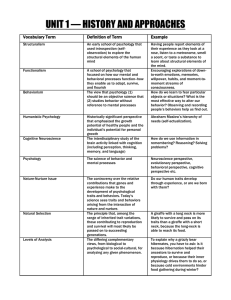
Wade Chapter 8 Learning
... Because of his groundbreaking work B. F. Skinner is often called the greatest American Psychologist. Believed that we could study private emotions and thought by observing our own sensory responses, the verbal reports of others, and the conditions under which such events occur. Thoughts cannot expla ...
... Because of his groundbreaking work B. F. Skinner is often called the greatest American Psychologist. Believed that we could study private emotions and thought by observing our own sensory responses, the verbal reports of others, and the conditions under which such events occur. Thoughts cannot expla ...
Operant Conditioning
... Classical Conditioning was a good start but… B. F. Skinner believed that more behaviors ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Also referred to as Instrumental Conditioning ...
... Classical Conditioning was a good start but… B. F. Skinner believed that more behaviors ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Also referred to as Instrumental Conditioning ...
I. BF Skinner
... Skinner believed that most human and animal behavior is learned through operant conditioning. To Skinner, personality is a pattern or collection of operant behaviors. ...
... Skinner believed that most human and animal behavior is learned through operant conditioning. To Skinner, personality is a pattern or collection of operant behaviors. ...
Psychology 111
... Key Question: What is consciousness for? Emphasis on adaptation Conceptually related to Evolutionary theory Wm. James ...
... Key Question: What is consciousness for? Emphasis on adaptation Conceptually related to Evolutionary theory Wm. James ...
Biological Influences on Learning
... prevention of learning when a stimulus intervenes between the conditioned and unconditioned stimuli or when a behavior occurs between the operant response and reinforcement. Long-delayed learning occurs as the absence of ...
... prevention of learning when a stimulus intervenes between the conditioned and unconditioned stimuli or when a behavior occurs between the operant response and reinforcement. Long-delayed learning occurs as the absence of ...
History of psychology 1:2
... • Pavlov dogs: Pavlov rang a tuning fork each time he gave dog meat. The dog would normally drool when he got the meat. After Pavlov repeated the procedure many times, the dogs would drool when it heard the ring of the tuning fork, even if no food appeared. It had been conditioned to associate the s ...
... • Pavlov dogs: Pavlov rang a tuning fork each time he gave dog meat. The dog would normally drool when he got the meat. After Pavlov repeated the procedure many times, the dogs would drool when it heard the ring of the tuning fork, even if no food appeared. It had been conditioned to associate the s ...
chapter 8 notes
... • Pavlov and Watson both underestimated – the importance of cognition and – how biological constraints effect an organism’s capacity to learn Example of cognition - spiking alcohol with a nausea drug doesn’t work to condition people not to drink because they THINK and blame their nausea on the drug ...
... • Pavlov and Watson both underestimated – the importance of cognition and – how biological constraints effect an organism’s capacity to learn Example of cognition - spiking alcohol with a nausea drug doesn’t work to condition people not to drink because they THINK and blame their nausea on the drug ...
IB Psych Semester 1 Review Sheet
... What is Psychology? Psychology is the study of human ____________________ and ___________________ processes. What are some of the research methods used in psychology? Case Study = ...
... What is Psychology? Psychology is the study of human ____________________ and ___________________ processes. What are some of the research methods used in psychology? Case Study = ...
Innate and Learned Behavior
... from their parents, and in determining behaviour later in life (such as courtship and mating) Imprinting occurs during a ...
... from their parents, and in determining behaviour later in life (such as courtship and mating) Imprinting occurs during a ...
Bolt ModEP7e LG19.65-68
... operant conditioning principles at school, at work, and at home. Skinner has been criticized for repeatedly insisting that external influences, not internal thoughts and feelings, shape behavior and for urging the use of operant principles to control people’s behavior. Critics argue that he dehumani ...
... operant conditioning principles at school, at work, and at home. Skinner has been criticized for repeatedly insisting that external influences, not internal thoughts and feelings, shape behavior and for urging the use of operant principles to control people’s behavior. Critics argue that he dehumani ...
02QUIZ08 ( 44K)
... 8. B. F. Skinner believed that teaching machines could promote effective learning because they allow for both: A) continuous reinforcement and latent learning. B) positive reinforcement and punishment. C) classical and operant conditioning. D) shaping and immediate reinforcement. E) observational le ...
... 8. B. F. Skinner believed that teaching machines could promote effective learning because they allow for both: A) continuous reinforcement and latent learning. B) positive reinforcement and punishment. C) classical and operant conditioning. D) shaping and immediate reinforcement. E) observational le ...
EDS 743 Spring 2017 Social Learning Theory of Albert Bandura
... emotional reactions of others. Bandura (1977) states: "Learning would be exceedingly laborious, not to mention hazardous, if people had to rely solely on the effects of their own actions to inform them what to do. Fortunately, most human behavior is learned observationally through modeling: from obs ...
