Observational Learning
... • Based on principle that punishment tells you what not to do, reinforcement tells you what to do – A swat is used only as backup to milder disciplinary tactics, like a time-out, removing them from reinforcing surroundings – Swatting with a generous dose of reasoning ...
... • Based on principle that punishment tells you what not to do, reinforcement tells you what to do – A swat is used only as backup to milder disciplinary tactics, like a time-out, removing them from reinforcing surroundings – Swatting with a generous dose of reasoning ...
unit 6 — learning - Mayfield City Schools
... behavior. The naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus in classical conditioning. A stimulus that unconditionallynaturally and automatically-triggers a response in classical conditioning. In classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (now conditioned) stim ...
... behavior. The naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus in classical conditioning. A stimulus that unconditionallynaturally and automatically-triggers a response in classical conditioning. In classical conditioning, the learned response to a previously neutral (now conditioned) stim ...
Course: Introduction to Psychology Presenters: Sandra Whyte and
... Operant conditioning Operant Conditioning deals with operants - intentional actions that have an effect on the surrounding environment. Skinner set out to identify the processes which made certain operant behaviours more or less likely to occur. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning was based on ...
... Operant conditioning Operant Conditioning deals with operants - intentional actions that have an effect on the surrounding environment. Skinner set out to identify the processes which made certain operant behaviours more or less likely to occur. Skinner's theory of operant conditioning was based on ...
ACHS Pyschology Syllabus
... **Formative Assessment: Formal and informal processes teachers and students use to gather evidence for the purpose of improving learning. Formative Assessments (for learning) will be used to determine if we are progressing toward the skills and understanding of content for the chapter/unit. These ma ...
... **Formative Assessment: Formal and informal processes teachers and students use to gather evidence for the purpose of improving learning. Formative Assessments (for learning) will be used to determine if we are progressing toward the skills and understanding of content for the chapter/unit. These ma ...
Down and Dirty study sheet for the AP Psy Exam Source: Mr. B`s
... Biological Physiology; genetics; nature Cognitive Mental Processes Psychoanalytical Unconscious, childhood Humanistic Freewill; basis goodness Multicultural Sociocultural; role of structure Gestalt Emphasizes the organization process in behavior. Focuses on problem of perception Personality: ...
... Biological Physiology; genetics; nature Cognitive Mental Processes Psychoanalytical Unconscious, childhood Humanistic Freewill; basis goodness Multicultural Sociocultural; role of structure Gestalt Emphasizes the organization process in behavior. Focuses on problem of perception Personality: ...
Memory - Peoria Public Schools
... Cognition & Operant Conditioning Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze (environment). ...
... Cognition & Operant Conditioning Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze (environment). ...
Quiz 3 ch 5 Sp 13
... C) Watson and Rayner were able to successfully undo the fears they conditioned in Little Albert. D) Upon hearing the loud noise, Little Albert “jumped violently, fell forward, and began to whimper.” E) Watson clearly showed a disregard for Little Albert’s welfare during the time he worked with him. ...
... C) Watson and Rayner were able to successfully undo the fears they conditioned in Little Albert. D) Upon hearing the loud noise, Little Albert “jumped violently, fell forward, and began to whimper.” E) Watson clearly showed a disregard for Little Albert’s welfare during the time he worked with him. ...
Learning - SchoolRack
... • Practice: the repetition of a task – helps to bind responses together – makes for smooth and fluent movement from response to response – psychologists have been interested in determining how to use time most efficiently and have found that it is usually better to practice over a period of time ins ...
... • Practice: the repetition of a task – helps to bind responses together – makes for smooth and fluent movement from response to response – psychologists have been interested in determining how to use time most efficiently and have found that it is usually better to practice over a period of time ins ...
Document
... one feature of the environment (stimulus) with another operant conditioning trial & error learning associate behavior with reward or punishment ...
... one feature of the environment (stimulus) with another operant conditioning trial & error learning associate behavior with reward or punishment ...
The Psychology of B.F. Skinner Adam Gallagher Learning
... questioning things in science and look deeper at the facts and situations, it becomes evident that there are numerous connections between people and ideas spanning multiple generations. One person’s ideas lead to another’s questioning them, and possibly forming another path. This cycle of constantly ...
... questioning things in science and look deeper at the facts and situations, it becomes evident that there are numerous connections between people and ideas spanning multiple generations. One person’s ideas lead to another’s questioning them, and possibly forming another path. This cycle of constantly ...
Lecture 2 theoretical perspectives
... The American psychologist Albert Bandura developed many of the principles of social learning an approach that emphasizes learning by observing the behaviour of another person, called a model Classical social learning theory maintains that people learn appropriate social behavior chiefly by observing ...
