Powerpoint - Blood Journal
... 125I-VT-1 binding to neutral glycolipid extracts from human PMNs, GMVECs, and monocytes.Glycolipids were extracted and separated as described in “Materials and methods.” Binding of 125I-VT-1 was visualized, using a phosphor-imager. ...
... 125I-VT-1 binding to neutral glycolipid extracts from human PMNs, GMVECs, and monocytes.Glycolipids were extracted and separated as described in “Materials and methods.” Binding of 125I-VT-1 was visualized, using a phosphor-imager. ...
Tissues in the lungs
... The respiratory pigment, when present, is dissolved in the plasma of the blood and there are no red corpuscles. ...
... The respiratory pigment, when present, is dissolved in the plasma of the blood and there are no red corpuscles. ...
All_the_circulatory_slides
... – hemorrhagic anemia - excessive blood loss – hemolytic anemia - destruction of RBCs or too little erythropoiesis – sickle-cell anemia and thalassemia • both caused by abnormal hemoglobin ...
... – hemorrhagic anemia - excessive blood loss – hemolytic anemia - destruction of RBCs or too little erythropoiesis – sickle-cell anemia and thalassemia • both caused by abnormal hemoglobin ...
Please click here to view Year 6 Science Plan
... plenty of rest too. Discuss the effect of tobacco, alcohol and other drugs on the body in general. What do they understand by the term ‘drug’? Explain that drugs are substances that cause chemical reactions in the body. Discuss the fact that there is a lot of pressure from peers (children of their o ...
... plenty of rest too. Discuss the effect of tobacco, alcohol and other drugs on the body in general. What do they understand by the term ‘drug’? Explain that drugs are substances that cause chemical reactions in the body. Discuss the fact that there is a lot of pressure from peers (children of their o ...
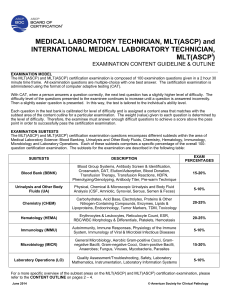
MEDICAL LABORATORY TECHNICIAN, MLT(ASCP) and
... IMPORTANT: Examination questions, which are related to the subtest areas outlined below, may be both theoretical and procedural. Theoretical questions measure skills necessary to apply knowledge, calculate results, and correlate patient results to disease states. Procedural questions measure skills ...
... IMPORTANT: Examination questions, which are related to the subtest areas outlined below, may be both theoretical and procedural. Theoretical questions measure skills necessary to apply knowledge, calculate results, and correlate patient results to disease states. Procedural questions measure skills ...
O. Henry Science
... up the carbon dioxide (a waste gas produced as our cells are working) and transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs where it is removed from the body when we exhale (breath out). There are about 5,000,000 Red Blood Cells in ONE drop of blood. Red blood cells do not have a nucleus and do not have D ...
... up the carbon dioxide (a waste gas produced as our cells are working) and transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs where it is removed from the body when we exhale (breath out). There are about 5,000,000 Red Blood Cells in ONE drop of blood. Red blood cells do not have a nucleus and do not have D ...
Sci7_C3_L5_Student_Page_Circulatory Reading and Questions
... oxygen to the cells it gathers up the carbon dioxide (a waste gas produced as our cells are working) and transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs where it is removed from the body when we exhale (breath out). There are about 5,000,000 Red Blood Cells in ONE drop of blood. Red blood cells do not h ...
... oxygen to the cells it gathers up the carbon dioxide (a waste gas produced as our cells are working) and transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs where it is removed from the body when we exhale (breath out). There are about 5,000,000 Red Blood Cells in ONE drop of blood. Red blood cells do not h ...
Science.7 Circulatory System Homework Due on
... up the carbon dioxide (a waste gas produced as our cells are working) and transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs where it is removed from the body when we exhale (breath out). There are about 5,000,000 Red Blood Cells in ONE drop of blood. Red blood cells do not have a nucleus and do not have D ...
... up the carbon dioxide (a waste gas produced as our cells are working) and transports carbon dioxide back to the lungs where it is removed from the body when we exhale (breath out). There are about 5,000,000 Red Blood Cells in ONE drop of blood. Red blood cells do not have a nucleus and do not have D ...
Unit 09 - fixurscore
... The vessel supplying the heart with blood is called the coronary artery. This is one of the most important arteries in the body because it supplies the heart with all the nutrients it needs. If this artery is blocked then the heart will slow down then stop causing a heart attack. This is how coronar ...
... The vessel supplying the heart with blood is called the coronary artery. This is one of the most important arteries in the body because it supplies the heart with all the nutrients it needs. If this artery is blocked then the heart will slow down then stop causing a heart attack. This is how coronar ...
Biology II - Mantachie High School
... --the bronchi branch into smaller and smaller tubes, the smallest of which are known as the bronchioles, which end in clusters of tiny air sacs called alveoli Gas Exchange and Transport In the lungs, gases are exchanged between the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries. Oxygen to be transported t ...
... --the bronchi branch into smaller and smaller tubes, the smallest of which are known as the bronchioles, which end in clusters of tiny air sacs called alveoli Gas Exchange and Transport In the lungs, gases are exchanged between the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries. Oxygen to be transported t ...
