SOP Template - Clinical Module
... and clock time of collection) polypropylene cryovials with added sodium or lithium heparin as anticoagulant. Store frozen (see section 8 below), do not thaw the sample after freezing. Plasma: Centrifuge sodium or lithium heparin anticoagulated whole blood within 60 minutes of sampling at 1000 – 3000 ...
... and clock time of collection) polypropylene cryovials with added sodium or lithium heparin as anticoagulant. Store frozen (see section 8 below), do not thaw the sample after freezing. Plasma: Centrifuge sodium or lithium heparin anticoagulated whole blood within 60 minutes of sampling at 1000 – 3000 ...
... 32. Notice the structure of the tail. It is made of a series of jointed rods. 33. Carefully examine the tail and look for any parasites which may be on it. Examine the scales. 34. Look for movement of a liquid between the rods. When you find the flowing liquid, you will be watching the fish’s blood ...
Objectives
... Cystitis – inflammation of the urinary bladder. Caused by bacterial infection or injury due to chemical exposure or mechanical injury. Renal calculi – kidney stones (excessive calcium crystals). Painful as the multi-faceted sediment moves through the ureters. ...
... Cystitis – inflammation of the urinary bladder. Caused by bacterial infection or injury due to chemical exposure or mechanical injury. Renal calculi – kidney stones (excessive calcium crystals). Painful as the multi-faceted sediment moves through the ureters. ...
chapter review questions
... The blood viscosity increases to levels that may induce heart attacks or strokes. The oxygen-carrying capacity remains unchanged despite elevated red blood cell counts. Red blood cell counts remain unchanged, but the number of reticulocytes increases. Blood viscosity levels decrease while oxygencarr ...
... The blood viscosity increases to levels that may induce heart attacks or strokes. The oxygen-carrying capacity remains unchanged despite elevated red blood cell counts. Red blood cell counts remain unchanged, but the number of reticulocytes increases. Blood viscosity levels decrease while oxygencarr ...
A major function of the most common plasma protein
... The blood viscosity increases to levels that may induce heart attacks or strokes. The oxygen-carrying capacity remains unchanged despite elevated red blood cell counts. Red blood cell counts remain unchanged, but the number of reticulocytes increases. Blood viscosity levels decrease while oxygencarr ...
... The blood viscosity increases to levels that may induce heart attacks or strokes. The oxygen-carrying capacity remains unchanged despite elevated red blood cell counts. Red blood cell counts remain unchanged, but the number of reticulocytes increases. Blood viscosity levels decrease while oxygencarr ...
Expanded Methods
... 2.5, Mg2+ 1.2, Cl- 128.7, HCO3- 25, SO42- 1.2, H2PO4- 1.2, and glucose 11. During the experiment, the solution at 37˚C was aerated with a gas mixture of 95 % O2 + 5 % CO2 (PO2 >200 mm Hg). Oxygen partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) was measured by an Oxygen Meter (Model 781, Strathkelvin Instrument, U. ...
... 2.5, Mg2+ 1.2, Cl- 128.7, HCO3- 25, SO42- 1.2, H2PO4- 1.2, and glucose 11. During the experiment, the solution at 37˚C was aerated with a gas mixture of 95 % O2 + 5 % CO2 (PO2 >200 mm Hg). Oxygen partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) was measured by an Oxygen Meter (Model 781, Strathkelvin Instrument, U. ...
Resolvigen 3
... homozygous test RBCs, giving what appears to be spurious reactions; in this case the most likely match is found and the related antibody specificities suggested, hinting at procedures for confirming them. Varying reaction scores of differently reacting RBCs are analyzed to identify different antibod ...
... homozygous test RBCs, giving what appears to be spurious reactions; in this case the most likely match is found and the related antibody specificities suggested, hinting at procedures for confirming them. Varying reaction scores of differently reacting RBCs are analyzed to identify different antibod ...
Lecture 3
... low and is not complete; vaginal hemorrhage is evident . 2. Moderate/high separation .This occurs when the separation is high in the uterine segment. The fetus is in grave danger because of lack of oxygen. External hemorrhage will probably not be present here. 3. Severe/complete separation .This occ ...
