pleasure principle”.
... Bandura , Social Cognitive Theory Cognitive – people try and understand Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience which results in a person’s belief about their own abilities/talents. This sense of self esteem will significantly affect ...
... Bandura , Social Cognitive Theory Cognitive – people try and understand Social – other people are an important source of information Self-efficacy – the result of experience which results in a person’s belief about their own abilities/talents. This sense of self esteem will significantly affect ...
introduction to psychology and key people
... Types of Psychology Basic research- conduct studies with a long-term goal to find out more about human and animal behavior Applied psychology- discovering ways to use what we already know about people to benefit others. ...
... Types of Psychology Basic research- conduct studies with a long-term goal to find out more about human and animal behavior Applied psychology- discovering ways to use what we already know about people to benefit others. ...
Operant Conditioning
... Operant conditioning uses operant or voluntary behavior Ask: Is the behavior something the animal can control? Does the animal have a choice in how to behave? ...
... Operant conditioning uses operant or voluntary behavior Ask: Is the behavior something the animal can control? Does the animal have a choice in how to behave? ...
Self-fulfilling Prophecy
... – People are motivated to have consistent attitudes and behavior – If a person’s attitude doesn’t match their behavior, they are motivated to change their… ...
... – People are motivated to have consistent attitudes and behavior – If a person’s attitude doesn’t match their behavior, they are motivated to change their… ...
Chapter 1: The Science of Psychology Module 1: Psychology`s
... Adaptive behaviors become habits: the “flywheel of society.” Like physical traits, useful behavioral traits could be passed to future generations. ...
... Adaptive behaviors become habits: the “flywheel of society.” Like physical traits, useful behavioral traits could be passed to future generations. ...
Historical Background of Animal Behavior
... Fechner & Wundt - 1850s German physicians - human behavior control -scientific approach in body Lloyd Morgan - 1894 - Habits & Instincts - tried to remove anthropomorphism and said animals do not learn - heavy on instincts Thorndike - 1900 - Skinner’s teacher - Law of Effect = reward an animal for a ...
... Fechner & Wundt - 1850s German physicians - human behavior control -scientific approach in body Lloyd Morgan - 1894 - Habits & Instincts - tried to remove anthropomorphism and said animals do not learn - heavy on instincts Thorndike - 1900 - Skinner’s teacher - Law of Effect = reward an animal for a ...
Animal behavior Unit
... response; motivation commands quicker learning. First described by B.F. Skinner, American psychologist; Invented the “Skinner Box” around 1930. ...
... response; motivation commands quicker learning. First described by B.F. Skinner, American psychologist; Invented the “Skinner Box” around 1930. ...
CHild Growth Notes on history and developmental theorists
... "takes off" and moves into completely new areas and capabilities ...
... "takes off" and moves into completely new areas and capabilities ...
BEHAVIORISM
... Started in the U.S. in the 1940s-50s--concern with mass population, consumerism, aggression (war) What matters is behavior (response to stimuli): observable, controllable, scientific Denial of Freudian inner substance, or heredity Behavioral engineering: First order conditioning (Ivan Pavlov): ringi ...
... Started in the U.S. in the 1940s-50s--concern with mass population, consumerism, aggression (war) What matters is behavior (response to stimuli): observable, controllable, scientific Denial of Freudian inner substance, or heredity Behavioral engineering: First order conditioning (Ivan Pavlov): ringi ...
TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION
... Initially, the basic behaviorist experiment works as follows: ◦ a rat/human is given several response options, each of which is associated with a reward/punishment. ◦ a rat is given the option of pressing 1of 2 levers Pressing one of the levers results in the delivery of sugar water or a food pelle ...
... Initially, the basic behaviorist experiment works as follows: ◦ a rat/human is given several response options, each of which is associated with a reward/punishment. ◦ a rat is given the option of pressing 1of 2 levers Pressing one of the levers results in the delivery of sugar water or a food pelle ...
Learning
... Variable-ratio: after random number of responses Fixed-interval: Fixed interval: after a set time interval Variable-interval: after random time intervals ...
... Variable-ratio: after random number of responses Fixed-interval: Fixed interval: after a set time interval Variable-interval: after random time intervals ...
Founders PowerPoint - Beavercreek City Schools
... Break down mental processes into basic parts Introspection- basic elements of consciousness Considered too subjective- lack of reliability Internal- cannot be accurately measured ...
... Break down mental processes into basic parts Introspection- basic elements of consciousness Considered too subjective- lack of reliability Internal- cannot be accurately measured ...
Structuralism and Functionalism
... Emphasized importance of internal and unconsciousness motives and thoughts in determining or predicting behavior. Freud studied human behavior by consulting with patients. People are good but have basic impulsive feelings, thoughts, and desires. Conflict arises when people cannot handle those desire ...
