Chapter 7. Magnetic Materials and Magnetic Circuit Analysis
... In general, magnetic materials can be classified as magnetically "soft" and "hard" materials. Soft materials are normally used as the magnetic core materials for inductors, transformers, actuators and rotating machines, in which the magnetic fields vary frequently, whereas hard materials, or permane ...
... In general, magnetic materials can be classified as magnetically "soft" and "hard" materials. Soft materials are normally used as the magnetic core materials for inductors, transformers, actuators and rotating machines, in which the magnetic fields vary frequently, whereas hard materials, or permane ...
Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh, Conceptual Integrated Science
... • Light is produced by the mutual induction of electric and magnetic fields • speed of light is the speed of emanation of these fields – too slow, the regenerating fields die out – too fast, fields build up in a crescendo of everincreasing energy – at speed c, just right! And, there is light! ...
... • Light is produced by the mutual induction of electric and magnetic fields • speed of light is the speed of emanation of these fields – too slow, the regenerating fields die out – too fast, fields build up in a crescendo of everincreasing energy – at speed c, just right! And, there is light! ...
Aberration-Corrected Analytical Electron Microscopy of Transition Metal Nitride and Silicon Nitride Multilayers
... the physical conditions. Solid solutions and nanocomposites are formed during the deposition of all the included elements at the same time while multilayers are usually formed by alternate deposition of the elements. Because of the possibility to control the layer deposition in multilayers, the prop ...
... the physical conditions. Solid solutions and nanocomposites are formed during the deposition of all the included elements at the same time while multilayers are usually formed by alternate deposition of the elements. Because of the possibility to control the layer deposition in multilayers, the prop ...
What about Current? Department of Mechanical
... because the high currents encountered can cause large amounts of heat energy to be released. ...
... because the high currents encountered can cause large amounts of heat energy to be released. ...
Principles of Technology
... Which set of statements is true: i. A motor uses a magnetic field to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. ii. A generator is a commercial device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy iii. Induced potential difference is also known as electromotive force (emf), symbolize ...
... Which set of statements is true: i. A motor uses a magnetic field to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. ii. A generator is a commercial device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy iii. Induced potential difference is also known as electromotive force (emf), symbolize ...
Cooling Systems
... A complete circuit with more than one path for current to flow Current flowing into each branch or leg varies according to the amount of resistance in that branch of the circuit The total resistance of a parallel circuit is always less than that of the smallest resistance of any branch of the entire ...
... A complete circuit with more than one path for current to flow Current flowing into each branch or leg varies according to the amount of resistance in that branch of the circuit The total resistance of a parallel circuit is always less than that of the smallest resistance of any branch of the entire ...
STRONG MAGNETIC FIELD INDUCED SEGREGATION AND SELF
... permanent magnetic moment. Their magnetisation is directly from the induction of an external magnetic field [10]. Therefore, less agglomeration presents for these materials when compared with magnetic materials, such as magnetic nanoparticles [11], which will be one of the advantages for future appl ...
... permanent magnetic moment. Their magnetisation is directly from the induction of an external magnetic field [10]. Therefore, less agglomeration presents for these materials when compared with magnetic materials, such as magnetic nanoparticles [11], which will be one of the advantages for future appl ...
Magnetic Magic Teacher Guide
... difference between true or geographic north, and magnetic north. And it is the number that Dena didn’t know in Magnetic Magic. That’s why she couldn’t find the treasure. Why is that number important? Because the earth’s magnetic field changes. It changes slowly, but it changes. The needle of a compa ...
... difference between true or geographic north, and magnetic north. And it is the number that Dena didn’t know in Magnetic Magic. That’s why she couldn’t find the treasure. Why is that number important? Because the earth’s magnetic field changes. It changes slowly, but it changes. The needle of a compa ...
science - Amazon Web Services
... fields. Scientists are studying magnetism of other planets and even the stars. Some magnetic fields extend far into space. A relationship exists between magnetic storms on the sun and poor radio reception on earth. Magnetic forces. Magnetic forces are the attractions felt by materials close to the m ...