... emotional reactions of others. Bandura (1977) states: "Learning would be exceedingly laborious, not to mention hazardous, if people had to rely solely on the effects of their own actions to inform them what to do. Fortunately, most human behavior is learned observationally through modeling: from obs ...
051 Classical Conditioning
... Vocabulary: Define the following terms in your own words Learning: ...
... Vocabulary: Define the following terms in your own words Learning: ...
Learning
... administered in a small examination room at a clinic. The drug itself causes increased heart rate but after several trips to the clinic, simply being in a small room causes an increased heart rate. Another example of classical conditioning is known as the appetizer effect. If there are otherwise neu ...
... administered in a small examination room at a clinic. The drug itself causes increased heart rate but after several trips to the clinic, simply being in a small room causes an increased heart rate. Another example of classical conditioning is known as the appetizer effect. If there are otherwise neu ...
File
... • Schedules –Fixed-ratio schedule –Variable-ratio schedule –Fixed-interval schedule –Variable-interval schedule ...
... • Schedules –Fixed-ratio schedule –Variable-ratio schedule –Fixed-interval schedule –Variable-interval schedule ...
AP Psychology Chapter 5—Learning Ms. Chauvin Learning— 3
... and of biological constraints on an organism’s capacity to ___________________ a. Biological Predispositions— 1) Garcia and Koelling’s work on 6. Pavlov’s Legacy— two important reasons why Pavlov’s work so important: *classical conditioning— *Pavlov showed us that 7. Applications of Classical Condi ...
... and of biological constraints on an organism’s capacity to ___________________ a. Biological Predispositions— 1) Garcia and Koelling’s work on 6. Pavlov’s Legacy— two important reasons why Pavlov’s work so important: *classical conditioning— *Pavlov showed us that 7. Applications of Classical Condi ...
Why Do Animals Behave - University of Arizona
... Operant conditioning occurs when an animal voluntarily modifies its behavior following positive or negative consequences. Reinforcement and punishment are the primary tools used by animal trainers to condition certain behaviors via operant conditioning. When a desired behavior is rewarded by positiv ...
... Operant conditioning occurs when an animal voluntarily modifies its behavior following positive or negative consequences. Reinforcement and punishment are the primary tools used by animal trainers to condition certain behaviors via operant conditioning. When a desired behavior is rewarded by positiv ...
Chap 5 LO`s
... 7. Describe the essential characteristics of insight learning, latent learning, and social learning. 8. Apply learning principles to explain emotional learning, taste aversion, superstitious behavior, and learned helplessness. 9. Suggest how behavior modification, biofeedback, coping strategies, and ...
... 7. Describe the essential characteristics of insight learning, latent learning, and social learning. 8. Apply learning principles to explain emotional learning, taste aversion, superstitious behavior, and learned helplessness. 9. Suggest how behavior modification, biofeedback, coping strategies, and ...
LEARNING
... A. Relatively permanent change in a behavior to a given situation brought about by repeated experiences in that situation – Changes can’t be explained by native response tendencies, maturation, or temporary states of the person or other animal (e.g. fatigue, drugs, etc) ...
... A. Relatively permanent change in a behavior to a given situation brought about by repeated experiences in that situation – Changes can’t be explained by native response tendencies, maturation, or temporary states of the person or other animal (e.g. fatigue, drugs, etc) ...
Laws of association
... • Comparative Cognition and Evolution of Intelligence • Charles Darwin expanded on Descartes ...
... • Comparative Cognition and Evolution of Intelligence • Charles Darwin expanded on Descartes ...
Learning
... Fixed interval (FI)—reinforcer is delivered for the first response after a fixed period of time has elapsed Variable interval (VI)—reinforcer is delivered for the first response after an average time has elapsed, differs between trials ...
... Fixed interval (FI)—reinforcer is delivered for the first response after a fixed period of time has elapsed Variable interval (VI)—reinforcer is delivered for the first response after an average time has elapsed, differs between trials ...
Skinner - Operant Conditioning
... environment. In the Skinner study, because food followed a particular behavior the rats learned to repeat that behavior, e.g. operant conditioning. • There is little difference between the learning that takes place in humans and that in other animals. Therefore research (e.g. operant conditioning) c ...
... environment. In the Skinner study, because food followed a particular behavior the rats learned to repeat that behavior, e.g. operant conditioning. • There is little difference between the learning that takes place in humans and that in other animals. Therefore research (e.g. operant conditioning) c ...
Behavioral Social-Learning Approach
... Watson’s main legacy is seen in the shift from subjective introspection into a system of explanation that advocated the operational definition of variables- that is- any variable studied needs to be defined in terms of specific operations that can be used to measure it and to quantify it. In additio ...
... Watson’s main legacy is seen in the shift from subjective introspection into a system of explanation that advocated the operational definition of variables- that is- any variable studied needs to be defined in terms of specific operations that can be used to measure it and to quantify it. In additio ...