaf and Marom (2001) demonstrated that cultured neuronal cells can ...
UNIT 10-Personality PP 2015-16
... Pros: -importance of one’s subjective view of reality -focusing on the issue of what makes a healthy personality Con: lack a strong research base, overly ...
... Pros: -importance of one’s subjective view of reality -focusing on the issue of what makes a healthy personality Con: lack a strong research base, overly ...
learning - Science of Psychology Home
... • Are there problems or negative side effects associated with the use of punishment? • Can we learn without undergoing classical or operant conditioning? • Does watching violent shows make children more violent? ...
... • Are there problems or negative side effects associated with the use of punishment? • Can we learn without undergoing classical or operant conditioning? • Does watching violent shows make children more violent? ...