... low and is not complete; vaginal hemorrhage is evident . 2. Moderate/high separation .This occurs when the separation is high in the uterine segment. The fetus is in grave danger because of lack of oxygen. External hemorrhage will probably not be present here. 3. Severe/complete separation .This occ ...
File
... presence or absence of the AB and Rh proteins. The presence of different blood types was not discovered until 1901. Wrong blood = cause clumping = death ...
... presence or absence of the AB and Rh proteins. The presence of different blood types was not discovered until 1901. Wrong blood = cause clumping = death ...
Presentation
... Common Types of Serology Commonly found rape cases are: Blood Hair Sperm ...
... Common Types of Serology Commonly found rape cases are: Blood Hair Sperm ...
Human Biology
... 3. Kill bacteria. The stomach is very acidic (pH 1) like battery acid. Chyme will even eat through clothing. 4. Some digestion: of proteins. 5. Some absorption: of water, alcohol (alcohol is absorbed in the mouth, too!) Food takes four hours to completely leave the stomach. ...
... 3. Kill bacteria. The stomach is very acidic (pH 1) like battery acid. Chyme will even eat through clothing. 4. Some digestion: of proteins. 5. Some absorption: of water, alcohol (alcohol is absorbed in the mouth, too!) Food takes four hours to completely leave the stomach. ...
………………….`s Revision cards Print out. Fold left to write and test
... 5. Why is heparin added to the patients blood before the blood enters the dialysis machine? 6. Why does the dialysis fluid contain glucose at the same concentration as a healthy human? 7. Why does the renal dialysis fluid have to be changed after a dialysis session? ...
... 5. Why is heparin added to the patients blood before the blood enters the dialysis machine? 6. Why does the dialysis fluid contain glucose at the same concentration as a healthy human? 7. Why does the renal dialysis fluid have to be changed after a dialysis session? ...
Direct Intravascular Blood Volume Analysis
... Clinical research has proven that intravascular blood volume measurement represents a critical consideration for diagnosis and treatment of several acute and chronic conditions. Published studies from leading institutions such as the Cleveland Clinic, Yale University School of Medicine, and Columbia ...
... Clinical research has proven that intravascular blood volume measurement represents a critical consideration for diagnosis and treatment of several acute and chronic conditions. Published studies from leading institutions such as the Cleveland Clinic, Yale University School of Medicine, and Columbia ...
circulatory system
... Lymph nodes filter foreign substances, such as bacteria and cancer cells, from the lymph before it is re-entered into the blood system through the larger veins. Lymph nodes, which are scattered among the lymph vessels, act as the body’s first defense against infection. ...
... Lymph nodes filter foreign substances, such as bacteria and cancer cells, from the lymph before it is re-entered into the blood system through the larger veins. Lymph nodes, which are scattered among the lymph vessels, act as the body’s first defense against infection. ...
circulatory system - Livingstone High School
... Lymph nodes filter foreign substances, such as bacteria and cancer cells, from the lymph before it is re-entered into the blood system through the larger veins. Lymph nodes, which are scattered among the lymph vessels, act as the body’s first defense against infection. ...
... Lymph nodes filter foreign substances, such as bacteria and cancer cells, from the lymph before it is re-entered into the blood system through the larger veins. Lymph nodes, which are scattered among the lymph vessels, act as the body’s first defense against infection. ...
Porter Medical Center Laboratory 115 Porter Drive Middlebury, VT 05753
... ⌧ Other specialized tubes COLLECTING A BLOOD SAMPLE General Information: ⌧ It is important to have all equipment, supplies and requisitions ready for the procedure. ⌧ Wash your hands before each patient. ⌧ Gloves must be worn when performing any venipuncture or capillary collections. Factors in Site ...
... ⌧ Other specialized tubes COLLECTING A BLOOD SAMPLE General Information: ⌧ It is important to have all equipment, supplies and requisitions ready for the procedure. ⌧ Wash your hands before each patient. ⌧ Gloves must be worn when performing any venipuncture or capillary collections. Factors in Site ...
