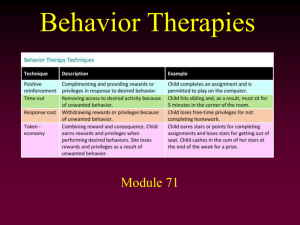
Module 71 - Behavioral Therapy
... • A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick ...
... • A type of counterconditioning that associates an unpleasant state (such as nausea) with an unwanted behavior • The person is replacing a positive (relaxing) but harmful response with a negative/aversive response • Example with alcoholism: Lace a drink with a drug that makes the person becomes sick ...
Option A.4 pt 2 - Peoria Public Schools
... • Compare and contrast reflex conditioning and operant conditioning. a. They are both types of learning. Reflex conditioning is initiated by the environment and experiences that occur before the response , operant conditioning is initiated by the animal testing out a behavior pattern and changes tha ...
... • Compare and contrast reflex conditioning and operant conditioning. a. They are both types of learning. Reflex conditioning is initiated by the environment and experiences that occur before the response , operant conditioning is initiated by the animal testing out a behavior pattern and changes tha ...
Learning Theories in Art Education A variety of
... • Watson took Pavlov’s findings to another level. • Emphasized that learning was observable or measurable, not cognitive. • Believed the key to learning was in conditioning a child from an early age based ...
... • Watson took Pavlov’s findings to another level. • Emphasized that learning was observable or measurable, not cognitive. • Believed the key to learning was in conditioning a child from an early age based ...
operant conditioning (part ii)
... Over justification effect, this phenomenon occurs when an already justifiable activity becomes over justified by the promise or reward. Intrinsic motivation undermines the desire to perform a behavior effectively and for its own sake. Extrinsic motivation is seeking external rewards and avoiding ...
... Over justification effect, this phenomenon occurs when an already justifiable activity becomes over justified by the promise or reward. Intrinsic motivation undermines the desire to perform a behavior effectively and for its own sake. Extrinsic motivation is seeking external rewards and avoiding ...
wp-psych-cond - WordPress.com
... consequences - thus they become more likely to repeat rewarded (reinforced) behaviors and less likely to repeat punished behaviors - ...
... consequences - thus they become more likely to repeat rewarded (reinforced) behaviors and less likely to repeat punished behaviors - ...
BEHAVIORISM JOHN BROADUS WATSON (1878
... Johns Hopkins University. founder and leading exponent of the school of psychology known as behaviorism, which restricts psychology to the study of objectively observable behavior and explains behavior in terms of stimulus and response. Animal Education (1903), Behavior (1914), Behaviorism (1925; re ...
... Johns Hopkins University. founder and leading exponent of the school of psychology known as behaviorism, which restricts psychology to the study of objectively observable behavior and explains behavior in terms of stimulus and response. Animal Education (1903), Behavior (1914), Behaviorism (1925; re ...
Selection by Consequences as a Causal Mode
... useful way of breaking down into more manageable form the original complete … function. ...
... useful way of breaking down into more manageable form the original complete … function. ...
Why do we use ABA? - Hope Center for Autism
... Some antecedents to ABA In the early 1900’s, while researching salivation rates in dogs, Physiologist Ivan Pavlov discovered what he called a conditioned reflex. He noticed the delivery of food (the unconditioned stimulus) would cause the dogs to salivate (the unconditioned response). After some ti ...
... Some antecedents to ABA In the early 1900’s, while researching salivation rates in dogs, Physiologist Ivan Pavlov discovered what he called a conditioned reflex. He noticed the delivery of food (the unconditioned stimulus) would cause the dogs to salivate (the unconditioned response). After some ti ...
History
... Study stimulus-response relations, but do NOT attempt to understand unobservable mental processes ...
... Study stimulus-response relations, but do NOT attempt to understand unobservable mental processes ...
Behavioral Ecology
... learning that is similar to the “cry-wolf” effect. Too much of a good thing can be detrimental in the long run… ...
... learning that is similar to the “cry-wolf” effect. Too much of a good thing can be detrimental in the long run… ...
Reinforcements from the environment ∙Operant conditioning: a type of
... by a “satisfying state of affairs” tend to be repeated and those that produced an “unpleasant state of affairs” were less likely to be repeated. 2. Reinforcement, punishment and the development of operant conditioning ∙ B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) developed the term operant behavior meaning to refer to ...
... by a “satisfying state of affairs” tend to be repeated and those that produced an “unpleasant state of affairs” were less likely to be repeated. 2. Reinforcement, punishment and the development of operant conditioning ∙ B.F. Skinner (1904-1990) developed the term operant behavior meaning to refer to ...