... fields. Scientists are studying magnetism of other planets and even the stars. Some magnetic fields extend far into space. A relationship exists between magnetic storms on the sun and poor radio reception on earth. Magnetic forces. Magnetic forces are the attractions felt by materials close to the m ...
Chapter 3 Additional Problems
... downward directed flux through this created loop is decreasing as the conductor moves to the left, Lenz's law requires that a current would flow out of the page of Fig. X3.6 through the conductor, if it could, to establish a B-field downward on the left side of the conductor, thereby opposing the de ...
... downward directed flux through this created loop is decreasing as the conductor moves to the left, Lenz's law requires that a current would flow out of the page of Fig. X3.6 through the conductor, if it could, to establish a B-field downward on the left side of the conductor, thereby opposing the de ...
Magnetic Fields - Eleanor Roosevelt High School
... Magnetic Fields Intensity of Magnetic Field of Electromagnet (B): Increased as the number of loops increased (B ~ N) Increased as the Current increased (B ~ I) Intensity is enhanced by the iron core (B ~ μ) ...
... Magnetic Fields Intensity of Magnetic Field of Electromagnet (B): Increased as the number of loops increased (B ~ N) Increased as the Current increased (B ~ I) Intensity is enhanced by the iron core (B ~ μ) ...
Physics II. :: 2. Electric current
... conductor by a factor of two is the same as the connection of another conductor in series to the original one, so the resistance is also increased by a factor of two. Therefore the resistance is proportional to the length of the wire. The increase of the cross-section of the conductor by a factor o ...
... conductor by a factor of two is the same as the connection of another conductor in series to the original one, so the resistance is also increased by a factor of two. Therefore the resistance is proportional to the length of the wire. The increase of the cross-section of the conductor by a factor o ...
Assignment 10
... This print-out should have 34 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page – find all choices before making your selection. The due time is Central time. these problem are extra credit homework, but the material will be in the final ...
... This print-out should have 34 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page – find all choices before making your selection. The due time is Central time. these problem are extra credit homework, but the material will be in the final ...
Notes - Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... By observation, the current in the left and right side of the loop is parallel or antiparallel to the magnetic field, so there will be no force on those sides. The top and bottom will have he same magnitude but opposite direction of force. By the right‐hand rule, the top will have a force out of ...
... By observation, the current in the left and right side of the loop is parallel or antiparallel to the magnetic field, so there will be no force on those sides. The top and bottom will have he same magnitude but opposite direction of force. By the right‐hand rule, the top will have a force out of ...
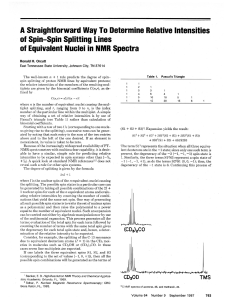
A straightforward way to determine relative intensities of spin
... equai tothe number of equivalent nuclei: Such an expansion can he carried out either by algebraic manipulation or by use of the multinomial expansion. This process generates all the terms; evaluation of the total spin for each term followed by counting the number of terms with the same total spin gi ...
... equai tothe number of equivalent nuclei: Such an expansion can he carried out either by algebraic manipulation or by use of the multinomial expansion. This process generates all the terms; evaluation of the total spin for each term followed by counting the number of terms with the same total spin gi ...
Giant magnetoresistance
Giant magnetoresistance (GMR) is a quantum mechanical magnetoresistance effect observed in thin-film structures composed of alternating ferromagnetic and non-magnetic conductive layers. The 2007 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Albert Fert and Peter Grünberg for the discovery of GMR.The effect is observed as a significant change in the electrical resistance depending on whether the magnetization of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are in a parallel or an antiparallel alignment. The overall resistance is relatively low for parallel alignment and relatively high for antiparallel alignment. The magnetization direction can be controlled, for example, by applying an external magnetic field. The effect is based on the dependence of electron scattering on the spin orientation.The main application of GMR is magnetic field sensors, which are used to read data in hard disk drives, biosensors, microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) and other devices. GMR multilayer structures are also used in magnetoresistive random-access memory (MRAM) as cells that store one bit of information.In literature, the term giant magnetoresistance is sometimes confused with colossal magnetoresistance of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic semiconductors, which is not related to the multilayer structure.