BLOOD DONATION Speakers Bureau Series
... Plasma: The liquid portion of blood that contains proteins that help treat severe bleeding problems. Plasma isn’t transfused as often as red blood cells or platelets, so once patient needs are met, plasma can be sent to manufacturers that make other treatment products such as albumin and immune glob ...
... Plasma: The liquid portion of blood that contains proteins that help treat severe bleeding problems. Plasma isn’t transfused as often as red blood cells or platelets, so once patient needs are met, plasma can be sent to manufacturers that make other treatment products such as albumin and immune glob ...
presentation - Harlem Children Society
... What is Melanoma? Melanoma is the most severe type of skin cancer that affects an estimated 100,000 people worldwide per year. It causes malignant tumors in the body. Melanoma is for the most part fatal with 94% of people having a 8.5 month survival rate,while the remaining 6% have a 5 year average ...
... What is Melanoma? Melanoma is the most severe type of skin cancer that affects an estimated 100,000 people worldwide per year. It causes malignant tumors in the body. Melanoma is for the most part fatal with 94% of people having a 8.5 month survival rate,while the remaining 6% have a 5 year average ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... 1. Observe: Blood in each chamber of the heart is represented by little balls. Observe the balls as they move through the heart and lungs. 2. Label: Turn on Show labels. Label the four chambers of the heart on the diagram. Then draw arrows to show the direction that blood flows through the heart. St ...
... 1. Observe: Blood in each chamber of the heart is represented by little balls. Observe the balls as they move through the heart and lungs. 2. Label: Turn on Show labels. Label the four chambers of the heart on the diagram. Then draw arrows to show the direction that blood flows through the heart. St ...
bio 241 – fall 2009 – examination #2
... play a role in humoral immunity but not cellular immunity. C) enhance production of memory and cytotoxic T cells. D) attract and stimulate the activity of macrophages. E) enhance nonspecific defenses ...
... play a role in humoral immunity but not cellular immunity. C) enhance production of memory and cytotoxic T cells. D) attract and stimulate the activity of macrophages. E) enhance nonspecific defenses ...
Blood culture
... and extravascular those that originate from bacteria entering the blood circulation through the lymphatic system from another site of infection. ...
... and extravascular those that originate from bacteria entering the blood circulation through the lymphatic system from another site of infection. ...
Types II and III: Antibody-Mediated and Antigen
... Causes, incidence, and risk factors Goodpasture syndrome is an autoimmune disorder, a condition that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissue. Persons with this syndrome develop substances that attack a protein called collagen in the tiny air sacs in the lung ...
... Causes, incidence, and risk factors Goodpasture syndrome is an autoimmune disorder, a condition that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissue. Persons with this syndrome develop substances that attack a protein called collagen in the tiny air sacs in the lung ...
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
... hemoglobin that carries oxygen to all cells and removes carbon dioxide • Each red blood cell lives only 90 to 120 days • New cells are manufactured by the red marrow or myeloid tissue in bones • The liver and spleen remove dead red blood cells Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... hemoglobin that carries oxygen to all cells and removes carbon dioxide • Each red blood cell lives only 90 to 120 days • New cells are manufactured by the red marrow or myeloid tissue in bones • The liver and spleen remove dead red blood cells Copyright 2003 by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Numbers Requiem for a stringed instrument
... Numbers flash like the prick of the needle that once left numbers on his wrist. TERESE KARM FI ...
... Numbers flash like the prick of the needle that once left numbers on his wrist. TERESE KARM FI ...
GCSE Physical Education
... • Veins: carry de-oxygenated blood back to the heart. This blood carries excess carbon dioxide and other waste products • Capillaries: the smallest blood vessels, which lie close to the muscle allowing oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass to & from the blood & the muscles ...
... • Veins: carry de-oxygenated blood back to the heart. This blood carries excess carbon dioxide and other waste products • Capillaries: the smallest blood vessels, which lie close to the muscle allowing oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass to & from the blood & the muscles ...
Slide 1
... • If Rh-positive blood is transfused into an Rh-negative person, the latter will gradually develop antibodies called anti-Rh agglutinins, that attach to the Rh-positive red blood cells, causing them to agglutinate / clumped together. • Could result in the death of the infant if the condition is not ...
... • If Rh-positive blood is transfused into an Rh-negative person, the latter will gradually develop antibodies called anti-Rh agglutinins, that attach to the Rh-positive red blood cells, causing them to agglutinate / clumped together. • Could result in the death of the infant if the condition is not ...
Blood type
A blood type (also called a blood group) is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele (or an alternative version of a gene) and collectively form a blood group system.Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 35 human blood group systems are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important ones are ABO and the RhD antigen; they determine someone's blood type (A, B, AB and O, with +, − or Null denoting RhD status).Many pregnant women carry a fetus with a blood type which is different from their own, which is not a problem. What can matter is whether the baby is RhD positive or negative. Mothers who are RhD- and carry a RhD+ baby can form antibodies against fetal RBCs. Sometimes these maternal antibodies are IgG, a small immunoglobulin, which can cross the placenta and cause hemolysis of fetal RBCs, which in turn can lead to hemolytic disease of the newborn called erythroblastosis fetalis, an illness of low fetal blood counts that ranges from mild to severe. Sometimes this is lethal for the fetus; in these cases it is called hydrops fetalis.