... The American psychologist Albert Bandura developed many of the principles of social learning an approach that emphasizes learning by observing the behaviour of another person, called a model Classical social learning theory maintains that people learn appropriate social behavior chiefly by observing ...
Who is the founding father of Psychology?
... Negative reinforcement and punishment are ____. A. The same B. The best ways to learn a new behavior C. Not the same because negative reinforcement increases behavior and punishment decreases behavior D. Not the same, even though they both decrease behavior C. Not the same because negative reinforc ...
... Negative reinforcement and punishment are ____. A. The same B. The best ways to learn a new behavior C. Not the same because negative reinforcement increases behavior and punishment decreases behavior D. Not the same, even though they both decrease behavior C. Not the same because negative reinforc ...
AP Psychology – Curricular Requirement 6: Learning (7
... observational learning (e.g., contingencies). ...
... observational learning (e.g., contingencies). ...
The Science of Psychology
... • Freud’s patients suffered from nervous disorders with no found physical cause. – Freud proposed that there is an unconscious (unaware) mind into which we push, or repress, all of our threatening urges and desires. – He believed that these repressed urges, in trying to surface, created nervous diso ...
... • Freud’s patients suffered from nervous disorders with no found physical cause. – Freud proposed that there is an unconscious (unaware) mind into which we push, or repress, all of our threatening urges and desires. – He believed that these repressed urges, in trying to surface, created nervous diso ...
Operant Conditioning - Fleming County Schools
... Reinforcement: increases likelihood behavior will be repeated Positive: something rewarding is added Negative: remove something negative (this is good!) ...
... Reinforcement: increases likelihood behavior will be repeated Positive: something rewarding is added Negative: remove something negative (this is good!) ...
human behavior - Randolph Township Schools
... Psychology initially developed as a combination of biology and philosophy; use of the scientific method for the study of psychology transformed the field into a true science. ...
... Psychology initially developed as a combination of biology and philosophy; use of the scientific method for the study of psychology transformed the field into a true science. ...
Cognition and Operant Conditioning
... type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment ...
... type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by reinforcement or diminished if followed by punishment ...
Learned behavior
... Instrumental conditioning is the process through which an organism learns to emit a response in order to obtain a reward or avoid an aversive stimulus. o Instrumental conditioning versus operant conditioning The law of effect postulated by Edward Thorndike, holds that any response that produces a re ...
... Instrumental conditioning is the process through which an organism learns to emit a response in order to obtain a reward or avoid an aversive stimulus. o Instrumental conditioning versus operant conditioning The law of effect postulated by Edward Thorndike, holds that any response that produces a re ...
General Psychology: Learning (II)
... • There are 4 major techniques or methods used in operant conditioning. • They result from combining: – the two major purposes of operant conditioning (increasing or decreasing the probability that a specific behavior will occur in the future), – the types of stimuli used (positive/pleasant or ...
... • There are 4 major techniques or methods used in operant conditioning. • They result from combining: – the two major purposes of operant conditioning (increasing or decreasing the probability that a specific behavior will occur in the future), – the types of stimuli used (positive/pleasant or ...
Principles in behavioral management: implications for effective
... Problem-solving is intuitive, rather than logical Child often can’t explain reasoning ...
... Problem-solving is intuitive, rather than logical Child often can’t explain reasoning ...
AP Psychology Unit Six Curriculum Map
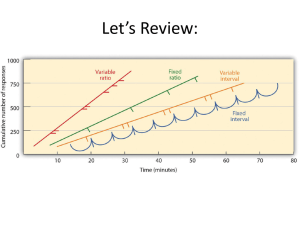
... variable-ratio (VR) schedule, fixed-interval (FI) schedule, experiments. variable-interval (VI) schedule, partial reinforcement extinction effect, punishment, learned helplessness, latent Provide examples of how biological constraints create learning, cognitive map, insight, observational learning, ...
... variable-ratio (VR) schedule, fixed-interval (FI) schedule, experiments. variable-interval (VI) schedule, partial reinforcement extinction effect, punishment, learned helplessness, latent Provide examples of how biological constraints create learning, cognitive map, insight, observational learning, ...
Classical and Operant Conditioning Notes
... 2. Behaviors followed by unpleasant consequences would most likely stop. How it works: Parents are praising or scolding their children as a consequence of the children’s actions. Positive and Negative Reinforcements Things that increase a behavior when they OCCUR is a POSITIVE (R+) Things that incre ...
... 2. Behaviors followed by unpleasant consequences would most likely stop. How it works: Parents are praising or scolding their children as a consequence of the children’s actions. Positive and Negative Reinforcements Things that increase a behavior when they OCCUR is a POSITIVE (R+) Things that incre ...