... Emphasized importance of internal and unconsciousness motives and thoughts in determining or predicting behavior. Freud studied human behavior by consulting with patients. People are good but have basic impulsive feelings, thoughts, and desires. Conflict arises when people cannot handle those desire ...
M O D U L E 1 0
... 18 an accidental pairing of a reinforcer and a behavior causes that behavior to occur again. 19 a program or rule that determines how and when a response will be rewarded. 20 if the removal of an aversive stimulus increases the chances of a response occurring again, it is called a __________ reinfor ...
... 18 an accidental pairing of a reinforcer and a behavior causes that behavior to occur again. 19 a program or rule that determines how and when a response will be rewarded. 20 if the removal of an aversive stimulus increases the chances of a response occurring again, it is called a __________ reinfor ...
History of Animal Behavior
... • This school of thought advocates the use of strict experimental procedures to study observable behaviors (or responses) in relation to environment (or stimuli) • Ethology (Zoologists) • This school of thought advocates studying behavior under naturalistic conditions. It explores animal behavior in ...
... • This school of thought advocates the use of strict experimental procedures to study observable behaviors (or responses) in relation to environment (or stimuli) • Ethology (Zoologists) • This school of thought advocates studying behavior under naturalistic conditions. It explores animal behavior in ...
psychology - History of - 2013
... that starts with the stimulus (the sympathetic nervous system or the parasympathetic Functionalist nervous system); and ends with a passionate feeling, a conscious - a psychologist emotional experience. who studied the function (rather than the structure) of consciousness. A major goal of emotion ...
... that starts with the stimulus (the sympathetic nervous system or the parasympathetic Functionalist nervous system); and ends with a passionate feeling, a conscious - a psychologist emotional experience. who studied the function (rather than the structure) of consciousness. A major goal of emotion ...
REDUCTIONISM - School of Psychology
... • Symmetry between electricity and magnetism: Explained the nature of light as electromagnetic waves moving at speed c. ...
... • Symmetry between electricity and magnetism: Explained the nature of light as electromagnetic waves moving at speed c. ...
Animal Behavior
... • Migrates upward during the day and descends at night • Also migrate from the west to the east during the day and return in the evening ...
... • Migrates upward during the day and descends at night • Also migrate from the west to the east during the day and return in the evening ...
Overview of the Behaviorist Approach
... emotions, we live in complex societies etc. To see humans as functioning in a mechanistic manner is to over-simplify human behavior. • (-) It excludes innate factors. We now know that genetic factors do play an enormous role in influencing human behavior and behaviorism simply does not acknowledge t ...
... emotions, we live in complex societies etc. To see humans as functioning in a mechanistic manner is to over-simplify human behavior. • (-) It excludes innate factors. We now know that genetic factors do play an enormous role in influencing human behavior and behaviorism simply does not acknowledge t ...
Define the main biological influences of psychology
... of a particular school of thought and reject the others, but many consider each as a method to understanding the human brain and are think that the schools of though are connected to one another. Today, psychology has been able to combine integrated perspectives towards understanding behavior, consc ...
... of a particular school of thought and reject the others, but many consider each as a method to understanding the human brain and are think that the schools of though are connected to one another. Today, psychology has been able to combine integrated perspectives towards understanding behavior, consc ...
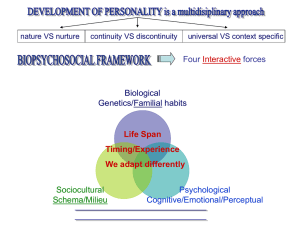
STUDY OF PERSONALITY FINAL REVIEW
... 12.) This man is one of the most famous psychologists because he founded the idea of psychoanalysis and discovered the importance of unconscious motives in human behavior. He also used mainly case studies for his experiments. His name is __________. 13.) Three cognitive psychologists are: a. b. c. ...
... 12.) This man is one of the most famous psychologists because he founded the idea of psychoanalysis and discovered the importance of unconscious motives in human behavior. He also used mainly case studies for his experiments. His name is __________. 13.) Three cognitive psychologists are: a. b. c. ...
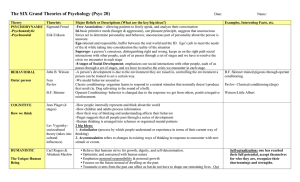
The SIX Grand Theories of Psychology (Psyc 20)
... Superego- a person’s conscious, distinguishing right and wrong, keeps us on the right path social interactions with other people, each of us passes through a set of stages and we have to resolve the crisis we encounter in each stage -8 stages of Social Development; emphasizes our social interactions ...
... Superego- a person’s conscious, distinguishing right and wrong, keeps us on the right path social interactions with other people, each of us passes through a set of stages and we have to resolve the crisis we encounter in each stage -8 stages of Social Development; emphasizes our social interactions ...