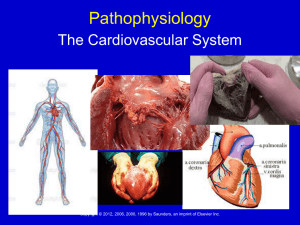
Introduction to the Cardiovascular System
... a protector of the body against diseases. Every cell in your body depends on your cardiovascular system. In this chapter, you will learn how your cardiovascular system works and how it helps to maintain homeostasis. The cardiovascular system shown in Figure 1.1 is the organ system that is made up of ...
... a protector of the body against diseases. Every cell in your body depends on your cardiovascular system. In this chapter, you will learn how your cardiovascular system works and how it helps to maintain homeostasis. The cardiovascular system shown in Figure 1.1 is the organ system that is made up of ...
full text pdf
... f. hemodilution after a massive RBC transfusion. g. certain medications. h. cardiac assist devices. Although less frequent (1% incidence), DIC can sometimes occur in patients with severe sepsis [5,11]. Stress-induced upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGI), either occult or visible, can develop in ...
... f. hemodilution after a massive RBC transfusion. g. certain medications. h. cardiac assist devices. Although less frequent (1% incidence), DIC can sometimes occur in patients with severe sepsis [5,11]. Stress-induced upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGI), either occult or visible, can develop in ...
A 57-Year-Old Man Presents with Worsening Shortness of Breath
... he noticed constant fatigue which was progressively worsening. The patient also complained of shortness of breath even on mild exertion and occasional light headedness. He reported subjective low grade night time fevers and sweats. In the three days before hospital presentation, the patient’s skin h ...
... he noticed constant fatigue which was progressively worsening. The patient also complained of shortness of breath even on mild exertion and occasional light headedness. He reported subjective low grade night time fevers and sweats. In the three days before hospital presentation, the patient’s skin h ...
Biology 5 to 8 - Dominican
... Other Test Questions 1. What substances does the blood carry? 2. Give the function of each of the following: (i) white blood cells, (ii) red blood cells and (iii) platelets. 3. What is the main function of the heart? 4. What are the four main chambers of the heart? 5. Draw a diagram of the heart. Id ...
... Other Test Questions 1. What substances does the blood carry? 2. Give the function of each of the following: (i) white blood cells, (ii) red blood cells and (iii) platelets. 3. What is the main function of the heart? 4. What are the four main chambers of the heart? 5. Draw a diagram of the heart. Id ...
1 lesson_16.1
... Red Blood Cells and White Blood Cells Red Blood Cells Red blood cells transport oxygen to the cells and tissues of the body. Formed in bone marrow, red blood cells contain hemoglobin. ...
... Red Blood Cells and White Blood Cells Red Blood Cells Red blood cells transport oxygen to the cells and tissues of the body. Formed in bone marrow, red blood cells contain hemoglobin. ...
Transfusion
... Once completed, flush tubing with normal saline if desired. Disconnect blood tubing when transfusion is completed - do not leave used blood tubing attached to the patient. Dispose of blood tubing and blood bags in a biohazard container unless hospital policy requires you to return the blood ba ...
... Once completed, flush tubing with normal saline if desired. Disconnect blood tubing when transfusion is completed - do not leave used blood tubing attached to the patient. Dispose of blood tubing and blood bags in a biohazard container unless hospital policy requires you to return the blood ba ...
Circulatory System— The Plasma Pipeline
... ● Understand that like other animals, human beings have body systems for obtaining and providing energy, defense, reproduction, and the coordination of body functions. ● Understand that the amount of food energy (calories) a person requires varies with body weight, age, sex, activity level, and natu ...
... ● Understand that like other animals, human beings have body systems for obtaining and providing energy, defense, reproduction, and the coordination of body functions. ● Understand that the amount of food energy (calories) a person requires varies with body weight, age, sex, activity level, and natu ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.