Model of Employee Behavior
... co-workers, and (B) being very competent and efficient in doing the job, what combination of the two aspects would you like best? (Use the scale below to make your response for this question.) 1 = 100% A 4 = 40% A, 60%B ...
... co-workers, and (B) being very competent and efficient in doing the job, what combination of the two aspects would you like best? (Use the scale below to make your response for this question.) 1 = 100% A 4 = 40% A, 60%B ...
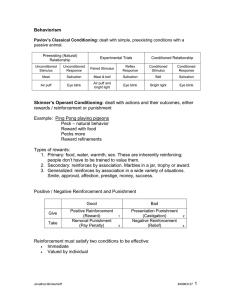
Behaviorism
... 3. Don’t get angry – keep the responsibility where it belongs. Effective: I’m sorry you’ve made the choice to loose part of your recess. Ineffective: How many times will I have to tell you to stop talking? 4. Don’t argue or debate 5. Accept feelings, then state the sad truth. I can see you’re upse ...
... 3. Don’t get angry – keep the responsibility where it belongs. Effective: I’m sorry you’ve made the choice to loose part of your recess. Ineffective: How many times will I have to tell you to stop talking? 4. Don’t argue or debate 5. Accept feelings, then state the sad truth. I can see you’re upse ...
057 Learning by Observation
... 7. ***Cite at least three pieces of evidence that watching violent programs may increase the likelihood of later violence OR a lack of empathy in viewers.*** ...
... 7. ***Cite at least three pieces of evidence that watching violent programs may increase the likelihood of later violence OR a lack of empathy in viewers.*** ...
Catalog Program and Course Descriptions
... students will take what they have learned in previous courses and practicum experience and apply it to behavior problems of social significance. Specifically, students will define behavioral excesses and deficits in behavioral terms, define environmental variables in observable and measurable terms, ...
... students will take what they have learned in previous courses and practicum experience and apply it to behavior problems of social significance. Specifically, students will define behavioral excesses and deficits in behavioral terms, define environmental variables in observable and measurable terms, ...
Theory - ocedtheories
... to schedules of reinforcement (e.g. interval versus ratio) and their effects on establishing and maintaining behavior. ...
... to schedules of reinforcement (e.g. interval versus ratio) and their effects on establishing and maintaining behavior. ...
learning memory anx disorders rv game (1)
... 3. Why did the mice in Tolman's experiment who had been exposed to the maze but not rewarded for completing it (at first) begin to complete the maze at much quicker rates when they began to be rewarded? 4. What is abstract learning? 5. What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivatio ...
... 3. Why did the mice in Tolman's experiment who had been exposed to the maze but not rewarded for completing it (at first) begin to complete the maze at much quicker rates when they began to be rewarded? 4. What is abstract learning? 5. What is the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivatio ...
Memories Part II Learning
... to teach students how to add several numbers together will often explain the principles behind the method and will then demonstrate the method by solving a sample problem. The students then learn by observing the teacher. This is true of sports as well (watching a team execute certain plays during a ...
... to teach students how to add several numbers together will often explain the principles behind the method and will then demonstrate the method by solving a sample problem. The students then learn by observing the teacher. This is true of sports as well (watching a team execute certain plays during a ...
Introduction to Psychology - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... The neutral stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response ...
... The neutral stimulus that, after association with an unconditioned stimulus, comes to trigger a conditioned response ...
Learning
... • Behaviorism: The view that (1) psychology should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes – Founded by Pavlov, Watson, and Skinner – Most psychologists today agree with (1) but not (2) ...
... • Behaviorism: The view that (1) psychology should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes – Founded by Pavlov, Watson, and Skinner – Most psychologists today agree with (1) but not (2) ...
13 May 2003: Introduction to Animal Behavior • Why study Animal
... • emphasized behavioral plasticity: learning most animals can learn many things – Originated among philosophers and psychologists in the United States. – even complex behavior is forged from simple stimulus-response interactions ...
... • emphasized behavioral plasticity: learning most animals can learn many things – Originated among philosophers and psychologists in the United States. – even complex behavior is forged from simple stimulus-response interactions ...
The Cognitive Revolution: a historical perspective
... What are the benefits of thinking of it as a unified science? What are the detriments? Should people from different disciplines comment regularly on each other’s work? ...