Document
... 1. A _________________________ is something that produces a reaction. 2. Classical _________________________ is a simple form of learning in which one stimulus comes to call forth the response that is usually associated with a different stimulus. 3. Russian physiologist Ivan ____________________ dis ...
... 1. A _________________________ is something that produces a reaction. 2. Classical _________________________ is a simple form of learning in which one stimulus comes to call forth the response that is usually associated with a different stimulus. 3. Russian physiologist Ivan ____________________ dis ...
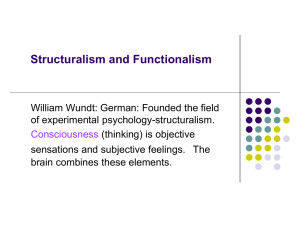
Structuralism and Functionalism
... B.F. Skinner: Skinner expanded behaviorist theory, added the concept of reinforcement. The Gestalt Theory: German/ Max Werthheimer and Wolfgang Kohler. Thought processes work as whole not in parts. The mind is actively learning and problem solving. Behavior is learned and adaptive. Sigmund Freud: Au ...
... B.F. Skinner: Skinner expanded behaviorist theory, added the concept of reinforcement. The Gestalt Theory: German/ Max Werthheimer and Wolfgang Kohler. Thought processes work as whole not in parts. The mind is actively learning and problem solving. Behavior is learned and adaptive. Sigmund Freud: Au ...
6AnimalBehavior
... 2. How does the animal’s experience during growth and development influence the response? (proximate) 3. How does the behavior aid survival and reproduction? (ultimate) 4. What is the behavior’s evolutionary history? (ultimate) ...
... 2. How does the animal’s experience during growth and development influence the response? (proximate) 3. How does the behavior aid survival and reproduction? (ultimate) 4. What is the behavior’s evolutionary history? (ultimate) ...
Applied Behavior Analysis Vocabulary Antecedent stimulus
... Operant conditioning – the arrangement of environmental variables to establish a functional relationship between a voluntary behavior & its consequences Positive Reinforcement – the contingent presentation of a stimulus immediately following a response, which increases the future rate and/or probabi ...
... Operant conditioning – the arrangement of environmental variables to establish a functional relationship between a voluntary behavior & its consequences Positive Reinforcement – the contingent presentation of a stimulus immediately following a response, which increases the future rate and/or probabi ...
9. What evidence led Thorndike to propose the “law of effect”? • Law
... Cat in a puzzle box: Thorndike used a fish reward to entice cats to find their way out of a puzzle box through a series of maneuvers. The cats’ performance tended to improve with successive trials. B.F. Skinner elaborated on Thorndike’s research 10. What is operant conditioning, and how is opera ...
... Cat in a puzzle box: Thorndike used a fish reward to entice cats to find their way out of a puzzle box through a series of maneuvers. The cats’ performance tended to improve with successive trials. B.F. Skinner elaborated on Thorndike’s research 10. What is operant conditioning, and how is opera ...
Week Three 7 11 12 Overview of Psychological Theories and OT
... Relationships to objects in environment are integral to development of ego OT uses activities requiring clients to interact with both human and non human objects Helps to have client reveal feelings and needs “The potential of activities in their own right to represent, reflect, and infers social, ...
... Relationships to objects in environment are integral to development of ego OT uses activities requiring clients to interact with both human and non human objects Helps to have client reveal feelings and needs “The potential of activities in their own right to represent, reflect, and infers social, ...
Stable change in behavior that results from repeated experiences 1
... Main focus 1. Classical conditioning 2. Operant conditioning ...
... Main focus 1. Classical conditioning 2. Operant conditioning ...
ANIMAL BEHAVIORS
... I. ANIMAL BEHAVIORS • Ethology: the study of animal behavior • Behavior (response to a stimulus)is influenced by: – Hormones – Nervous system ...
... I. ANIMAL BEHAVIORS • Ethology: the study of animal behavior • Behavior (response to a stimulus)is influenced by: – Hormones – Nervous system ...
Behaviorism: Applied Logical Positivism
... Edward Tolman: Purposive Behaviorism Argued for a molar, not molecular perspective (reflexes, S-R pairs are molecular) Articulated an intervening variable theory of learning, not a stimulus-response theory Animals and humans engage in latent learning: build up knowledge of their environment from en ...
... Edward Tolman: Purposive Behaviorism Argued for a molar, not molecular perspective (reflexes, S-R pairs are molecular) Articulated an intervening variable theory of learning, not a stimulus-response theory Animals and humans engage in latent learning: build up knowledge of their environment from en ...