... What are the benefits of thinking of it as a unified science? What are the detriments? Should people from different disciplines comment regularly on each other’s work? ...
Chapter_8-Learning
... Associated Learning • We learn by association • Simpler animals can learn simple associations • Learning that certain events occur together. The events may be two stimuli (classical conditioning) or a response and consequence (operant conditioning) • Examples: Bread, sea snail, seal Gray wolves Onl ...
... Associated Learning • We learn by association • Simpler animals can learn simple associations • Learning that certain events occur together. The events may be two stimuli (classical conditioning) or a response and consequence (operant conditioning) • Examples: Bread, sea snail, seal Gray wolves Onl ...
History of Psychology
... • Soon, just the fluffy objects/animals caused crying • Proving FEAR could be LEARNED! • Raised ethical issues! ...
... • Soon, just the fluffy objects/animals caused crying • Proving FEAR could be LEARNED! • Raised ethical issues! ...
Chapter 1 - The Evolution of Psychology
... Experimental psychology- the focus on sensation, perception, learning, conditioning, motivation, and emotion Physiological psychology- the influence of genetic factors on behavior Cognitive psychology- the focus of higher mental processes Personality- involves describing individuals' consistency in ...
... Experimental psychology- the focus on sensation, perception, learning, conditioning, motivation, and emotion Physiological psychology- the influence of genetic factors on behavior Cognitive psychology- the focus of higher mental processes Personality- involves describing individuals' consistency in ...
The Behaviorist Revolution
... nervous reflex. This is a genuine scientific conception, since it implies necessity. It may be summed up as follows: An external or internal stimulus falls on some one or other nervous receptor and gives rise to a nervous impulse; this nervous impulse is transmitted along nerve fibres to the central ...
... nervous reflex. This is a genuine scientific conception, since it implies necessity. It may be summed up as follows: An external or internal stimulus falls on some one or other nervous receptor and gives rise to a nervous impulse; this nervous impulse is transmitted along nerve fibres to the central ...
Behaviorism and Cognitivism
... Behaviorism Behaviorism is a theory of learning that is based on the assumptions of the external behavior. It was the most dominate theory is history for several years. Psychology, behavior was the only way of study about people’s learning styles or approaches. In other words, the way you acted or ...
... Behaviorism Behaviorism is a theory of learning that is based on the assumptions of the external behavior. It was the most dominate theory is history for several years. Psychology, behavior was the only way of study about people’s learning styles or approaches. In other words, the way you acted or ...
Chapter 6 Types of Learning
... conditioning for that advertisement in a short presentation. To make this activity more interactive, have the group bring in the item that the advertisement is for to use as a “prop” during their presentation. ...
... conditioning for that advertisement in a short presentation. To make this activity more interactive, have the group bring in the item that the advertisement is for to use as a “prop” during their presentation. ...
Learning Day 2 Student
... Behaviorist: Only cares about behavior – what a person does – what can be observed or proven Learning is mechanical – you behave the way you do because of external stimuli – no internal processes are required (learning by thinking about something or watching it) Cogntivist: ...
... Behaviorist: Only cares about behavior – what a person does – what can be observed or proven Learning is mechanical – you behave the way you do because of external stimuli – no internal processes are required (learning by thinking about something or watching it) Cogntivist: ...
Learning Theories
... Behaviorism only focuses on the what can be observed in the way of learning. Learning is viewed in three ways. ...
... Behaviorism only focuses on the what can be observed in the way of learning. Learning is viewed in three ways. ...
Universidade do Algarve
... Behaviors conditioned through a classical conditioning procedure are not maintained by consequences. They both, however, form the core of behavior analysis and have grown ...
... Behaviors conditioned through a classical conditioning procedure are not maintained by consequences. They both, however, form the core of behavior analysis and have grown ...
Unit 1 History and Approaches 2017
... terms of whole parts rather than by analyzing their small parts • The whole is greater than the sum of its parts • Max Wetheimer ...
... terms of whole parts rather than by analyzing their small parts • The whole is greater than the sum of its parts • Max Wetheimer ...
Learning - Ms. Brown Apex High School
... Pavlov found that if he waited a few hours before ringing the fork again, the dogs would salivate to the ringing after the pause ...
... Pavlov found that if he waited a few hours before ringing the fork again, the dogs would salivate to the ringing after the pause ...